ASTM E545-99(2004)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Determining Image Quality in Direct Thermal Neutron Radiographic Examination
Standard Test Method for Determining Image Quality in Direct Thermal Neutron Radiographic Examination
SCOPE
1.1 This method covers the use of an Image Quality Indicator system to determine the relative quality of radiographic images produced by direct, thermal neutron radiographic examination. The requirements expressed in this method are not intended to control the quality level of materials and components.
1.2 This standard does not purport to address the safety problems, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: E 545 – 99 (Reapproved 2004)
Standard Test Method for
Determining Image Quality in Direct Thermal Neutron
Radiographic Examination
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E 545; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 4. Summary of Test Method
1.1 This test method covers the use of an Image Quality 4.1 The judgment of the quality of a neutron radiograph is
Indicator (IQI) system to determine the relative quality of based upon the evaluation of images obtained from indicators
radiographic images produced by direct, thermal neutron that are exposed along with the test object. In cases of limited
radiographic examination. The requirements expressed in this filmsizeorextendedobjectsize,theindicatorsmaybeexposed
test method are not intended to control the quality level of on another film immediately prior to or following exposure of
materials and components. the test object under exactly the same conditions (refer to
1.2 This standard does not purport to address the safety ProcessControlRadiographs,Section10).TheIQIvaluesmust
concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility be determined from films with an optical density between 2.0
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and to 3.0. Two types of IQIs are used.
health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory 4.1.1 Beam Purity Indicator (BPI)—The BPI is a device
limitations prior to use. usedforquantitativedeterminationofradiographicquality.Itis
1.3 ThevaluesstatedinSIunitsareregardedtobestandard. a polytetrafluoroethylene block containing two boron nitride
disks, two lead disks, and two cadmium wires.Akey feature of
2. Referenced Documents
the BPI is the ability to make a visual analysis of its image for
2.1 ASTM Standards: subjective information, such as image unsharpness and film
E 543 Practice for Agencies Performing Nondestructive
and processing quality. Densitometric measurements of the
Testing image of the device permit quantitative determination of the
E 748 Practices for Thermal Neutron Radiography of Ma-
effectivevalueforthethermalneutroncontent,gammacontent,
terials
pairproductioncontent,andscatteredneutroncontent.TheBPI
E 803 Method for Determining the L/D Ratio of Neutron shall be constructed in accordance with Practice E 2003.
Radiography Beams
Optionally, any BPI fabricated prior to publication of Practice
E 1316 Terminology for Nondestructive Examinations E 2003 which conforms to Test Method E 545 - 81 through 91
E 2003 Practice for Fabrication of Neutron Radiographic
may be used.
Beam Purity Indicators 4.1.2 Sensitivity Indicator (SI)—The SI is one of several
E 2023 Practice for Fabrication of Neutron Radiographic
devices used for qualitative determination of the sensitivity of
Sensitivity Indicators detail visible on a neutron radiograph. The SI is a step-wedge
device containing gaps and holes of known dimensions. Visual
3. Terminology
inspection of the image of this device provides subjective
3.1 Definitions—For definitions of terms used in this test
information regarding total radiographic sensitivity with re-
method, see Terminology E 1316, Section H.
spect to the step-block material. The SI shall be in accordance
with Practice E 2023. Optionally, any SI fabricated prior to
publication of Practice E 2023 which conforms toTest Method
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E07 on
E 545-81 through 91 may be used.
Nondestructive Testing and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E07.05 on
4.2 NeutronradiographypracticesarediscussedinPractices
Neutron Radiography.
Current edition approved May 1, 2004. Published June 2004. Originally
E 748.
approved in 1975. Last previous edition approved in 1999 as E 545 - 99.
The numerical values obtained in the calculations described herein may vary
5. Significance and Use
between different film processing systems, film types, and within one processing
system if processing variables changes. 5.1 The BPI is designed to yield quantitative information
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
concerning neutron beam and image system parameters that
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
contribute to film exposure and thereby affect overall image
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
quality. In addition, the BPI can be used to verify the
the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
E 545 – 99 (2004)
day-to-day consistency of the neutron radiographic quality. 7.9 For the purpose of determining image quality, the
Gadolinium conversion screens and single-emulsion silver- background optical density shall be between 2.0 and 3.0
halide films, exposed together in the neutron imaging beam, measured at the hole in the center of the BPI.
were used in the development and testing of the BPI. Use of 7.10 The only true measurement of the beam uniformity is
alternative detection systems may produce densitometric read- with a radiograph made without objects. Background film
ings that are not valid for the equations used in Section 9. optical density in the range from 2.0 to 3.0 across the film
5.2 The only truly valid sensitivity indicator is a reference should not vary more than 65 % from the numerical mean of
standard part. A reference standard part is a material or five measurements: one measurement at the center and one
component that is the same as the object being neutron measurement approximately 25 to 30 mm toward the center
radiographed except with a known standard discontinuity, from each corner of the film. If the beam diameter is smaller
inclusion, omission, or flaw. The sensitivity indicators were than the film, the four outside measurements shall be taken 25
designed to substitute for the reference standard and provide to 30 mm from the edge of the beam located at 90° intervals.
qualitative information on hole and gap sensitivity. 7.11 Radiographs shall be free of any blemish that may
5.3 The number of areas or objects to be radiographed and interfere with subsequent examination of the image.
the film acceptance standard used should be specified in the 7.12 Determine the thermal neutron content (NC), scattered
contract, purchase order, specification, or drawings. neutron content (S), gamma content (g), and pair production
content (P) by densitometric analysis of the BPI image. Make
6. Basis of Application
a determination of the constituents of film exposure by
6.1 Qualification of Nondestructive Agencies—If specified
measuring the densities in the BPI image as shown in Table 1.
in the contractual agreement, NDT agencies shall be qualified Calculate the various exposure contributors by the equations
and evaluated in accordance with Practice E 543. The appli-
given in Section 9.
cable revision of Practice E 543 shall be specified in the 7.13 Determine the sensitivity level by visually analyzing
contractual agreement.
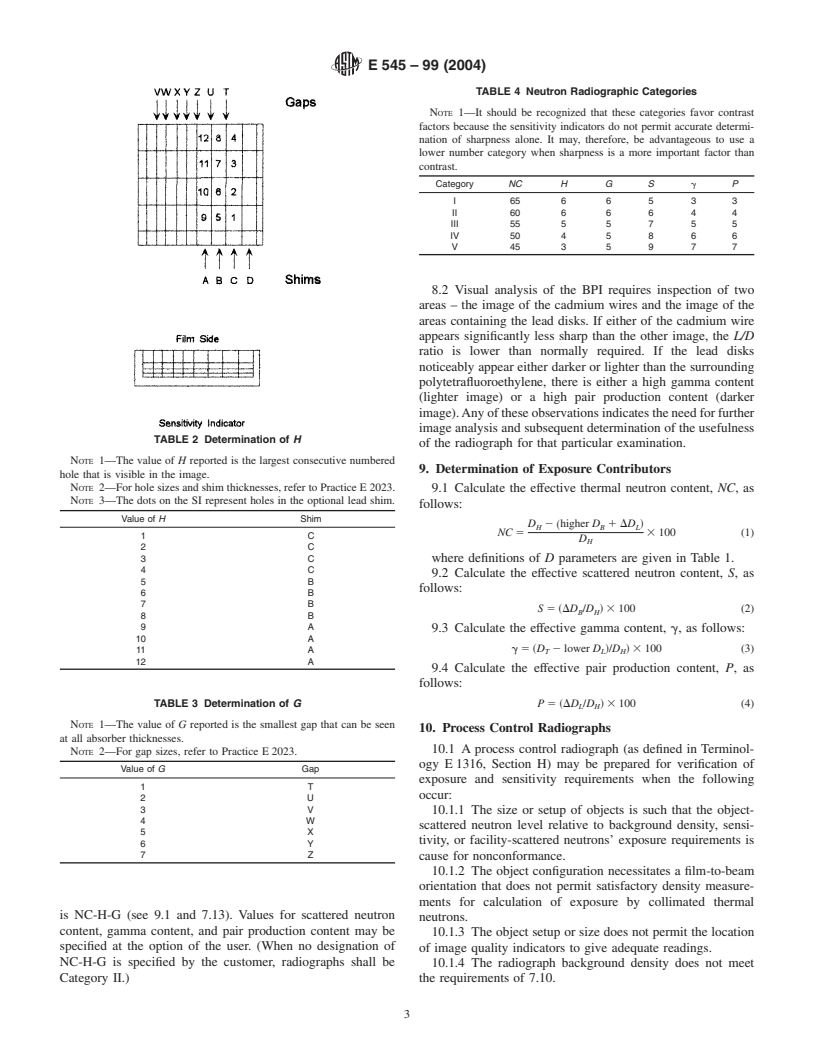
the image of the SI. Determine the values for G and H using
6.2 Procedures and Techniques—The procedures and tech-
Tables 2 and 3.
niques to be utilized shall be as described in this test method
7.14 Determine the neutron radiographic category from
unless otherwise specified. Specific techniques may be speci-
Table 4.
fied in contractual documents.
7.15 Visually compare the images of
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.