ASTM D92-01
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Flash and Fire Points by Cleveland Open Cup
Standard Test Method for Flash and Fire Points by Cleveland Open Cup
SCOPE
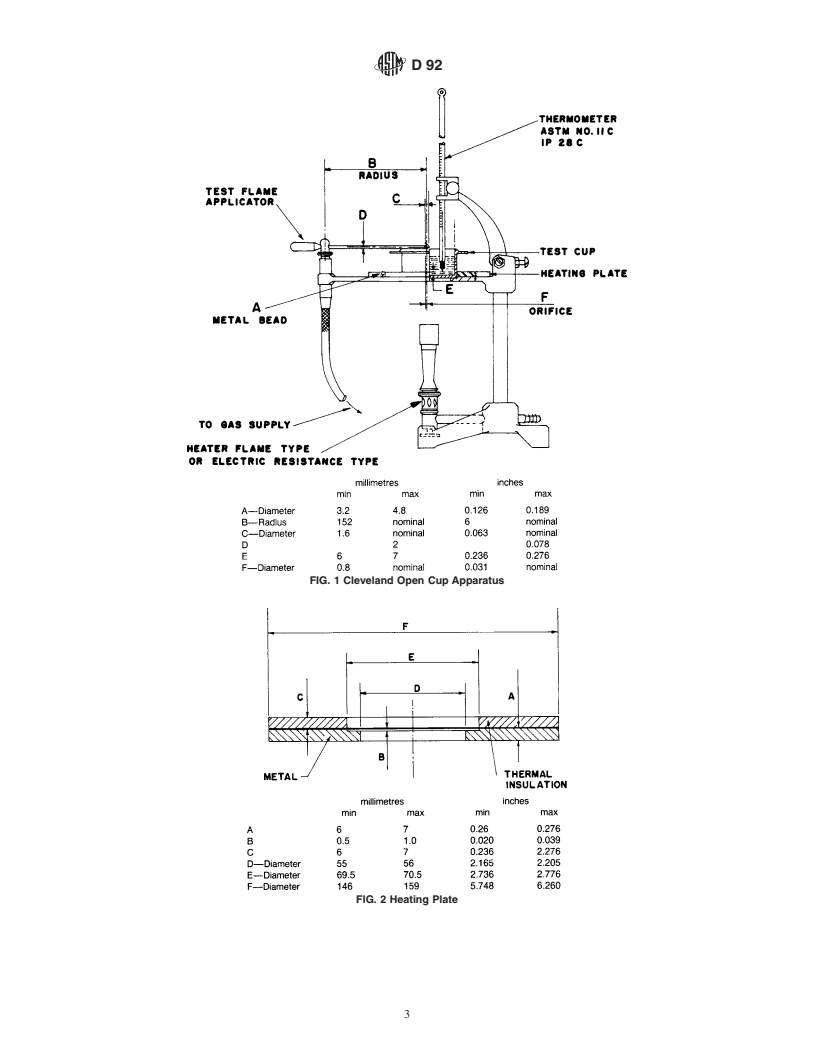
1.1 This test method describes the determination of the flash and fire point of petroleum products by a manual Cleveland open cup apparatus or an automated Cleveland open cup apparatus.
Note 1—The precisions for fire point were not determined in the current interlaboratory program. Fire point is a parameter which is not commonly specified, although in some cases, knowledge of this flammability temperature may be desired.
1.2 This test method is applicable to all petroleum products with flash points above 79° C (175° F) and below 400° C (752° F) except fuel oils.
Note 2—This test method may occasionally be specified for the determination of the fire point of a fuel oil. For the determination of the flash points of fuel oils, use Test Method D 93. Test Method D 93 should also be used when it is desired to determine the possible presence of small, but significant concentrations of lower flash point substances which may escape detection by Test Method D 92. Test Method D 1310 can be employed if the flash point is known to be below 79° C (175° F).
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific hazard statements, see 6.4, 7.1, 11.1.3, and 11.2.4.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
An American National Standard
Designation:D92–01 American Association State
Highway and Transportation Officials Standard
AASHTO No.: T48
DIN 51 376
Designation: 36/84 (89)
Standard Test Method for
1
Flash and Fire Points by Cleveland Open Cup
ThisstandardisissuedunderthefixeddesignationD 92;thenumberimmediatelyfollowingthedesignationindicatestheyearoforiginal
adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.Asuperscript
epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This test method was adopted as a joint ASTM-IP standard in 1965.
This test method has been adopted for use by government agencies to replace Method 1103.7 of Federal Test Method Standard No. 791b,
and Method 4294 of Federal Test Method Standard No. 141A.
INTRODUCTION
This flash point and fire point test method is a dynamic method and depends on definite rates of
temperature increases to control the precision of the test method. Its primary use is for viscous
materials having flash point of 79°C (175°F) and above. It is also used to determine fire point, which
is a temperature above the flash point, at which the test specimen will support combustion for a
minimum of 5 s. Do not confuse this test method with Test Method D 4206, which is a sustained
burning test, open cup type, at a specific temperature of 49°C (120°F).
1. Scope * 1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
1.1 Thistestmethoddescribesthedeterminationoftheflash
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
point and fire point of petroleum products by a manual
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
Cleveland open cup apparatus or an automated Cleveland open
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific hazard
cup apparatus.
statements, see 6.4, 7.1, 11.1.3, and 11.2.4.
NOTE 1—The precisions for fire point were not determined in the
current interlaboratory program. Fire point is a parameter that is not
2. Referenced Documents
commonly specified, although in some cases, knowledge of this flamma-
2.1 ASTM Standards:
bility temperature may be desired.
D 93 Test Methods for Flash Point by Pensky-Martens
1.2 This test method is applicable to all petroleum products 2
Closed Cup Tester
with flash points above 79°C (175°F) and below 400°C 3
D 140 Practice for Sampling Bituminous Materials
(752°F) except fuel oils.
D 1310 Test Method for Flash Point and Fire Point of
4
Liquids by Tag Open-Cup Apparatus
NOTE 2—This test method may occasionally be specified for the
determination of the fire point of a fuel oil. For the determination of the
D 4057 Practice for Manual Sampling of Petroleum and
5
flash points of fuel oils, use Test Method D 93. Test Method D 93 should
Petroleum Products
alsobeusedwhenitisdesiredtodeterminethepossiblepresenceofsmall,
D 4177 Practice for Automatic Sampling of Petroleum and
but significant, concentrations of lower flash point substances that may
5
Petroleum Products
escape detection by Test Method D 92. Test Method D 1310 can be
D 4206 Test Method for Sustained Burning of Liquid Mix-
employed if the flash point is known to be below 79°C (175°F).
6
tures Using the Small Scale Open-Cup Apparatus
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
7
E 1 Specification for ASTM Thermometers
standard. The values given in parentheses are for information
only.
2
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 05.01.
1 3
This test method is under the joint jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 04.03.
4
Petroleum Products and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 06.01.
5
D02.08 on Volatility. In the IP, this test method is under the jurisdiction of the Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 05.02.
6
Standardization Committee. Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 06.01.
7
Current edition approved Aug. 10, 2001. Published September 2001. Originally Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 14.03.
published as D 92 – 21. Last previous edition D 92 – 98a.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D92
8
E 300 Practice for Sampling Industrial Chemicals trolled laboratory conditions. It is only one of a number of
9
2.2 IP Standard: properties that should be considered in assessing the overall
Specifications for IP Standard Thermometers flammability hazard of a material.
10
2.3 ISO Standards:
5.2 Flash point is used in shipping and safety regulations to
Guide 34 Quality Systems Guidelines for the Production of
define flammable and combustible materials. Consult the
Reference Materials
particular regulation involved for precise definitions of these
Guide 35 Certification of Reference Material—General and
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.