ASTM D6286-98(2006)
(Guide)Standard Guide for Selection of Drilling Methods for Environmental Site Characterization
Standard Guide for Selection of Drilling Methods for Environmental Site Characterization
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
The selection of particular method(s) for drilling monitoring wells (see Table 1) requires that specific characteristics of each site be considered. These characteristics would include, but are not limited to, the ambient hydrogeologic parameters and conditions existing at the site. This guide is intended to make the user aware of some of the various drilling methods available and the applications, advantages and disadvantages of each with respect to determing groundwater chemistry and other hydrogeologic properties data.
This guide can be used in conjunction with Guide D6169. There are several guides that deal with individual drilling methods (see Guides D5781, D5782, D5783, D5784, D5872, D5875, and D5876) and how to the complete them for water quality monitoring device installation (see Practice D5092).
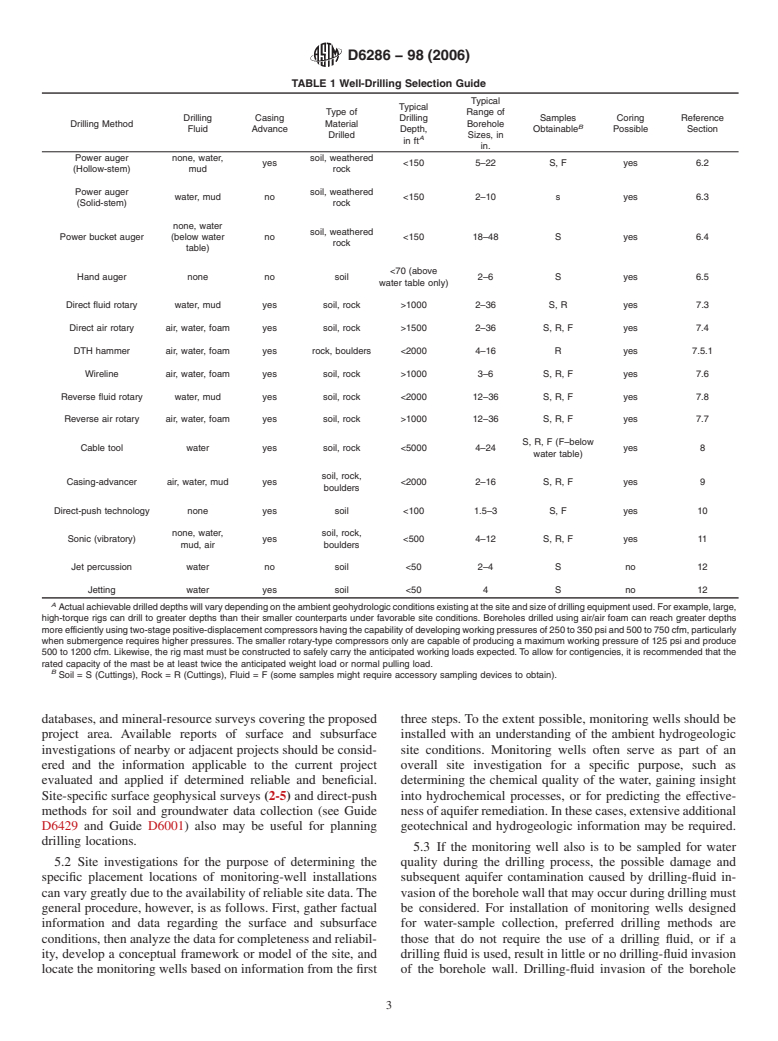
TABLE 1 Well-Drilling Selection Guide Drilling MethodDrilling
FluidCasing
AdvanceType of
Material
DrilledTypical
Drilling
Depth,
in ftATypical
Range of
Borehole
Sizes, in
in.Samples
ObtainableBCoring
PossibleReference
Section Power auger
(Hollow-stem)none, water, mudyessoil, weathered rock1505–22S, Fyes6.2 Power auger
(Solid-stem)water, mudnosoil, weathered rock1502–10syes6.3 Power bucket augernone, water (below water table)nosoil, weathered rock15018–48Syes6.4 Hand augernonenosoil70 (above water table only)2–6Syes6.5 Direct fluid rotarywater, mudyessoil, rock>10002–36S, Ryes7.3 Direct air rotaryair, water, foamyessoil, rock>15002–36S, R, Fyes7.4 DTH hammerair, water, foamyesrock, boulders20004–16Ryes7.5.1 Wirelineair, water, foamyessoil, rock>10003–6S, R, Fyes7.6 Reverse fluid rotarywater, mudyessoil, rock200012–36S, R, Fyes7.8 Reverse air rotaryair, water, foamyessoil, rock>100012–36S, R, Fyes7.7 Cable toolwateryessoil, rock50004–24S, R, F (F–below water table)yes8 Casing-advancerair, water, mudyessoil, rock, boulders20002–16S, R, Fyes9 Direct-push technologynoneyessoil1001.5–3S, Fyes10 Sonic (vibratory)none, wa...
SCOPE
1.1 This guide provides descriptions of various drilling methods for environmental site characterization along with advantages and disadvantages associated with each method discussed. A comprehensive description of these drilling methods can be found in individual ASTM standards, see Section 2. This guide is intended to aid in the selection of drilling method(s) for environmental soil and rock borings and the installation of monitoring wells and other water-quality monitoring devices.
1.2 This guide does not address methods of well construction, well development, or well completion. These topics are covered in other ASTM documents, see Section 2.
1.3 This guide cannot address all possible subsurface conditions that may occur such as, geologic, topographic, climatic, or anthropogenic. Site evaluation for engineering, design, and construction purposes is addressed in Guide D420.
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. Because dimensions of materials used in the drilling industry are given in inch-pound units by convention, inch-pound units also are used in this guide.
1.5 This guide does not specifically address methods of lithologic sample collection, such as coring, that may require the use of a specific drilling method. Other ASTM guides should be consulted for sampling methods (see Guide D6169) and equipment necessary for specific projects.
1.6 This guide does not purport to comprehensively address all of the methods and the issues associated with drilling for environmental purposes. Users should seek qualified professionals for decisions as to the proper equipment and methods that would be most successful for their site investigation. Other methods may be available for drilling and qualified professionals should have flexibility to exercise judgment as to possible alternatives not covered in this guide. The guide is current at the time of issue, but new alternative methods may b...
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D6286 − 98 (Reapproved2006)
Standard Guide for
Selection of Drilling Methods for Environmental Site
1
Characterization
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D6286; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope the time of issue, but new alternative methods may become
available prior to revisions; therefore, users should consult
1.1 This guide provides descriptions of various drilling
with manufacturers or producers prior to specifying program
methods for environmental site characterization along with
requirements.
advantages and disadvantages associated with each method
discussed.Acomprehensive description of these drilling meth- 1.7 Pertinent guides addressing specific drilling methods,
ods can be found in individualASTM standards, see Section 2. equipment and procedures are listed in 2.1. A comprehensive
This guide is intended to aid in the selection of drilling list of guides, methods, practices, and terminology for drilling
method(s) for environmental soil and rock borings and the is contained in Guide D5730. Other documents covering
installation of monitoring wells and other water-quality moni- procedures for environmental site investigations with specific
toring devices. objectives or in particular geographic settings may be available
from federal, state, and other agencies or organizations. The
1.2 This guide does not address methods of well
appropriate agency or organization should be contacted to
construction, well development, or well completion. These
determine the availability and most current edition of such
topics are covered in other ASTM documents, see Section 2.
documents.
1.3 This guide cannot address all possible subsurface con-
1.8 This standard does not purport to address all of the
ditions that may occur such as, geologic, topographic, climatic,
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
or anthropogenic. Site evaluation for engineering, design, and
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
construction purposes is addressed in Guide D420.
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
standard. Because dimensions of materials used in the drilling
1.9 This guide offers an organized collection of information
industry are given in inch-pound units by convention, inch-
or a series of options and does not recommend a specific
pound units also are used in this guide.
course of action. This document cannot replace education and
experienceandshouldbeusedinconjunctionwithprofessional
1.5 This guide does not specifically address methods of
judgement. Not all aspects of this guide may be applicable in
lithologic sample collection, such as coring, that may require
all circumstances. This ASTM standard is not intended to
the use of a specific drilling method. Other ASTM guides
represent or replace the standard of care by which the
should be consulted for sampling methods (see Guide D6169)
adequacy of a given professional service must be judged, nor
and equipment necessary for specific projects.
should this document be applied without consideration of a
1.6 This guide does not purport to comprehensively address
project’s many unique aspects. The word “Standard” in the
all of the methods and the issues associated with drilling for
title of this document means only that the document has been
environmental purposes. Users should seek qualified profes-
approved through the ASTM consensus process.
sionals for decisions as to the proper equipment and methods
thatwouldbemostsuccessfulfortheirsiteinvestigation.Other
2. Referenced Documents
methods may be available for drilling and qualified profession-
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
als should have flexibility to exercise judgment as to possible
D420 Guide to Site Characterization for Engineering Design
alternatives not covered in this guide. The guide is current at
3
and Construction Purposes (Withdrawn 2011)
1 2
This guide is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee D18 on Soil and Rock For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D18.21 on Groundwater and contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Vadose Zone Investigations. Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
Current edition approved July 1, 2006. Published July 2006. Originaly approved the ASTM website.
3
in 1998. Last previous edition approved in 1998 as D6286 – 98.
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.