ASTM D4984-20
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Carbon Dioxide in Natural Gas Using Length-of-Stain Detector Tubes
Standard Test Method for Carbon Dioxide in Natural Gas Using Length-of-Stain Detector Tubes
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 The measurement of carbon dioxide in natural gas is important, because of gas quality specifications, the corrosive nature of carbon dioxide on pipeline materials, and the affects of carbon dioxide on utilization equipment.
5.2 This test method provides inexpensive field screening of carbon dioxide. The system design is such that it may be used by nontechnical personnel with a minimum of proper training.
SCOPE
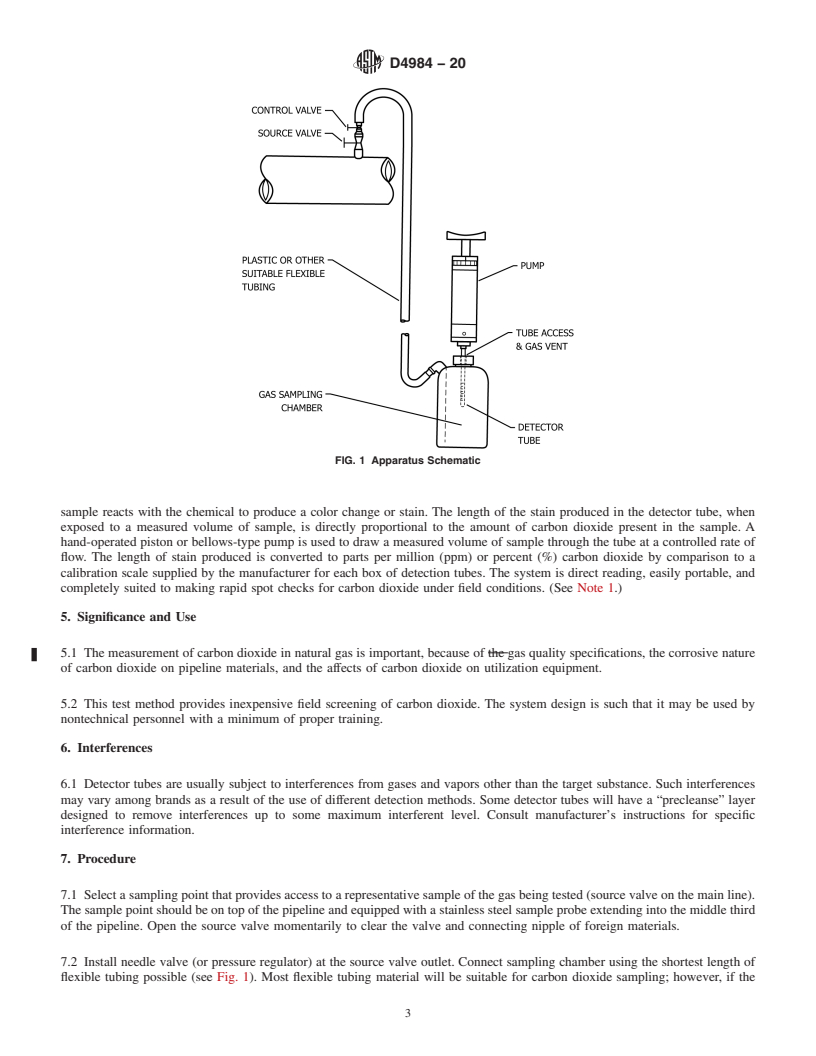
1.1 This test method covers a rapid and simple field determination of carbon dioxide in natural gas pipelines. Available detector tubes provide a total measuring range of 100 ppm (parts per million) up to 60 % by volume, although the majority of applications will be on the lower end of this range (that is, under 5 %). At least one manufacturer provides a special kit for measurements from 10 to 100 % CO2, but the normal 100 cc hand pump is not used. See Note 1.
Note 1: High-range carbon dioxide detector tubes will have measuring ranges in percent (%) CO2, and low-range tubes will be in parts per million (ppm). To convert percent to ppm, multiply by 10 000 (1 % = 10 000 ppm).
1.2 Units—The values stated in SI units are regarded as standard. The inch-pound units in parentheses are for information only.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: D4984 − 20
Standard Test Method for
Carbon Dioxide in Natural Gas Using Length-of-Stain
1
Detector Tubes
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D4984; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
3
1. Scope 2.2 GPA Standard:
2337 Test for Hydrogen Sulfide and Carbon Dioxide in
1.1 This test method covers a rapid and simple field deter-
Natural Gas Using Length-of-Stain Tubes
mination of carbon dioxide in natural gas pipelines. Available
detector tubes provide a total measuring range of 100 ppm
3. Terminology
(parts per million) up to 60 % by volume, although the majority
3.1 Definitions—For definitions of general terms used in
of applications will be on the lower end of this range (that is,
D03 Gaseous Fuels standards, refer to Terminology D4150.
under 5 %). At least one manufacturer provides a special kit for
measurements from 10 to 100 % CO , but the normal 100 cc
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
2
hand pump is not used. See Note 1.
3.2.1 detector tube pump, n—a hand-operated pump of a
piston or bellows type.
NOTE 1—High-range carbon dioxide detector tubes will have measuring
3.2.1.1 Discussion—It must be capable of drawing 100 mL
ranges in percent (%) CO , and low-range tubes will be in parts per
2
million (ppm). To convert percent to ppm, multiply by 10 000 per stroke of sample through the detector tube with a volume
4
(1 % = 10 000 ppm).
tolerance of 65 mL. It must be specifically designed for use
with detector tubes.
1.2 Units—The values stated in SI units are regarded as
3.2.1.2 Discussion—A detector tube and pump together
standard. The inch-pound units in parentheses are for informa-
form a unit and must be used as such. Each manufacturer
tion only.
calibrates detector tubes to match the flow characteristics of
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
their specific pump. Crossing brands of pumps and tubes is not
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
permitted, as considerable loss of system accuracy is likely to
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
4
occur.
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
3.2.2 gas sampling chamber, n—any container that provides
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
for access of the detector tube into a uniform flow of sample
1.4 This international standard was developed in accor-
gas at atmospheric pressure and isolates the sample from the
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
surrounding atmosphere.
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
3.2.2.1 Discussion—A stainless steel needle valve (or pres-
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
sure regulator) is placed between the source valve and the
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
sampling chamber for the purpose of throttling the sample
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
flow. Flow rate should approximate 1 to 2 volume changes per
minute or, at minimum, provide exit gas flow throughout the
2. Referenced Documents
detector tube-sampling period.
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
3.2.2.2 Discussion—A suitable sampling chamber may be
D4150 Terminology Relating to Gaseous Fuels
devised from a polyethylene wash bottle of nominal 500 mL
(16 oz) or 1 L (32 oz) size. The wash bottle’s internal delivery
tube provides for delivery of sample gas to the bottom of the
1
1
bottle. A 14.7 mm ( ⁄2 in.) hole cut in the bottle’s cap provides
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D03 on Gaseous
Fuels and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D03.06.03 on Analysis by
access for the detector tube and vent for the purge gas (see Fig.
Spectroscopy.
1). (An alternate flow-through sampler may be fashioned using
Current edition approved Dec. 15, 2020. Published January 2021. Originally
approved in 1989. Last previous edition approved in 2015 as D4984 – 06(2015).
DOI: 10.1520/D4984-20.
2 3
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or Available from Gas Processors Association (GPA), 6060 American Plaza, Suite
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM 700, Tulsa, OK 74135, http://www.gpaglobal.org.
4
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Direct Reading Colorimetric Indicator Tubes Manual, Second Edition, Ameri-
the ASTM website. can Industrial
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D4984 − 06 (Reapproved 2015) D4984 − 20
Standard Test Method for
Carbon Dioxide in Natural Gas Using Length-of-Stain
1
Detector Tubes
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D4984; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method covers a rapid and simple field determination of carbon dioxide in natural gas pipelines. Available detector
tubes provide a total measuring range of 100 ppm (parts per million) up to 60 % by volume, although the majority of applications
will be on the lower end of this range (that is, under 5 %). At least one manufacturer provides a special kit for measurements from
10 to 100 % CO , but the normal 100-cc100 cc hand pump is not used. See Note 1.
2
NOTE 1—High-range carbon dioxide detector tubes will have measuring ranges in percent (%) CO , and low-range tubes will be in parts per million (ppm).
2
To convert percent to ppm, multiply by 10 000 (1 % = 10 000 ppm).
1.2 Units—The values stated in SI units are regarded as standard. The inch-pound units in parentheses are for information only.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety safety, health, and healthenvironmental practices and determine the
applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D4150 Terminology Relating to Gaseous Fuels
3
2.2 Gas Processors Association GPA Standard:
2337 Test for Hydrogen Sulfide and Carbon Dioxide in Natural Gas Using Length-of-Stain Tubes
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions—For definitions of general terms used in D03 Gaseous Fuels standards, refer to Terminology D4150.
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
1
This test method is issued under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D03 on Gaseous Fuels and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D03.07 on Analysis of
Chemical Composition of Gaseous Fuels.
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2015Dec. 15, 2020. Published December 2015January 2021. Originally approved in 1989. Last previous edition approved in 20112015
as D4984D4984 – 06–06 (2011). (2015). DOI: 10.1520/D4984-06R15.10.1520/D4984-20.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
Available from Gas Processors Association, 6526 East 60th St., Tulsa, OK 74145.Association (GPA), 6060 American Plaza, Suite 700, Tulsa, OK 74135,
http://www.gpaglobal.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D4984 − 20
3.2.1 detector tube pump—pump, n—a hand-operated pump of a piston or bellows type. It must be capable of drawing 100 mL
per stroke of sample through the detector tube with a volume tolerance of 65 mL. It must be specifically designed for use with
detector tubes.
3.2.1.1 Discussion—
4
It must be capable of drawing 100 mL per stroke of sample through the detector tube with a volume tolerance of 65 mL. It must
be specifically designed for use with detector tubes.
3.2.1.2 Discussion—
A detector tube and pump together form a unit and must be used as such. Each manufacturer calibrates detector tubes to match
the flow characteristics of their specific pump. Crossing brands of pumps and tubes is not permitted, as considerable loss of system
4
accuracy is likely to occur.
3.1.1.1 Discussion—A detector tube and pump together form a unit and must be used as such. Each manufacturer calibrates
detector tubes to match the flow characteristics of their specific pump. Crossing brands of pumps and tubes is not permitted, as
3
considerable loss of system accuracy is likely to occur.
3.2.2 gas sampling chamber—chamber, n—any container
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.