ASTM G137-97(2017)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Ranking Resistance of Plastic Materials to Sliding Wear Using a Block-On-Ring Configuration
Standard Test Method for Ranking Resistance of Plastic Materials to Sliding Wear Using a Block-On-Ring Configuration
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 The specific wear rates determined by this test method can be used as a guide in ranking the wear resistance of plastic materials. The specific wear rate is not a material property and will therefore differ with test conditions and test geometries. The significance of this test will depend on the relative similarity to the actual service conditions.
5.2 This test method seeks only to describe the general test procedure and the procedure for calculating and reporting data.
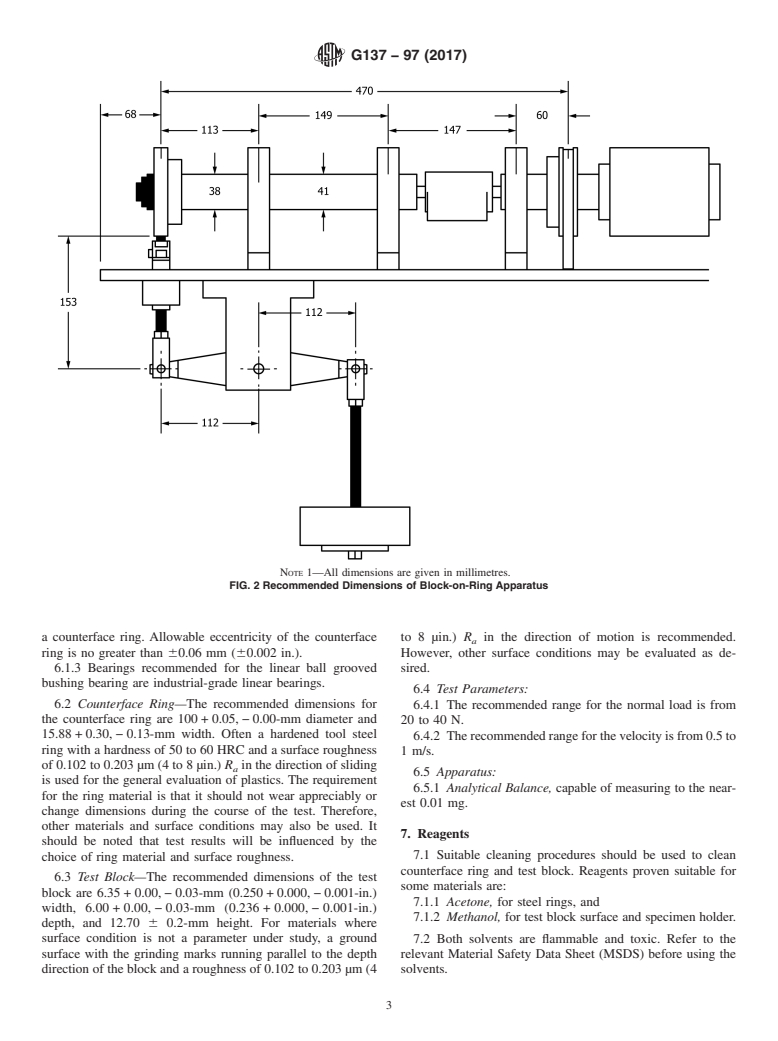
Note 2: This test configuration allows steady state specific wear rates to be achieved very quickly through the use of high loads and speeds. The thrust washer configuration described in Test Method D3702 does not allow for the use of such high speeds and loads because of possible overheating (which may cause degradation or melting, or both) of the specimen. Despite the differences in testing configurations, a good correlation in the ranking of wear resistance is achieved between the two tests (Table X2.1).
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers a laboratory procedure to measure the resistance of plastic materials under dry sliding conditions. The test utilizes a block-on-ring geometry to rank materials according to their sliding wear characteristics under various conditions.
1.2 The test specimens are small so that they can be molded or cut from fabricated plastic parts. The test may be run at the load, velocity, and temperature which simulate the service condition.
1.3 Wear test results are reported as specific wear rates calculated from volume loss, sliding distance, and load. Materials with superior wear resistance have lower specific wear rates.
1.4 This test method allows the use of both single- and multi-station apparatus to determine the specific wear rates.
1.5 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.7 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: G137 − 97 (Reapproved 2017)
Standard Test Method for
Ranking Resistance of Plastic Materials to Sliding Wear
1
Using a Block-On-Ring Configuration
This standard is issued under the fixed designation G137; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 2. Referenced Documents
2
1.1 This test method covers a laboratory procedure to 2.1 ASTM Standards:
measure the resistance of plastic materials under dry sliding D618 Practice for Conditioning Plastics for Testing
conditions. The test utilizes a block-on-ring geometry to rank D3702 Test Method for Wear Rate and Coefficient of Fric-
materials according to their sliding wear characteristics under tion of Materials in Self-Lubricated Rubbing Contact
various conditions. Using a Thrust Washer Testing Machine
E122 Practice for Calculating Sample Size to Estimate, With
1.2 The test specimens are small so that they can be molded
Specified Precision, the Average for a Characteristic of a
or cut from fabricated plastic parts. The test may be run at the
Lot or Process
load, velocity, and temperature which simulate the service
G40 Terminology Relating to Wear and Erosion
condition.
G77 Test Method for Ranking Resistance of Materials to
1.3 Wear test results are reported as specific wear rates
Sliding Wear Using Block-on-Ring Wear Test
calculated from volume loss, sliding distance, and load. Mate-
G117 Guide for Calculating and Reporting Measures of
rials with superior wear resistance have lower specific wear
Precision Using Data from Interlaboratory Wear or Ero-
3
rates.
sion Tests (Withdrawn 2016)
1.4 This test method allows the use of both single- and
3. Terminology
multi-station apparatus to determine the specific wear rates.
3.1 Definitions:
1.5 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
3.1.1 wear—damage to a solid surface, generally involving
standard. The values given in parentheses are for information
progressive loss of material, due to relative motion between
only.
that surface and a contacting substance or substances.
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the
3.1.2 Additional definitions relating to wear are found in
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
Terminology G40.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
3.2.1 specific wear rate—the volume loss per unit sliding
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
distance, divided by the load. It can be calculated as the volume
1.7 This international standard was developed in accor-
loss per unit time, divided by the load and the sliding velocity.
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the 3.2.2 steady state specific wear rate—the specific wear rate
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom- that is established during that part of the test when the specific
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical wear rate remains substantially constant (the specific wear rate
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee. versus sliding distance curve flattens out considerably with less
than 30 % difference between the specific wear rates) during a
1 2
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee G02 on Wear For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
and Erosion and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee G02.40 on Non- contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Abrasive Wear. Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2017. Published December 2017. Originally the ASTM website.
3
approved in 1995. Last previous edition appeared in 2009 as G137 – 97 (2009). The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
DOI: 10.1520/G0137-97R17. www.astm.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
G137 − 97 (2017)
minimum of three time intervals spanning a total time duration will therefore differ with test conditions and test geometries.
of at least 18 h, with ideally no single interval exceeding 8 h. The significance of this test will depend on the relative
However, one
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.