ASTM D1871-04
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Adhesion Between Tire Bead Wire and Rubber
Standard Test Method for Adhesion Between Tire Bead Wire and Rubber
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
To contribute to the mechanical properties required in a product, tire bead wire must have good adhesion to the rubber matrix. This allows the rubber to absorb part of the energy, distributing it uniformly between the reinforcing material and the rubber compound. This test method is considered satisfactory for acceptance testing of commercial shipments of wire since it has been used extensively in the trade for this purpose. This test method may be used for purchase specification requirements or manufacturing control of bead wire.
5.1.1 If there are differences of practical significance between reported test results for two laboratories (or more), comparative tests should be performed to determine if there is a statistical bias between them, using competent statistical assistance. As a minimum, test samples should be used that are as homogeneous as possible, that are drawn from the material from which the disparate test results were obtained, and that are randomly assigned in equal numbers to each laboratory for testing. Other materials with established test values may be used for this purpose. The test results from the two laboratories should be compared using a statistical test for unpaired data, at a probability level chosen prior to the testing series. If a bias is found, either its cause must be found and corrected, or future test results for that material must be adjusted in consideration of the known bias.
The characteristics of single filament steel wires that affect the adhesion property are wire diameter, coating composition, and coating mass. The storage conditions, age, and vulcanization conditions of the rubber compound will affect the test results and must be specified by the supplier of the rubber compound.
SCOPE
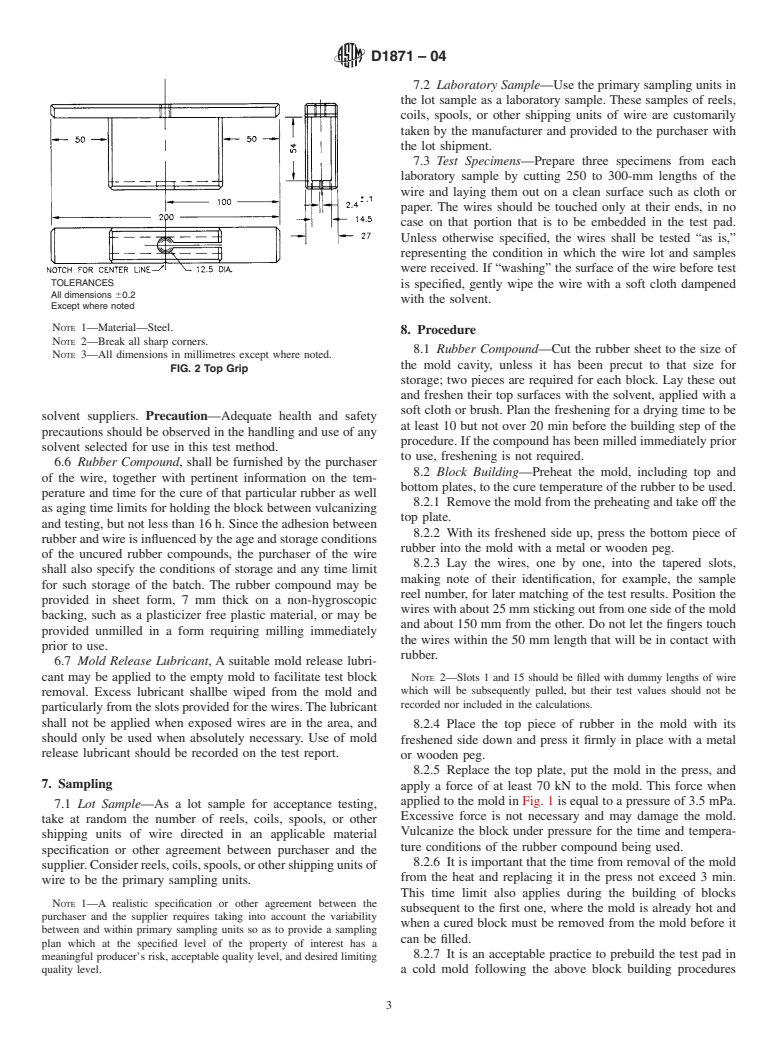
1.1 This test method cover procedures for testing the strength of adhesion of single-filament wire to vulcanized rubber compounds. The method applies to, but is not limited to, wire made from brass, bronze, or zinc coated steel wire. The adhesion strength is expressed as the magnitude of the pull-out force for the single filament of wire.
1.2 This test method is applicable to single-filament wires used in reinforced rubber products as single filaments and is normally used to evaluate the adhesion of samples of wire to a standard rubber applied under specified conditions. It is primarily used to evaluate tire bead wire and may be applied, with modifications and by agreement between supplier and customer, to various wire types used in rubber product reinforcing.
1.3 This test method is written in SI units.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. See 6.5.1.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
Designation:D1871–04
Standard Test Method for
1
Adhesion Between Tire Bead Wire and Rubber
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D1871; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 3. Terminology
1.1 This test method cover procedures for testing the 3.1 Definitions:
strength of adhesion of single-filament wire to vulcanized 3.1.1 Fordefinitionsoftermsrelatingtotirecord,beadwire,
rubbercompounds.Themethodappliesto,butisnotlimitedto, hose wire, and tire cord fabrics, refer to Terminology D6477
wire made from brass, bronze, or zinc coated steel wire. The 3.1.1.1 The following terms are relevant to this standard:
adhesion strength is expressed as the magnitude of the pull-out adhesion, curing, holland cloth, hose reinforcing wire, mill
force for the single filament of wire. grain, rubber, rubber compound, as used in the manufacture of
1.2 This test method is applicable to single-filament wires rubber articles, tire bead, tire bead wire, and vulcanization.
used in reinforced rubber products as single filaments and is 3.1.2 For definitions of terms relating to rubber, refer to
normally used to evaluate the adhesion of samples of wire to a Terminology D1566
standard rubber applied under specified conditions. It is prima- 3.1.3 For definitions of terms relating to testing and statis-
rily used to evaluate tire bead wire and may be applied, with tical concepts, refer to Terminology D4392 or E456.
modifications and by agreement between supplier and cus- 3.1.4 For definitions of other terms related to textiles, refer
tomer,tovariouswiretypesusedinrubberproductreinforcing. to Terminology D123.
1.3 This test method is written in SI units.
4. Summary of Test Methods
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
4.1 The wires are vulcanized into a block or pad of rubber
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro- and the force necessary to pull the wires out of the rubber is
measured. The direction of pull-out is axial, that is, along the
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. See 6.5.1. wire.
2. Referenced Documents 5. Significance and Use
5.1 To contribute to the mechanical properties required in a
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D76 Specification for Tensile Testing Machines for Textiles product, tire bead wire must have good adhesion to the rubber
matrix. This allows the rubber to absorb part of the energy,
D123 Terminology Relating to Textiles
D1566 Terminology Relating to Rubber distributing it uniformly between the reinforcing material and
the rubber compound. This test method is considered satisfac-
D2906 Practice for Statements on Precision and Bias for
2
Textiles tory for acceptance testing of commercial shipments of wire
since it has been used extensively in the trade for this purpose.
D3182 Practice for Rubber—Materials, Equipment, and
Procedures for Mixing Standard Compounds and Prepar- This test method may be used for purchase specification
requirements or manufacturing control of bead wire.
ing Standard Vulcanized Sheets
D4392 Terminology for Statistically Related Terms 5.1.1 If there are differences of practical significance be-
tween reported test results for two laboratories (or more),
D6477 Terminology Relating to Tire Cord, Bead Wire,
Hose Reinforcing Wire, and Fabrics comparative tests should be performed to determine if there is
a statistical bias between them, using competent statistical
E456 Terminology Relating to Quality and Statistics
assistance.As a minimum, test samples should be used that are
as homogeneous as possible, that are drawn from the material
1
Thistest method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee D13 on Textiles
from which the disparate test results were obtained, and that
and are the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D13.19 on Tire Cord and Fabric.
are randomly assigned in equal numbers to each laboratory for
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2004. Published Octber 2004. Originally
published as D1871 – 61 T. Last previous edition D1871 – 02. DOI: 10.1520/
testing. Other materials with established test values may be
D1871-04.
used for this purpose.The test results from the two laboratories
2
Withdrawn. The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced
should be compared using a statistical test for unpaired data, at
on www.astm.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ------
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.