ASTM D3658-01
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Determining the Torque Strength of Ultraviolet (UV) Light-Cured Glass/Metal Adhesive Joints
Standard Test Method for Determining the Torque Strength of Ultraviolet (UV) Light-Cured Glass/Metal Adhesive Joints
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
This test method provides reasonably accurate information with regard to the ability of UV curing adhesives to withstand torsional shearing forces. It may be used to determine the effect of environment on torsional shear strength.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the simplistic comparison of strengths of glass/metal joints when the adhesive is cured by ultraviolet (UV) radiation and standard specimens are used and tested under specified conditions of preparation, radiation, and load.
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are provided for information purposes only.
1.3 This test method involves torque loading UV-bonded hexagonal metal blocks to glass plates.
1.4 This test method may be used to obtain comparative torque strength-to-failure data for other bonded joint systems, radiation cured or not.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D 3658 – 01
Standard Test Method for
Determining the Torque Strength of Ultraviolet (UV) Light-
1
Cured Glass/Metal Adhesive Joints
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 3658; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope B 265 Specification for Titanium and Titanium Alloy Strip,
5
Sheet, and Plate
1.1 This test method covers the simplistic comparison of
6
D 907 Terminology of Adhesives
strengths of glass/metal joints when the adhesive is cured by
D 1002 Test Method forApparent Shear Strength of Single-
ultraviolet (UV) radiation and standard specimens are used and
Lap-Joint Adhesively Bonded Metal Specimens by Ten-
tested under specified conditions of preparation, radiation, and
6
sion Loading (Metal-to-Metal)
load.
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
3. Terminology
as the standard. The values given in parentheses are provided
3.1 Definitions—Many of the terms in this test method are
for information purposes only.
defined in Terminology D 907.
1.3 This test method involves torque loading UV-bonded
hexagonal metal blocks to glass plates.
4. Significance and Use
1.4 This test method may be used to obtain comparative
4.1 This test method provides reasonably accurate informa-
torque strength-to-failure data for other bonded joint systems,
tion with regard to the ability of UV curing adhesives to
radiation cured or not.
withstand torsional shearing forces. It may be used to deter-
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the
mine the effect of environment on torsional shear strength.
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
5. Apparatus
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
5.1 Test system consisting of apparatus capable of transfer-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
ring a uniform and continuous torque to the bonded hexagonal
block (schematically shown in Fig. 1), and a safety shield or
2. Referenced Documents
other safety device to prevent injury from possible shattering
2.1 ASTM Standards:
glass.
A 109 Specification for Steel, Strip, Carbon, (0.25 Maxi-
5.2 An accurate and reliable means of recording load to
2
mum Percent), Cold-Rolled
failure, that is, x-y or strip chart recorder, should also be part of
A 167 Specification for Stainless and Heat-Resisting
the test system.
2
Chromium-Nickel Steel Plate, Sheet, and Strip
B 36 Specification for Brass Plate, Sheet, Strip, and Rolled
6. Test Specimens
3
Bar
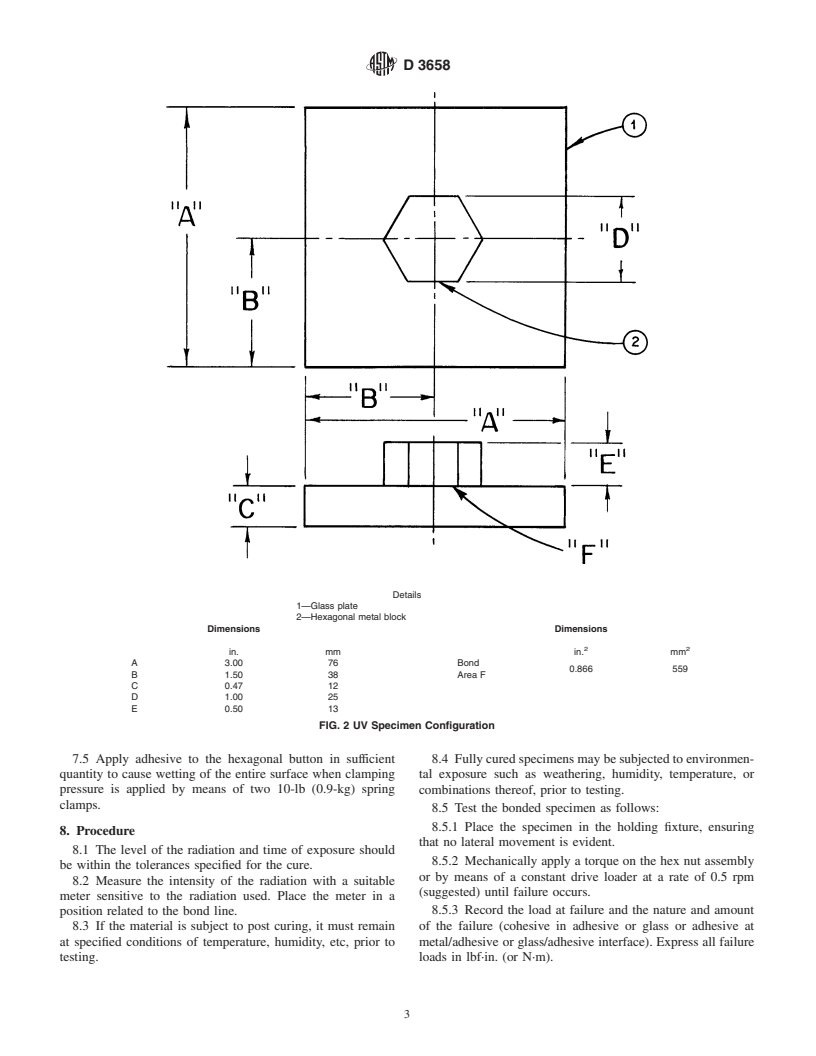
6.1 Recommended specimens are as shown in Fig. 2.
B 152 Specification for Copper Sheet, Strip, Plate and
6.2 Selection of the test metal for hexagonal blocks is at the
3
Rolled Bar
discretion of the user; however, the following grades are
B 209 Specification for Aluminum and Aluminum-Alloy
4 recommended (see Test Method D 1002):
Sheet and Plate
Metal Specification
Brass B 36, Alloy 8
Copper B 152, Type A
Aluminum B 209, Alloy 2024, T3 Temper
1
Steel A 109, Grade 2
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D14 on
Corrosion-resisting steel A 167, Type 302
Adhesives and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D 14.80 on Metal
Titanium B 265
Bonding Adhesives.
Current edition approved March 10, 2001. Published May 2001. Originally
published as D 3658 – 78. Last previous edition D 3658 – 90 (1995).
2
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 01.03.
3 5
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 02.01. Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 02.04.
4 6
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 02.02. Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 15.06.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D 3658
Details
1—Base plate
2—Upright
3—Mounting bracket
4—Lebow socket wrench sensor Model 2133-103
5—Pillow block—Boston #PPB10
6—Extension—Armstrong #4-105 A
7—1-in. (25.4-mm) hexagonal socket–Armstrong #A4-632
8—UV specimen (see Fig. 2)
9—Adjustable side guides (Fig. 2)
10—Neoprene pad (bonded to Detail 9) (Fig. 2)
Dimensions
in. mm
A 0.50 13
B 3.75 95
C 0.62 16
D 5.50 140
E 0.50 13
F 6.75 170
G 6.25 160
H 2.62 66
FIG. 1 UV Testing Apparatus
7
6.3 Hexagonal blocks may be reused after testing by bond- light scrubbing with an absorbent cleaning tissue. Then
ing the opposite end of the block or by cleaning the original thoroughly rinse the glass plates with distilled or deionized
bonded end by sanding or grinding and taking care to ensure water and air dry.
1
that ends are smooth and parallel.
7.4 Metal hexagonal b
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.