ASTM D5827-09
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Analysis of Engine Coolant for Chloride and Other Anions by Ion Chromatography
Standard Test Method for Analysis of Engine Coolant for Chloride and Other Anions by Ion Chromatography
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
This test method provides for the qualitative and quantitative determination of common anions in engine coolant in the milligrams per litre to low percent range and requires only a few millilitres or microlitres of sample per test, with results available in less than 30 min. Acceptable levels of chloride and other anions vary with manufacturer's blending specifications and applicable ASTM minimum or maximum specifications.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the chemical analysis of engine coolant for chloride ion by high-performance ion chromatography (HPIC). Several other common anions found in engine coolant can be determined in one chromatographic analysis by this test method.
1.2 This test method is applicable to both new and used engine coolant.
1.3 Coelution of other ions may cause interferences for any of the listed anions. In the case of unfamiliar formulations, identification verification should be performed by either or both fortification and dilution of the sample matrix with the anions of interest.
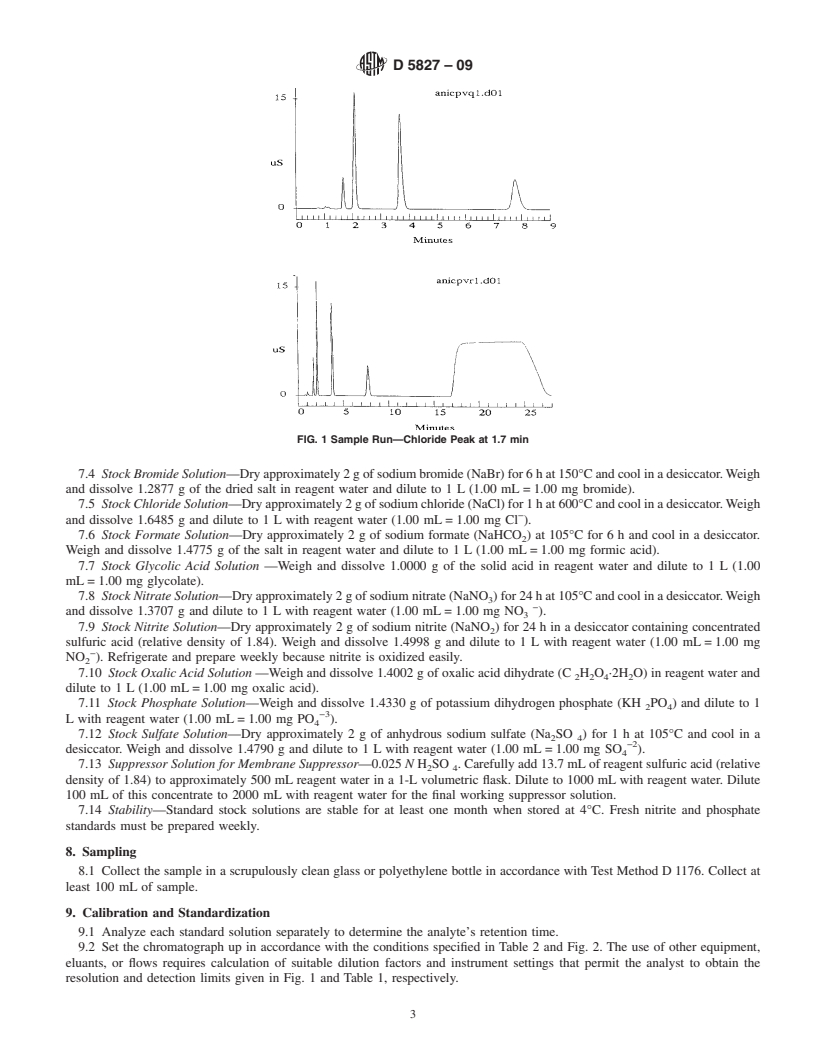
1.4 Analysis can be performed directly by this test method without pretreatment, other than dilution, as required by the linear ranges of the equipment. Table 1 indicates several applicable anions and approximate detection limits.
1.5 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to its use.
TABLE 1 Analytes and Minimum Detection Limits AnalyteDetection Limit, mg/LA Chloride (Cl−) 2.0 Nitrite (NO2−) 5.0 Bromide (Br) 4.0 Nitrate (NO3−) 7.1 o-Phosphate (HPO4)2−20.0 Sulfate (SO4)2− 8.0 Oxalate (C2O4)2−12.0
A Determined using 100-μL sample volume. Sample diluted 99 + 1 (v/v) with chromatographic eluant 30-μS/cm full scale, suppressed conductivity detection. Dionex AS4ASC column with AG4ASC guard columns. Other systems will require MDL determinations using chosen dilution factors, eluants, columns, and detector.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:D5827–09
Standard Test Method for
Analysis of Engine Coolant for Chloride and Other Anions
1
by Ion Chromatography
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D5827; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
TABLE 1 Analytes and Minimum Detection Limits
1. Scope*
A
Analyte Detection Limit, mg/L
1.1 This test method covers the chemical analysis of engine
−
Chloride (Cl)2.0
coolant for chloride ion by high-performance ion chromatog-
−
Nitrite (NO)5.0
2
raphy (HPIC). Several other common anions found in engine
Bromide (Br) 4.0
−
coolant can be determined in one chromatographic analysis by
Nitrate (NO)7.1
3
2−
o-Phosphate (HPO ) 20.0
this test method. 4
2−
Sulfate (SO ) 8.0
4
1.2 This test method is applicable to both new and used
2−
Oxalate (C O ) 12.0
2 4
engine coolant.
A
Determined using 100-µL sample volume. Sample diluted 99 + 1 (v/v) with
1.3 Coelution of other ions may cause interferences for any
chromatographic eluant 30-µS/cm full scale, suppressed conductivity detection.
of the listed anions. In the case of unfamiliar formulations, Dionex AS4ASC column with AG4ASC guard columns. Other systems will require
MDL determinations using chosen dilution factors, eluants, columns, and detector.
identification verification should be performed by either or
both fortification and dilution of the sample matrix with the
E177 Practice for Use of the Terms Precision and Bias in
anions of interest.
ASTM Test Methods
1.4 Analysis can be performed directly by this test method
without pretreatment, other than dilution, as required by the
3. Summary of Test Method
linear ranges of the equipment. Table 1 indicates several
3.1 A small volume of working sample is prepared by
applicable anions and approximate detection limits.
dilution of the sample with the method eluant. This diluted
1.5 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
sample is filtered and pumped through two ion exchange
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
columnsandasuppressorandintoaconductivitydetector.Ions
standard.
are separated based on their affinity for exchange sites of the
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the
resin with respect to the resin’s affinity for the eluant. The
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
suppressor increases the sensitivity of the method by both
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
increasing the conductivity of the analytes and decreasing the
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
conductivity of the eluant. The suppressor converts the eluant
bility of regulatory limitations prior to its use.
and the analytes to the corresponding hydrogen form acids.
Anions are quantitated by integration of their response com-
2. Referenced Documents
pared with an external calibration curve and are reported as
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
milligrams per litre (mg/L).
D1193 Specification for Reagent Water
D1176 Practice for Sampling and Preparing Aqueous So-
4. Significance and Use
lutions of Engine Coolants or Antirusts for Testing Pur-
4.1 This test method provides for the qualitative and quan-
poses
titative determination of common anions in engine coolant in
E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
the milligrams per litre to low percent range and requires only
Determine the Precision of a Test Method
a few millilitres or microlitres of sample per test, with results
availableinlessthan30min.Acceptablelevelsofchlorideand
other anions vary with manufacturer’s blending specifications
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee D15 on Engine
and applicable ASTM minimum or maximum specifications.
Coolants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D15.04 on Chemical
Properties.
5. Interferences
Current edition approved March 1, 2009. Published April 2009. Originally
approved in 1995. Last previous edition approved in 2002 as D5827-95(02).
5.1 Interferences can be caused by substances with similar
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
retention times, especially if they are in high concentration
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
compared to those of the analyte of interest. Sample dilution
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. will be used to minimize or solve most interference problems.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohock
...
This document is not anASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of anASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation:D5827–95 (Reapproved 2002) Designation:D5827–09
Standard Test Method for
Analysis of Engine Coolant for Chloride and Other Anions
1
by Ion Chromatography
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D5827; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope*
1.1 This test method covers the chemical analysis of engine coolant for chloride ion by high-performance ion chromatography
(HPIC). Several other common anions found in engine coolant can be determined in one chromatographic analysis by this test
method.
1.2 This test method is applicable to both new and used engine coolant.
1.3 Coelution of other ions may cause interferences for any of the listed anions. In the case of unfamiliar formulations,
identification verification should be performed by either or both fortification and dilution of the sample matrix with the anions of
interest.
1.4 Analysis can be performed directly by this test method without pretreatment, other than dilution, as required by the linear
ranges of the equipment. Table 1 indicates several applicable anions and approximate detection limits.
1.5The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.5 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to its use.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D1193 Specification for Reagent Water
D1176 Test Method for Sampling and Preparing Aqueous Solutions of Engine Coolants or Antirusts for Testing Purposes
Practice for Sampling and Preparing Aqueous Solutions of Engine Coolants or Antirusts for Testing Purposes
E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to Determine the Precision of a Test Method
E177 Practice for Use of the Terms Precision and Bias in ASTM Test Methods
3. Summary of Test Method
3.1 A small volume of working sample is prepared by dilution of the sample with the method eluant. This diluted sample is
filteredandpumpedthroughtwoionexchangecolumnsandasuppressorandintoaconductivitydetector.Ionsareseparatedbased
on their affinity for exchange sites of the resin with respect to the resin’s affinity for the eluant. The suppressor increases the
sensitivity of the method by both increasing the conductivity of the analytes and decreasing the conductivity of the eluant. The
suppressor converts the eluant and the analytes to the corresponding hydrogen form acids.Anions are quantitated by integration
of their response compared with an external calibration curve and are reported as milligrams per litre (mg/L).
4. Significance and Use
4.1 This test method provides for the qualitative and quantitative determination of common anions in engine coolant in the
milligrams per litre to low percent range and requires only a few millilitres or microlitres of sample per test, with results available
inlessthan30min.Acceptablelevelsofchlorideandotheranionsvarywithmanufacturer’sblendingspecificationsandapplicable
ASTM minimum or maximum specifications.
1
ThistestmethodisunderthejurisdictionofASTMCommitteeD15onEngineCoolantsandisthedirectresponsibilityofSubcommitteeD15.04onChemicalProperties.
Current edition approved Sept. 10, 1995. Published November 1995.
Current edition approved March 1, 2009. Published April 2009. Originally approved in 1995. Last previous edition approved in 2002 as D5827-95(02).
2
ForreferencedASTMstandards,visittheASTMwebsite,www.astm.org,orcontactASTMCustomerServiceatservice@astm.org.ForAnnualBookofASTMStandards
, Vol 11.01.volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D5827–09
TABLE 1 Analytes and Minimum Detection Limits
A
Analyte Detection Limit, mg/L
−
Chloride (Cl)2.0
−
Nitrite (NO)5.0
2
Bromide (Br) 4.0
−
Nitrate (NO)
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.