ASTM D3800-99(2010)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Density of High-Modulus Fibers
Standard Test Method for Density of High-Modulus Fibers
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
Fiber density is useful in the evaluation of new materials at the research and development level and is one of the material properties normally given in fiber specifications.
Fiber density is used to determine fiber strength and modulus both of a fiber bundle and an individual filament. These properties are based on load or modulus slope over an effective area. Fiber density may be used with lineal mass of the fiber to give an approximation of effective tow area. Tow area divided by the average number of filaments in a tow gives an approximation of the effective area of an individual filament.
Fiber density is used as a constituent property when determining reinforcement volume and void volume based on reinforcement mass and laminate density.
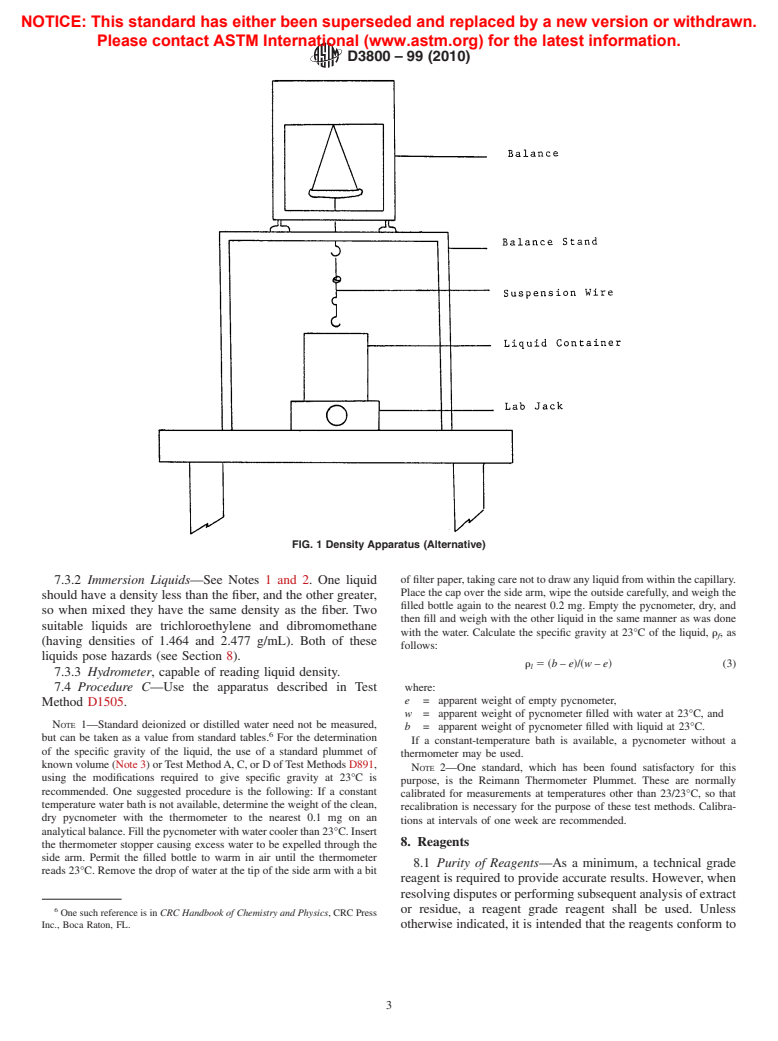
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the density of high-modulus fibers and is applicable to both continuous and discontinuous fibers.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard.
1.3 This standard may involve hazardous materials, operations, and equipment. This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. See Section 9 for additional information.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Please contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
Designation: D3800 – 99 (Reapproved 2010)
Standard Test Method for
1
Density of High-Modulus Fibers
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D3800; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope E177 Practice for Use of the Terms Precision and Bias in
ASTM Test Methods
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the density
ofhigh-modulusfibersandisapplicabletobothcontinuousand
3. Terminology
discontinuous fibers.
3.1 Definitions—Terminology D3878 defines terms relating
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
tocompositematerials.TerminologyE12definestermsrelating
standard.
to density. Practice E177 defines terms relating to statistics. In
1.3 This standard may involve hazardous materials, opera-
theeventofaconflictbetweenterms,TerminologyD3878shall
tions, and equipment. This standard does not purport to
have precedence over other standards.
address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its
3.2 Symbols:
use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to
establish appropriate safety and health practices and deter-
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
r = density of standard
s
See Section 9 for additional information.
r = density of liquid
l
r = density of fiber
f
2. Referenced Documents
r = density of the measured fiber containing sizing
mf
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
r = density of the measured liquid containing sur-
ml
D891 Test Methods for Specific Gravity, Apparent, of
factant
Liquid Industrial Chemicals r = density of surfactant
sur
D1505 Test Method for Density of Plastics by the Density- r = density of sizing
sz
Gradient Technique r = density of water
w
s = standard deviation
D3878 Terminology for Composite Materials
M = weight of suspension wire in air
D5229/D5229M Test Method for Moisture Absorption 1
M = weight of suspension wire in liquid (to immer-
2
Properties and Equilibrium Conditioning of Polymer Ma-
sion point)
trix Composite Materials
M = weight of suspension wire plus item whose
3
D6308 Guide for Identification of Composite Materials in
density is to be determined (in air)
3
Computerized Material Property Databases
M = weight of suspension wire plus item whose
4
E12 Terminology Relating to Density and Specific Gravity
density is to be determined (in liquid)
3
of Solids, Liquids, and Gases
M –M = weight of item for density to be determined in
3 1
air
M –M = weight of item for density to be determined in
1
4 2
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D30 onCom-
liquid
posite Materials and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D30.03 on
Constituent/Precursor Properties.
Current edition approved April 1, 2010. Published May 2010. Originally 4. Summary of Test Method
approved in 1979. Last previous edition approved in 2004 as D3800 – 99 (2004).
4.1 General—Usingrandomselectiontechniques,asuitable
DOI: 10.1520/D3800-99R10.
2
size sample of high-modulus fiber can be tested by any of the
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
three procedures described in this test method. Procedure A
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
using water with a surfactant as the liquid medium is preferred
the ASTM website.
3 due to environmental and safety considerations. The other
Withdrawn. The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced
on www.astm.org. methods shall not be used if Procedure A is adequate. Interim
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Please contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
D3800 – 99 (2010)
use of Procedures B or C is allowed while a comparison is
where
made to results using Procedure A.
x = mass of sizing as a percentage of the total mass of the
4.2 Procedure A—Buoyancy (Archimedes) Method:
measured fiber.
4.2.1 The sample is weighed in air and weighed in a liquid
6.1.5 Effect of Surfactant Density—The addition of a sur-
that will thoroughly wet the sample and is of a lower density.
factant to a liquid may produce bias if not considered. The
4.2.2 The difference in weight of the sample in the two
effect may be shown by the following equation:
media is the buoyancy force.
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.