ASTM D7347-15
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Determination of Olefin Content in Denatured Ethanol by Supercritical Fluid Chromatography (Withdrawn 2024)
Standard Test Method for Determination of Olefin Content in Denatured Ethanol by Supercritical Fluid Chromatography (Withdrawn 2024)
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 Olefinic hydrocarbons that may be present in denatured ethanol have been demonstrated to contribute to photochemical reactions in the atmosphere, and this can result in the formation of smog in susceptible urban areas.
5.2 The California Air Resources Board (CARB) has specified a maximum allowable limit of total olefins in spark ignition engine fuel. Denatured ethanol will be added at the terminals as an oxygenate additive and can contain olefinic species contributing to the total olefins present in spark ignition engine fuel. An analytical method is therefore necessary to determine total olefins in denatured ethanol intended for spark ignition engine fuel use. The test method is intended to be used by both regulators and producers.
5.3 The present test method is automated, does not require any sample preparation, and has a relatively short analysis time of approximately 20 min.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the total amount of olefins in denatured ethanol to be used as an oxygenate additive in blended spark ignition engine fuels. The method of determination is supercritical fluid chromatography (SFC). The application range is from 0.1 mass percent to 1.0 mass percent total olefins. Results are expressed in terms of mass percent olefins.
1.2 This test method can be used for the analysis of denatured ethanol that is intended to be used as an oxygenate additive in commercial spark ignition engine fuels.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
WITHDRAWN RATIONALE
This test method covered the determination of the total amount of olefins in denatured ethanol to be used as an oxygenate additive in blended spark ignition engine fuels. The method of determination is supercritical fluid chromatography (SFC). The application range is from 0.1 mass percent to 1.0 mass percent total olefins. Results are expressed in terms of mass percent olefins.
Formerly under the jurisdiction of Committee D02 on Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants, this test method was withdrawn in January 2024 in accordance with section 10.6.3 of the Regulations Governing ASTM Technical Committees, which requires that standards shall be updated by the end of the eighth year since the last approval date.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation:D7347 −15
Standard Test Method for
Determination of Olefin Content in Denatured Ethanol by
1
Supercritical Fluid Chromatography
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D7347; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* 3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions:
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the total
3.1.1 critical pressure, n—that pressure needed to condense
amount of olefins in denatured ethanol to be used as an
oxygenate additive in blended spark ignition engine fuels. The a gas at the critical temperature.
method of determination is supercritical fluid chromatography
3.1.2 critical temperature, n—highest temperature at which
(SFC). The application range is from 0.1 mass percent to 1.0
a gaseous fluid can be converted to a liquid by means of
mass percent total olefins. Results are expressed in terms of
compression.
mass percent olefins.
3.1.3 supercritical fluid, n—fluid maintained in a thermody-
1.2 This test method can be used for the analysis of
namic state above its critical temperature and critical pressure.
denatured ethanol that is intended to be used as an oxygenate
3.1.4 supercritical fluid chromatography, n— class of chro-
additive in commercial spark ignition engine fuels.
matography that employs supercritical fluids as mobile phases.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
standard. The values given in parentheses are for information
4. Summary of Test Method
only.
4.1 A small aliquot of the denatured alcohol sample is
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
injectedontoasetofthreeanalyticalchromatographiccolumns
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
connected in series. The sample is transported through the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
columns using supercritical carbon dioxide (CO)asthe
2
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
mobile phase. The first column is packed with polyvinyl
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
alcohol(PVA).Thesecondcolumnintheseriesisananalytical
column packed with high surface area silica gel particles, and
2. Referenced Documents
the third column is packed with silica particles coated with
strong cation exchange material loaded with silver ions.
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D4052 Test Method for Density, Relative Density, and API 4.2 Two six-port switching valves are used to direct the
different classes of components through the chromatographic
Gravity of Liquids by Digital Density Meter
D5186 Test Method for Determination of the Aromatic system to the detector. In a forward flow mode, saturates,
aromatics,andolefinspassontotheanalyticalsilicagelcolumn
Content and Polynuclear Aromatic Content of Diesel
Fuels and Aviation Turbine Fuels By Supercritical Fluid whilethealcoholisretainedonthePVAcolumn.Thesaturates,
Chromatography aromatics, and olefins are maintained on the silica column,
D6550 Test Method for Determination of Olefin Content of whilethealcoholisback-flushedtothedetector.Thisstepfrees
Gasolines by Supercritical-Fluid Chromatography the flow path of alcohol species allowing for the separation of
the olefins from saturates and aromatics. The forward flow
mode is resumed after the alcohol is eliminated and saturates
are carried to the detector, while the aromatics are retained on
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on
the silica column and the olefinic species are trapped on the
Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of
Subcommittee D02.04.0C on Liquid Chromatography.
silver-loaded column. The next step is to back-flush the olefins
Current edition approved Dec. 1, 2015. Published February 2016. Originally
from the silver-loaded column to the detector. Finally the
ɛ1
approved in 2007. Last previous edition approved in 2007 as D7347 – 07 . DOI:
aromatics are carried from the silica column to the detector in
10.1520/D7347-15.
2
a forward flow mode, bypassing the silver-loaded column.
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
4.3 A flame ionization detector (FID) is used for quantita-
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. tion. Calibration is based on the area of the chromatographic
*A Summary of Changes section appears at th
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
´1
Designation: D7347 − 07 D7347 − 15
Standard Test Method for
Determination of Olefin Content in Denatured Ethanol by
1
Supercritical Fluid Chromatography
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D7347; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1
ε NOTE—Added research report footnote to Section 13 editorially in October 2008.
1. Scope Scope*
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the total amount of olefins in denatured ethanol to be used as an oxygenate
additive in blended spark ignition engine fuels. The method of determination is supercritical fluid chromatography (SFC). The
application range is from 0.1 mass percent to 1.0 mass percent total olefins. Results are expressed in terms of mass percent olefins.
1.2 This test method can be used for the analysis of denatured ethanol that is intended to be used as an oxygenate additive in
commercial spark ignition engine fuels.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D4052 Test Method for Density, Relative Density, and API Gravity of Liquids by Digital Density Meter
D5186 Test Method for Determination of the Aromatic Content and Polynuclear Aromatic Content of Diesel Fuels and Aviation
Turbine Fuels By Supercritical Fluid Chromatography
D6550 Test Method for Determination of Olefin Content of Gasolines by Supercritical-Fluid Chromatography
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions:
3.1.1 critical pressure, n—that pressure needed to condense a gas at the critical temperature.
3.1.2 critical temperature, n—highest temperature at which a gaseous fluid can be converted to a liquid by means of
compression.
3.1.3 supercritical fluid, n—fluid maintained in a thermodynamic state above its critical temperature and critical pressure.
3.1.4 supercritical fluid chromatography, n— class of chromatography that employs supercritical fluids as mobile phases.
4. Summary of Test Method
4.1 A small aliquot of the denatured alcohol sample is injected onto a set of three analytical chromatographic columns connected
in series. The sample is transported through the columns using supercritical carbon dioxide (CO ) as the mobile phase. The first
2
column is packed with polyvinyl alcohol (PVA). The second column in the series is an analytical column packed with high surface
area silica gel particles, and the third column is packed with silica particles coated with strong cation exchange material loaded
with silver ions.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
D02.04.0C on Liquid Chromatography.
Current edition approved Aug. 1, 2007Dec. 1, 2015. Published September 2007February 2016. Originally approved in 2007. Last previous edition approved in 2007 as
ɛ1
D7347 – 07 . DOI: 10.1520/D7347-07E01.10.1520/D7347-15.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D7347 − 15
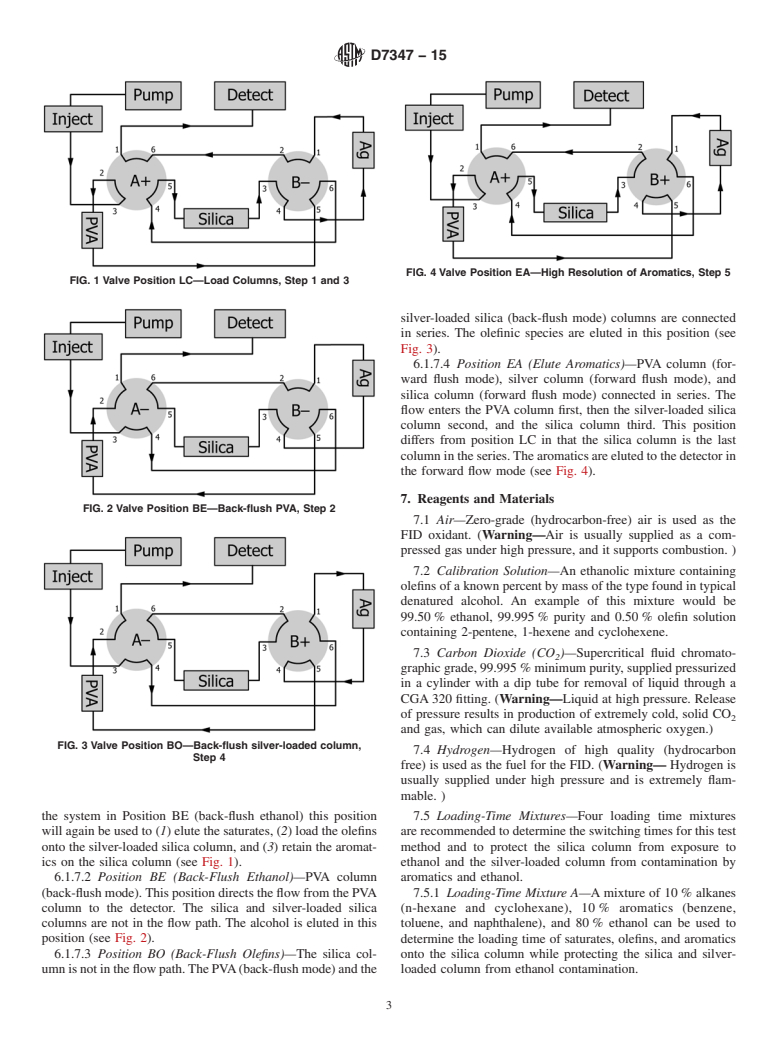
4.2 Two six-port switching valves are used to direct the different classes of components through the chromatographic system
to the detector. In a forward flow mode, saturates, aromatics, and olefins pass onto the analytical silica gel column while the alcohol
is retained on the PVA column. The saturates, aromatics, and olefins are maintained on the silica column, while the alcohol is
back-flushed to the detector. This step frees the flow path of alcohol species allowing for the separation of the olefins from saturates
and aromatics. The forward flow mode is resumed after the
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.