ASTM D4327-11
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Anions in Water by Suppressed Ion Chromatography
Standard Test Method for Anions in Water by Suppressed Ion Chromatography
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
Ion chromatography provides for both qualitative and quantitative determination of seven common anions, F−, Cl−, NO2−, HPO4−2, Br−, NO3−, and SO4−2, in the milligram per liter range from a single analytical operation requiring only a few milliliters of sample and taking approximately 10 to 15 min for completion. Additional anions, such as carboxylic acids, can also be quantified.
Note 2—This test method may be used to determine fluoride if its peak is in the water dip by adding one mL of eluent (at 100× the concentration in 8.3) to all 100-mL volumes of samples and standards to negate the effect of the water dip. (See 6.3, and also see 6.4.) The quantitation of unretained peaks should be avoided. Anions such as low molecular weight organic acids (formate, acetate, propionate, etc.) that are conductive coelute with fluoride and would bias fluoride quantitation in some drinking waters and most wastewaters. The water dip can be further minimized if measures are taken to remove carbonic acid which remain in the eluent after suppression using carbonate based eluents. There is no water dip if hydroxide eluents are used.
Anion combinations such as Cl−/Br− and NO2−/NO3−, which may be difficult to distinguish by other analytical methods, are readily separated by ion chromatography.
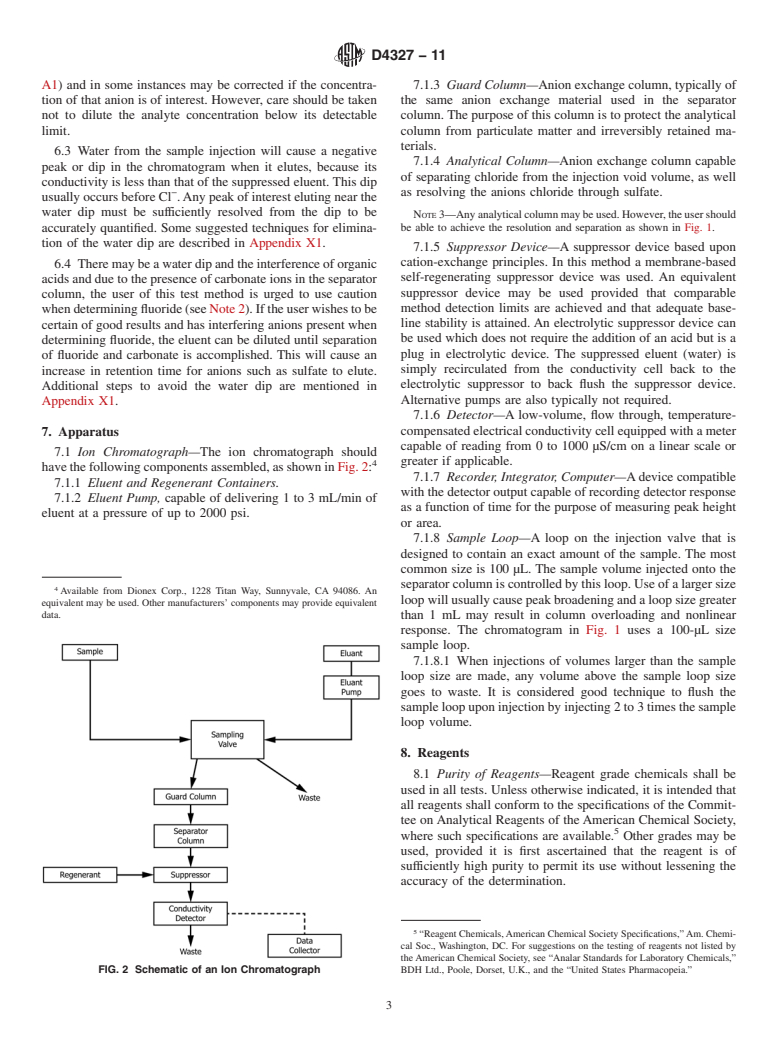
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the sequential determination of fluoride, chloride, nitrite, ortho-phosphate, bromide, nitrate, and sulfate ions in water by suppressed ion chromatography.
Note 1—Order of elution is dependent upon the column used; see Fig. 1.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D4327 − 11
Standard Test Method for
1
Anions in Water by Suppressed Ion Chromatography
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D4327; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* limitshavebeenobservedwithnewerinstrumentation,column
2
technology and eluents. The analyst must assure optimum
1.1 Thistestmethod coversthesequentialdeterminationof
instrument performance to maintain a stable baseline at more
fluoride, chloride, nitrite, ortho-phosphate, bromide, nitrate,
sensitive conductivity full-scale settings.
and sulfate ions in water by suppressed ion chromatography.
1.5 The upper limit of this test method is dependent upon
NOTE 1—Order of elution is dependent upon the column used; see Fig.
total anion concentration and may be determined experimen-
1.
tally as described in AnnexA1. These limits may be extended
1.2 This test method is applicable to drinking and wastewa-
byappropriatedilutionorbyuseofasmallerinjectionvolume.
ters.Therangestestedforthistestmethodforeachanionwere
1.6 Using alternate separator column and eluents may per-
as follows (measured in mg/L):
mit additional anions such as acetate, formate or citrate to be
Fluoride 0.26 to 8.49
determined. This is not the subject of this test method.
Chloride 0.78 to 26.0
Nitrite-N 0.36 to 12.0
1.7 This method update approves the use of Electrolytically
Bromide 0.63 to 21.0
Nitrate-N 0.42 to 14.0 generated eluent, electrolytically regenerated eluent, electro-
o-Phosphate 0.69 to 23.1
lytic suppression (not autozeroing) and electrolytic trap col-
Sulfate 2.85 to 95.0
umns also known as Reagent Free Ion Chromatography. This
1.3 Itistheuser’sresponsibilitytoensurethevalidityofthis
approval is based on acceptance by the US EPAas referenced
test method for other matrices.
in Appendix X2
1.4 Concentrations as low as 0.01 mg/L were determined
1.8 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
depending upon the anions to be quantified, in single labora-
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
tory work. Utilizing a 50-µL sample volume loop and a
standard.
sensitivity of 3 µS/cm full scale, the approximate detection
1.9 This standard does not purport to address all of the
limits shown in Table 1 can be achieved. Lower detection
safety problems, if any, associated with its use. It is the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee D19 on Water
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D19.05 on Inorganic Constituents
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
in Water.
Current edition approved Jan. 15, 2011. Published March 2011. Originally
2. Referenced Documents
approved in 1984. Last previous edition approved in 2003 as D4327–03. DOI:
10.1520/D4327-11.
3
2.1 ASTM Standards:
2
The following references may be consulted for additional information:
D1066Practice for Sampling Steam
Small, H., Stevens, T. S., and Bauman, W. C., “Novel Ion Exchange Chromato-
graphic Method Using Conductrimetric Detection,” Analytical Chemistry, Vol 47,
D1129Terminology Relating to Water
1975, p. 1801.
D1193Specification for Reagent Water
Stevens, T. S., Turkelson, V. T., and Alve, W. R., “Determination of Anions in
D2777Practice for Determination of Precision and Bias of
BoilerBlowDownWaterwithIonChromatography,” Analytical Chemistry,Vol49,
1977, p. 1176. Applicable Test Methods of Committee D19 on Water
Sawicki, E., Mulik, J. D., and Witgenstein, E., Editors, Ion Chromatographic
D3370Practices for Sampling Water from Closed Conduits
Analysis of Environmental Pollutants, Ann Arbor Science Publishers, Ann Arbor,
D5810Guide for Spiking into Aqueous Samples
MI, 1978.
D5847Practice for Writing Quality Control Specifications
Mulik, J. D., and Sawicki, E., Editors, Ion Chromatographic Analysis of
Environmental Pollutants,Vol/No.2,AnnArborSciencePublishers,AnnArbor,MI,
for Standard Test Methods for Water Analysis
1979.
Weiss, J., Handbook of Ion Chromatography, Dionex Corp., Sunnyvale, CA,
1986.
3
Waters Innovative Methods forAnionAnalysis,WatersChromatographyDivision For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
of Millipore, Method A 107 and A 116, 1990. contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Haddad, P. R., and Jackson, P. E., Ion Chromatography: Principles and Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
Applications, Elsevier Scientific Publishing Co., 1990. the ASTM website.
...
This document is not anASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of anASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation:D4327–03 Designation:D4327–11
Standard Test Method for
Anions in Water by Chemically Suppressed Ion
1
Chromatography
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D4327; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope*
2
1.1 This test method covers the sequential determination of fluoride, chloride, nitrite, ortho-phosphate, bromide, nitrate, and
sulfate ions in water by chemically suppressed ion chromatography.
NOTE 1—Order of elution is dependent upon the column used; see Fig. 1.
1.2 This test method is applicable to drinking and wastewaters. The ranges tested for this test method for each anion were as
follows (measured in mg/L):
Fluoride 0.26 to 8.49
Chloride 0.78 to 26.0
Nitrite-N 0.36 to 12.0
Bromide 0.63 to 21.0
Nitrate-N 0.42 to 14.0
o-Phosphate 0.69 to 23.1
Sulfate 2.85 to 95.0
1.3 It is the user’s responsibility to ensure the validity of this test method for other matrices.
1.4 Concentrations as low as 0.01 mg/L were determined depending upon the anions to be quantitated,quantified, in single
laboratory work. Utilizing a 50-µL sample volume loop and a sensitivity of 3 µS/cm full scale, the approximate detection limits
shown in Table 1 can be achieved. If lower detection levels are required, the sensitivity may be improved by using a lower scale
setting (<3 µS/cm) or a larger sample injection loop (>100 µL). The analyst must assure optimum instrument performance to
maintain a stable baseline at more sensitive conductivity full-scale settings. can be achieved. Lower detection limits have been
observed with newer instrumentation, column technology and eluents. The analyst must assure optimum instrument performance
to maintain a stable baseline at more sensitive conductivity full-scale settings.
1.5 The upper limit of this test method is dependent upon total anion concentration and may be determined experimentally as
described in Annex A1. These limits may be extended by appropriate dilution or by use of a smaller injection volume.
1.6Using alternate separator column and eluents may permit additional anions such as formate or citrate to be determined.This
is not the subject of this test method.
1.7
1.6 Using alternate separator column and eluents may permit additional anions such as acetate, formate or citrate to be
determined. This is not the subject of this test method.
1.7 This method update approves the use of Electrolytically generated eluent, electrolytically regenerated eluent, electrolytic
suppression (not autozeroing) and electrolytic trap columns also known as Reagent Free Ion Chromatography. This approval is
based on acceptance by the US EPA as referenced in Appendix X2
1.8 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.9 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety problems, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
1
ThistestmethodisunderthejurisdictionofASTMCommitteeD19onWaterandisthedirectresponsibilityofSubcommitteeD19.05onInorganicConstituentsinWater.
Current edition approved Jan. 10, 2003.15, 2011. Published January 2003.March 2011. Originally approved in 1984. Last previous edition approved in 19972003 as
D4327–97.D4327–03. DOI: 10.1520/D4327-03.10.1520/D4327-11.
2
The following references may be consulted for additional information:
Small, H., Stevens, T. S., and Bauman, W. C., “Novel Ion Exchange Chromatographic Method Using Conductrimetric Detection,” Analytical Chemistry, Vol 47, 1975,
p. 1801.
Stevens, T. S., Turkelson, V. T., andAlve, W. R., “Determination ofAnions in Boiler Blow Down Water with Ion Chromatography,” Analytical Chemistry, Vol 49, 1977,
p. 1176.
Sawicki, E., Mulik, J. D., andWitgenstein, E., Editors, Ion Chromatographic Analysis of Environmental Pollutants,AnnArbor Science Publishers,AnnArbor, MI, 1978.
Mulik, J. D., and Sawicki, E., Editors, Ion Chromatographic Analysis of Environmental Pollutants, Vol/No. 2, Ann Arbor Science Publishers, Ann Arbor, MI, 1979.
Weiss, J., Handbook of Ion Chromatography, Dionex Corp., Sunnyvale, CA, 1986.
Waters Innovative Methods for Anion Analysis, Waters Chromatography Division of Millipore, Method A 107 and A 116, 1990.
Haddad, P. R., and Jackson, P. E., Ion Chromatography: Principles and Applications, Elsevier Scient
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.