ASTM D3609-00(2010)
(Practice)Standard Practice for Calibration Techniques Using Permeation Tubes
Standard Practice for Calibration Techniques Using Permeation Tubes
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
Most analytical methods used in air pollutant measurements are comparative in nature and require calibration or standardization, or both, often with known blends of the gas of interest. Since many of the important air pollutants are reactive and unstable, it is difficult to store them as standard mixtures of known concentration for extended calibration purposes. An alternative is to prepare dynamically standard blends as required. This procedure is simplified if a constant source of the gas of interest can be provided. Permeation tubes provide this constant source, if properly calibrated and if maintained at constant temperature. Permeation tubes have been specified as reference calibration sources, for certain analytical procedures, by the Environmental Protection Agency (3).
SCOPE
1.1 This practice describes a means for using permeation tubes for dynamically calibrating instruments, analyzers, and analytical procedures used in measuring concentrations of gases or vapors in atmospheres (1,2).
1.2 Typical materials that may be sealed in permeation tubes include: sulfur dioxide, nitrogen dioxide, hydrogen sulfide, chlorine, ammonia, propane, and butane (1).
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D3609 − 00(Reapproved 2010)
Standard Practice for
Calibration Techniques Using Permeation Tubes
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D3609; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 4.3 Permeation tubes are held at constant temperature in a
carrier-gas stream of dry air or nitrogen to produce a gas
1.1 This practice describes a means for using permeation
concentrationdependentonthepermeationrateandtheflowof
tubes for dynamically calibrating instruments, analyzers, and
the carrier gas.
analytical procedures used in measuring concentrations of
gases or vapors in atmospheres (1,2).
5. Significance and Use
1.2 Typicalmaterialsthatmaybesealedinpermeationtubes
5.1 Most analytical methods used in air pollutant measure-
include: sulfur dioxide, nitrogen dioxide, hydrogen sulfide,
ments are comparative in nature and require calibration or
chlorine, ammonia, propane, and butane (1).
standardization, or both, often with known blends of the gas of
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
interest. Since many of the important air pollutants are reactive
standard.
andunstable,itisdifficulttostorethemasstandardmixturesof
known concentration for extended calibration purposes. An
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
alternative is to prepare dynamically standard blends as re-
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
quired. This procedure is simplified if a constant source of the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
gas of interest can be provided. Permeation tubes provide this
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
constant source, if properly calibrated and if maintained at
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
constant temperature. Permeation tubes have been specified as
2. Referenced Documents
reference calibration sources, for certain analytical procedures,
by the Environmental Protection Agency (3).
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D1356 Terminology Relating to Sampling and Analysis of
6. Interferences and Precautions
Atmospheres
6.1 Permeation tubes are essentially devices to provide a
D3195 Practice for Rotameter Calibration
constant rate of emission of a specific gaseous substance over
3. Terminology
periodoftime.Theyconsistofatwo-phase(gas-liquid)system
to maintain a constant vapor pressure (at constant temperature)
3.1 Definitions—refer to Terminology D1356.
which is the driving force for emission of the gas through a
4. Summary of Practice
semipermeable membrane (tube walls). They can be expected
to maintain a constant emission rate that is temperature
4.1 Aliquefiable gas, when enclosed in an inert plastic tube,
dependent as long as a significant amount of liquid is present
escapes by permeating the tubing wall at a constant,
inthedevice.Theliquidshallbepure,elseitscompositionmay
reproducible, temperature-dependent rate.
change during the life time of the tube, due to differential
4.2 Permeationtubesarecalibratedgravimetrically,withthe
evaporation, with consequent vapor pressure changes. Care
weight loss of the tube equated to the weight of the escaping
must also be exercised that the diffusion membrane (tube
material.
walls) is not damaged or altered during use. The contents of
permeation tubes are under relatively high pressure.
1 Accordingly, there is the possibility of violent rupture of tube
This practice is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee D22 on Air Quality
and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D22.01 on Quality Control.
walls under high temperature exposure. Permeation rates have
Current edition approved April 1, 2010. Published June 2010. Originally
temperature coefficients up to 10 % per degree Celsius. When
approved in 1977. Last previous edition approved in 2005 as D3609 - 00 (2005).
temperature coefficients are large, above 3 % per degree
DOI: 10.1520/D3609-00R10.
Celsius, stringent temperature control is required. Furthermore
The boldface numbers in parentheses refer to a list of references at the end of
this standard.
permeation tubes exhibit temperature hysteresis so that they
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
must be temperature equilibrated from 2 to 24 h before use,
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
depending upon the temperature differential between storage
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. and use (4). It is important that permeation tubes are filled with
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
D3609 − 00 (2010)
NOTE 1—This system has the advantage of smaller uncertainty of the temperature of the permeation tube.
FIG. 1 Optional System for Laboratory Use of a Permeation Tube
anhydrous constituents of high purity. They shall be handled being held at constant temperature. If lower concentrations are
with care to minimize contact with moisture, oil, and foreign desired, a second gas supply (diluent gas) with its control and
substances. measurement devices may be needed to mix with the gas from
the permeation tube chamber. Equipment of this kind is
6.2 Sulfur dioxide (SO ) permeation tubes are relatively
available commercially. A typical system contains a thermo-
insensitive to interferences.
electrically temperature-controlled permeation tube chamber
6.3 Nitrogen dioxide (NO ) permeation tubes are sensitive
with temperature control within 60.1 °C over the range from
to moisture, hence they should be stored in dry atmospheres
15 to 35 °C. Such equipment is well suited to field usage.
and used with relatively dry carrier gases (<10 % relative
7.3 A typical system for laboratory use that can be as-
humidity). Permeation of moisture into the contents of a tube
sembled from readily available parts is shown schematically in
may damage the walls and also cause progressive decreases in
Fig. 1. The parts required are described in the following
the permeation rate. Moisture incorporated in the contents
subsections.
during manufacture can cause the same effect (4).
7.3.1 Flowmeters—Several, sufficient to cover the range
6.4 Hydrogen sulfide (H S) permeation tubes may turn
from 0 to 15 L/min, calibrated by Practice D3195.
white during use in the presence of oxygen because of inverse
7.3.2 Copper Tubing—Approximately 1 m long [3 ft] by
permeation and formation of collodial sulfur. This phenom-
6.25 mm [0.25 in.] in outside diameter for use as a heat
enon may affect the permeation rate, if severe, hence is a
exchanger in the water bath.
reason for recalibration. However, in an inert gas stream, the
7.3.3 Ball Joints (Ungreased) and Tubing, for the necessary
tubes are relatively stable.
connections. Butt seals may also be used made with inert
6.5 Materials of construction shall be compatible with the
materials such as polyethylene.
contents of the tube. For instance, some fluorocarbons may
7.3.4 Mixing Bulb—to ensure adequate mixing of the per-
cause FEP tubes to swell and possibly to rupture.
meated gas and the diluent gas stream. A Kjeldahl trap is
recommended.
7. Apparatus
7.3.5 Long Condenser, with large bore in which a thermom-
7.1 Permeation Tube sized in accordance with and cali-
eter and a permeation tube can be inserted.
brated to concentrations needed or expected for the analysis
7.3.6 Temperature Controlled Water Bath—About 8-L [2-
method. The user should check calibration as described in
gal] capacity, capable of 60.1 °C or better water temperature
Section 9.1.
control, with a variable temperature control range from about
7.2 Flow and Temperature Control System—Prepare or 15 to 35 °C, preferably equipped with a positive displacement
purchase a system that will dry the carrier gas, and control and type recirculating pump with at least 1-L/min liquid flow rate
measure its flow as it passes over the permeation tube that is to supply water to the condenser.
D3609 − 00 (2010)
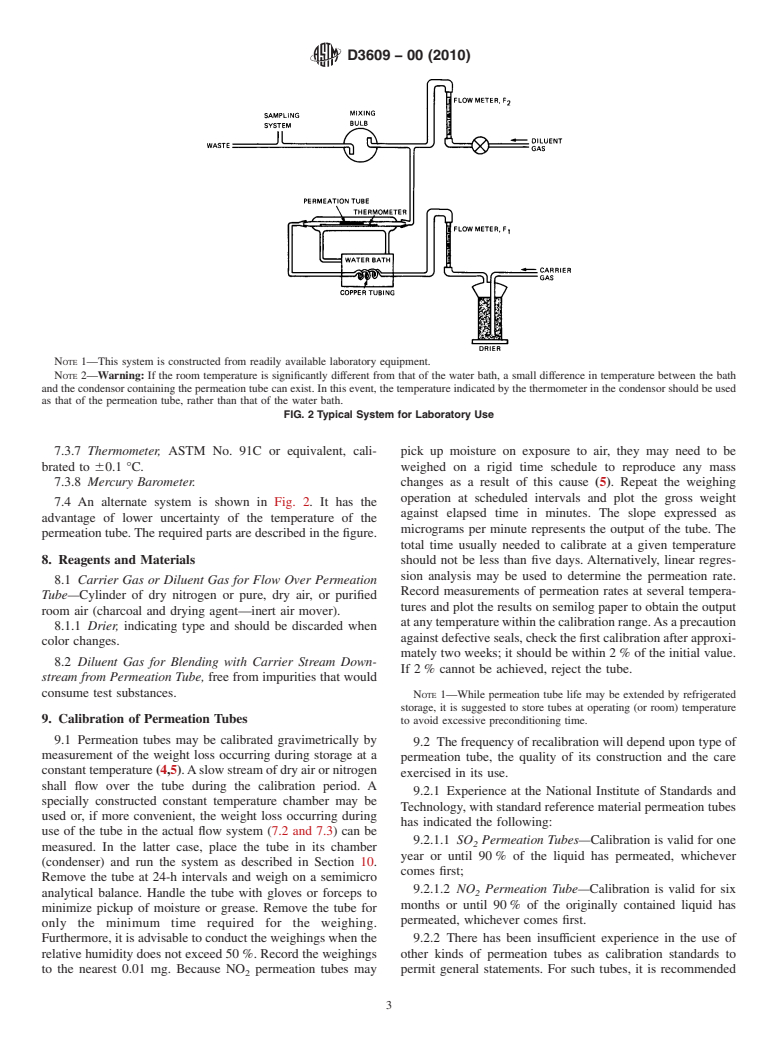
NOTE 1—This system is constructed from readily available laboratory equipment.
NOTE 2—Warning: If the room temperature is significantly different from that of the water bath, a small difference in temperature between the bath
and the condensor containing the permeation tube can exist. In this event, the temperature indicated by the thermometer in the condensor should be used
as that of the permeation tube, rather than that of the water bath.
FIG. 2 Typical System for Laboratory Use
7.3.7 Thermometer, ASTM No. 91C or equivalent, cali- pick up moisture on exposure to air, they may need to be
brated to 60.1 °C. weighed on a rigid time schedule to reproduce any mass
7.3.8 Mercury Barometer.
changes as a result of this cause (5). Repeat the weighing
operation at scheduled intervals and plot the gross weight
7.4 An alternate system is shown in Fig. 2. It has the
against elapsed time in minutes. The slope expressed as
advantage of lower uncertainty of the temperature of the
micrograms per minute represents the output of the tube. The
permeation tube.The required parts are described in the figure.
total time usually needed to calibrate at a given temperature
8. Reagents and Materials should not be less than five days. Alternatively, linear regres-
sion analysis may
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.