ASTM D7343-12
(Practice)Standard Practice for Optimization, Sample Handling, Calibration, and Validation of X-ray Fluorescence Spectrometry Methods for Elemental Analysis of Petroleum Products and Lubricants
Standard Practice for Optimization, Sample Handling, Calibration, and Validation of X-ray Fluorescence Spectrometry Methods for Elemental Analysis of Petroleum Products and Lubricants
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
3.1 Accurate elemental analyses of samples of petroleum and petroleum products are required for the determination of chemical properties, which are in turn used to establish compliance with commercial and regulatory specifications.
SCOPE
1.1 This practice covers information relating to sampling, calibration and validation of X-ray fluorescence instruments for elemental analysis, including all kinds of wavelength dispersive (WDXRF) and energy dispersive (EDXRF) techniques. This practice includes sampling issues such as the selection of storage vessels, transportation, and sub-sampling. Treatment, assembly, and handling of technique-specific sample holders and cups are also included. Technique-specific requirements during analytical measurement and validation of measurement for the determination of trace elements in samples of petroleum and petroleum products are described. For sample mixing, refer to Practice D5854. Petroleum products covered in this practice are considered to be a single phase and exhibit Newtonian characteristics at the point of sampling.
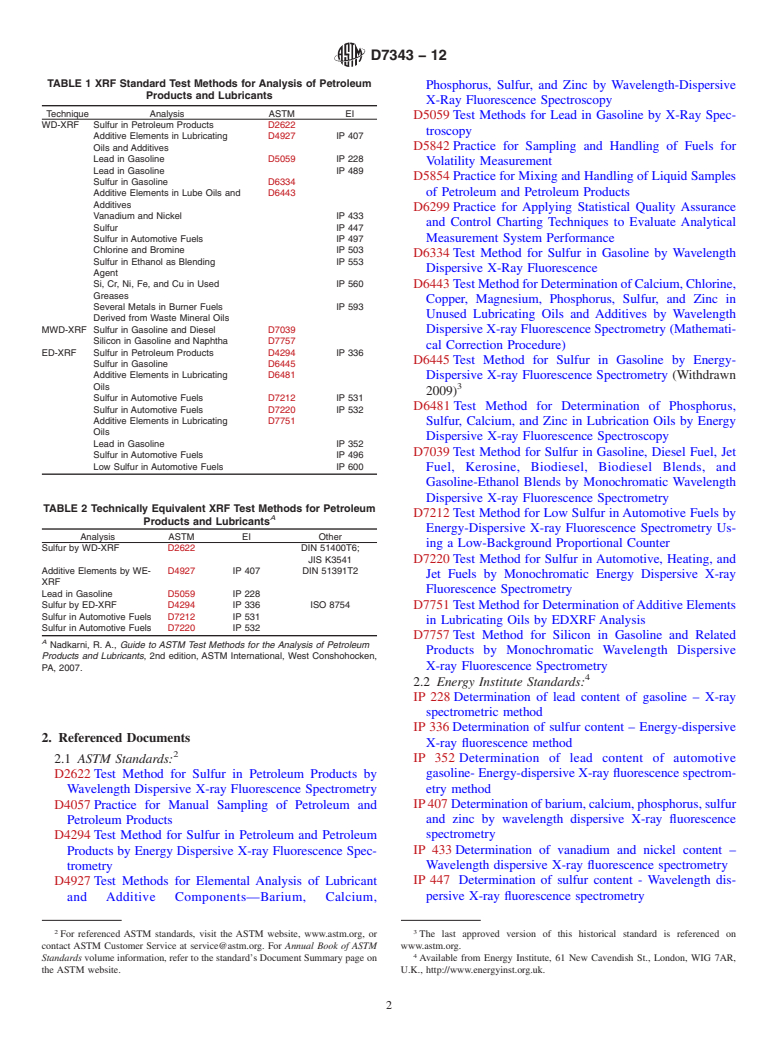
1.2 Applicable Test Methods—This practice is applicable to the XRF methods under the jurisdiction of ASTM Subcommittee D02.03 on Elemental Analysis, and those under the jurisdiction of the Energy Institute’s Test Method Standardization Committee (Table 1). Some of these methods are technically equivalent though they may differ in details (Table 2).TABLE 1 XRF Standard Test Methods for Analysis of Petroleum Products and Lubricants
Technique
Analysis
ASTM
EI
WD-XRF
Sulfur in Petroleum Products
D2622
Additive Elements in Lubricating Oils and Additives
D4927
IP 407
Lead in Gasoline
D5059
IP 228
Lead in Gasoline
IP 489
Sulfur in Gasoline
D6334
Additive Elements in Lube Oils and Additives
D6443
Vanadium and Nickel
IP 433
Sulfur
IP 447
Sulfur in Automotive Fuels
IP 497
Chlorine and Bromine
IP 503
Sulfur in Ethanol as Blending Agent
IP 553
Si, Cr, Ni, Fe, and Cu in Used Greases
IP 560
Several Metals in Burner Fuels Derived from Waste Mineral Oils
IP 593
MWD-XRF
Sulfur in Gasoline and Diesel
D7039
Silicon in Gasoline and Naphtha
D7757
ED-XRF
Sulfur in Petroleum Products
D4294
IP 336
Sulfur in Gasoline
D6445
Additive Elements in Lubricating Oils
D6481
Sulfur in Automotive Fuels
D7212
IP 531
Sulfur in Automotive Fuels
D7220
IP 532
Additive Elements in Lubricating Oils
D7751
Lead in Gasoline
IP 352
Sulfur in Automotive Fuels
IP 496
Low Sulfur in Automotive Fuels
IP 600
TABLE 2 Technically Equivalent XRF Test Methods for Petroleum Products and LubricantsA
Analysis
ASTM
EI
Other
Sulfur by WD-XRF
D2622
DIN 51400T6;
JIS K3541
Additive Elements by WE-XRF
D4927
IP 407
DIN 51391T2
Lead in Gasoline
D5059
IP 228
Sulfur by ED-XRF
D4294
IP 336
ISO 8754
Sulfur in Automotive Fuels
D7212
IP 531
Sulfur in Automotive Fuels
D7220
IP 532
A Nadkarni, R. A., Guide to ASTM Test Methods for the Analysis of Petroleum Products and Lubricants, 2nd edition, ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, 2007.
1.3 Applicable Fluids—This practice is applicable to petroleum and petroleum products with vapor pressures at sampling and storage temperatures less than or equal to 101 kPa (14.7 psi). Use Practice D4057 or IP 475 to sample these materials. Refer to Practice D5842 when sampling materials that also require Reid vapor pressure (RVP) determination.
1.4 Non-applicable Fluids—Petroleum products whose vapor pressure at sampling and sample storage conditions are above 101...
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D7343 − 12
Designation: 558/07
Standard Practice for
Optimization, Sample Handling, Calibration, and Validation
of X-ray Fluorescence Spectrometry Methods for Elemental
1
Analysis of Petroleum Products and Lubricants
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D7343; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* tion Committee (Table 1). Some of these methods are techni-
cally equivalent though they may differ in details (Table 2).
1.1 This practice covers information relating to sampling,
calibration and validation of X-ray fluorescence instruments
1.3 Applicable Fluids—This practice is applicable to petro-
for elemental analysis, including all kinds of wavelength
leum and petroleum products with vapor pressures at sampling
dispersive (WDXRF) and energy dispersive (EDXRF) tech-
and storage temperatures less than or equal to 101 kPa (14.7
niques. This practice includes sampling issues such as the
psi). Use Practice D4057 or IP 475 to sample these materials.
selection of storage vessels, transportation, and sub-sampling.
Refer to Practice D5842 when sampling materials that also
Treatment, assembly, and handling of technique-specific
require Reid vapor pressure (RVP) determination.
sample holders and cups are also included. Technique-specific
1.4 Non-applicable Fluids—Petroleum products whose va-
requirements during analytical measurement and validation of
por pressure at sampling and sample storage conditions are
measurement for the determination of trace elements in
above 101 kPa (14.7 psi) and liquefied gases (that is, LNG,
samples of petroleum and petroleum products are described.
LPG, etc.) are not covered by this practice.
For sample mixing, refer to Practice D5854. Petroleum prod-
ucts covered in this practice are considered to be a single phase
1.5 Sampling Methods—The physical sampling and meth-
and exhibit Newtonian characteristics at the point of sampling.
ods of sampling from a primary source are not covered by this
guide. It is assumed that samples covered by this practice are
1.2 Applicable Test Methods—This practice is applicable to
a representative sample of the primary source liquid. Refer to
the XRF methods under the jurisdiction ofASTM Subcommit-
Practice D4057 or IP 475 for detailed sampling procedures.
tee D02.03 on Elemental Analysis, and those under the
jurisdiction of the Energy Institute’s Test Method Standardiza-
1.6 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
standard. The values given in parentheses are for information
1
This practice is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee D02 on Petroleum
only.
Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of Subcom-
1.7 This standard does not purport to address all of the
mittee D02.03 on Elemental Analysis.
Current edition approved Dec. 1, 2012. Published December 2012. Originally
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
approved in 2007. Last previous edition approved in 2007 as D7343–07. DOI:
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
10.1520/D7343-07.
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
This practice was jointly prepared by ASTM International and the Energy
Institute. bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D7343 − 12
1
---------------------- Page: 2 ----------------------
D7343 − 12
TABLE 1 XRF Standard Test Methods for Analysis of Petroleum
Phosphorus, Sulfur, and Zinc by Wavelength-Dispersive
Products and Lubricants
X-Ray Fluorescence Spectroscopy
Technique Analysis ASTM EI
D5059 Test Methods for Lead in Gasoline by X-Ray Spec-
WD-XRF Sulfur in Petroleum Products D2622
troscopy
Additive Elements in Lubricating D4927 IP 407
D5842 Practice for Sampling and Handling of Fuels for
Oils and Additives
Lead in Gasoline D5059 IP 228
Volatility Measurement
Lead in Gasoline IP 489
D5854 Practice for Mixing and Handling of Liquid Samples
Sulfur in Gasoline D6334
Additive Elements in Lube Oils and D6443 of Petroleum and Petroleum Products
Additives
D6299 Practice for Applying Statistical Quality Assurance
Vanadium and Nickel IP 433
and Control Charting Techniques to Evaluate Analytical
Sulfur IP 447
Sulfur in Automotive Fuels IP 497 Measurement System Performance
Chlorine and Bromine IP 503
D6334 Test Method for Sulfur in Gasoline by Wavelength
Sulfur in Ethano
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D7343 − 07 D7343 − 12
Designation: 558/07
Standard Practice for
Optimization, Sample Handling, Calibration, and Validation
of X-ray Fluorescence Spectrometry Methods for Elemental
1
Analysis of Petroleum Products and Lubricants
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D7343; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope Scope*
1.1 This practice covers information relating to sampling, calibration and validation of X-ray fluorescence instruments for
elemental analysis, including all kinds of wavelength dispersive (WDXRF) and energy dispersive (EDXRF) techniques. This
practice includes sampling issues such as the selection of storage vessels, transportation, and sub-sampling. Treatment, assembly,
and handling of technique-specific sample holders and cups are also included. Technique-specific requirements during analytical
measurement and validation of measurement for the determination of trace elements in samples of petroleum and petroleum
products are described. For sample mixing, refer to Practice D5854. Petroleum products covered in this practice are considered
to be a single phase and exhibit Newtonian characteristics at the point of sampling.
1.2 Applicable Test Methods—This practice is applicable to the XRF methods under the jurisdiction of ASTM Subcommittee
D02.03 on Elemental Analysis:Analysis, D2622, D4294, D5059, D6334, D6443, D6445, D6481, D7039, D7212, and D7220 and
those under the jurisdiction of the Energy Institute’s Test Method Standardization Committee: IPCommittee (Table 1 228, IP 336,
IP 352, IP 407, IP 433, IP 447, IP 475, IP ). Some of these methods are technically equivalent though they may differ in details
(Table 2489, IP 496, IP 497, IP 503, IP 531, and IP 532.).
1.3 Applicable Fluids—This practice is applicable to petroleum and petroleum products with vapor pressures at sampling and
storage temperatures less than or equal to 101 kPa (14.7 psi). Use Practice D4057 or IP 475 to sample these materials. Refer to
Practice D5842 when sampling materials that also require Reid vapor pressure (RVP) determination.
1.4 Non-applicable Fluids—Petroleum products whose vapor pressure at sampling and sample storage conditions are above 101
kPa (14.7 psi) and liquefied gases (that is, LNG, LPG, etc.) are not covered by this practice.
1.5 Sampling Methods—The physical sampling and methods of sampling from a primary source are not covered by this guide.
It is assumed that samples covered by this practice are a representative sample of the primary source liquid. Refer to Practice
D4057 or IP 475 for detailed sampling procedures.
1.6 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.7 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D2622 Test Method for Sulfur in Petroleum Products by Wavelength Dispersive X-ray Fluorescence Spectrometry
D4057 Practice for Manual Sampling of Petroleum and Petroleum Products
D4294 Test Method for Sulfur in Petroleum and Petroleum Products by Energy Dispersive X-ray Fluorescence Spectrometry
1
This practice is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on Petroleum Products and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D02.03 on
Elemental Analysis.
Current edition approved Aug. 1, 2007Dec. 1, 2012. Published September 2007December 2012. Originally approved in 2007. Last previous edition approved in 2007 as
D7343–07. DOI: 10.1520/D7343-07.
This practice was jointly prepared by ASTM International and the Energy Institute. DOI: 10.1520/D7343-07.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- P
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.