ASTM E1316-14
(Terminology)Standard Terminology for Nondestructive Examinations
Standard Terminology for Nondestructive Examinations
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
3.1 The terms found in this standard are intended to be used uniformly and consistently in all nondestructive testing standards. The purpose of this standard is to promote a clear understanding and interpretation of the NDT standards in which they are used.
SCOPE
1.1 This standard defines the terminology used in the standards prepared by the E07 Committee on Nondestructive Testing. These nondestructive testing (NDT) methods include: acoustic emission, electromagnetic testing, gamma- and X-radiology, leak testing, liquid penetrant testing, magnetic particle testing, neutron radiology and gauging, ultrasonic testing, and other technical methods.
1.2 Committee E07 recognizes that the terms examination, testing and inspection are commonly used as synonyms in nondestructive testing. For uniformity and consistency in E07 nondestructive testing standards, Committee E07 encourages the use of the term examination and its derivatives when describing the application of nondestructive test methods. There are, however, appropriate exceptions when the term test and its derivatives may be used to describe the application of a nondestructive test, such as measurements which produce a numeric result (for example, when using the leak testing method to perform a leak test on a component, or an ultrasonic measurement of velocity). Additionally, the term test should be used when referring to the NDT method, that is, Radiologic Testing (RT), Ultrasonic Testing (UT), and so forth. (Example: Radiologic Testing (RT) is often used to examine material to detect internal discontinuities.)
1.3 Section A defines terms that are common to multiple NDT methods, whereas, the subsequent sections define terms pertaining to specific NDT methods.
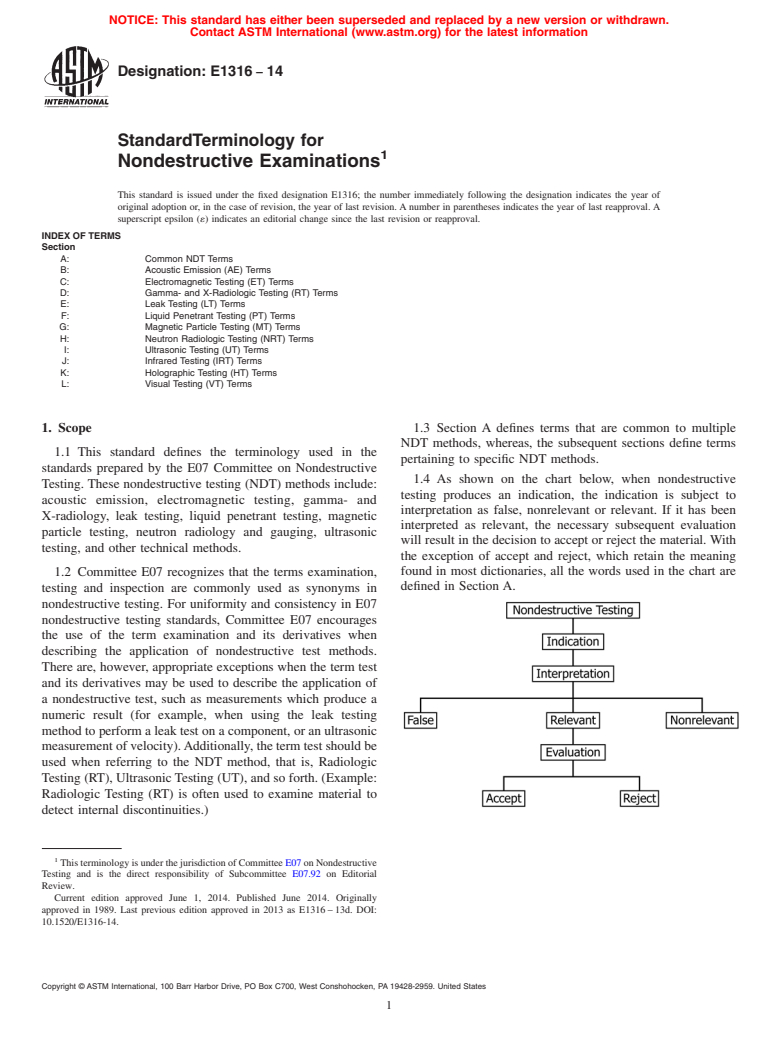
1.4 As shown on the chart below, when nondestructive testing produces an indication, the indication is subject to interpretation as false, nonrelevant or relevant. If it has been interpreted as relevant, the necessary subsequent evaluation will result in the decision to accept or reject the material. With the exception of accept and reject, which retain the meaning found in most dictionaries, all the words used in the chart are defined in Section A.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: E1316 − 14
StandardTerminology for
1
Nondestructive Examinations
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E1316; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
INDEX OF TERMS
Section
A: Common NDT Terms
B: Acoustic Emission (AE) Terms
C: Electromagnetic Testing (ET) Terms
D: Gamma- and X-Radiologic Testing (RT) Terms
E: Leak Testing (LT) Terms
F: Liquid Penetrant Testing (PT) Terms
G: Magnetic Particle Testing (MT) Terms
H: Neutron Radiologic Testing (NRT) Terms
I: Ultrasonic Testing (UT) Terms
J: Infrared Testing (IRT) Terms
K: Holographic Testing (HT) Terms
L: Visual Testing (VT) Terms
1. Scope 1.3 Section A defines terms that are common to multiple
NDT methods, whereas, the subsequent sections define terms
1.1 This standard defines the terminology used in the
pertaining to specific NDT methods.
standards prepared by the E07 Committee on Nondestructive
1.4 As shown on the chart below, when nondestructive
Testing. These nondestructive testing (NDT) methods include:
testing produces an indication, the indication is subject to
acoustic emission, electromagnetic testing, gamma- and
interpretation as false, nonrelevant or relevant. If it has been
X-radiology, leak testing, liquid penetrant testing, magnetic
interpreted as relevant, the necessary subsequent evaluation
particle testing, neutron radiology and gauging, ultrasonic
will result in the decision to accept or reject the material.With
testing, and other technical methods.
the exception of accept and reject, which retain the meaning
found in most dictionaries, all the words used in the chart are
1.2 Committee E07 recognizes that the terms examination,
defined in Section A.
testing and inspection are commonly used as synonyms in
nondestructive testing. For uniformity and consistency in E07
nondestructive testing standards, Committee E07 encourages
the use of the term examination and its derivatives when
describing the application of nondestructive test methods.
There are, however, appropriate exceptions when the term test
and its derivatives may be used to describe the application of
a nondestructive test, such as measurements which produce a
numeric result (for example, when using the leak testing
methodtoperformaleaktestonacomponent,oranultrasonic
measurementofvelocity).Additionally,thetermtestshouldbe
used when referring to the NDT method, that is, Radiologic
Testing (RT), UltrasonicTesting (UT), and so forth. (Example:
Radiologic Testing (RT) is often used to examine material to
detect internal discontinuities.)
1
ThisterminologyisunderthejurisdictionofCommitteeE07onNondestructive
Testing and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E07.92 on Editorial
Review.
Current edition approved June 1, 2014. Published June 2014. Originally
approved in 1989. Last previous edition approved in 2013 as E1316–13d. DOI:
10.1520/E1316-14.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
E1316 − 14
2. Referenced Documents 3. Significance and Use
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
3.1 Thetermsfoundinthisstandardareintendedtobeused
uniformly and consistently in all nondestructive testing stan-
NOTE 1—This standard defines the terminology used in the standards
prepared by Committee E07 on Nondestructive Testing and published in dards. The purpose of this standard is to promote a clear
the Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Volume 03.03.
understanding and interpretation of the NDT standards in
which they are used.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
4. Terminology
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website.
Section A: Common NDT Terms
The terms defined in Section A are the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E07.92, Editorial Review.
acceptable quality level—the maximum percent defective or flaw characterization, n—the process of quantifying the size,
the maximum number of units defective per hundred units shape, orientation, location, growth, or other properties, of a
that, for the purpose of sampling test, can be considered flaw based on NDT response.
satisfactory as a process average.
imperfection, n—a departure of a quality characteristic from
its intended condition.
calibration, instrument, n—the comparison of an instrument
with, or the adjustment of an instrument to, a known
indication—the response or evidence from a nondestructive
reference(s) often traceable to the Nat
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: E1316 − 13d E1316 − 14
Standard Terminology for
1
Nondestructive Examinations
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E1316; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
colwidth="1.67*"/COLSPECcolwidth="8.33*"/COLSPEC
INDEX OF TERMS
INDEX OF TERMS
Section
Section
A: Common NDT Terms
B: Acoustic Emission (AE) Terms
C: Electromagnetic Testing (ET) Terms
D: Gamma- and X-Radiologic Testing (RT) Terms
E: Leak Testing (LT) Terms
F: Liquid Penetrant Testing (PT) Terms
G: Magnetic Particle Testing (MT) Terms
H: Neutron Radiologic Testing (NRT) Terms
I: Ultrasonic Testing (UT) Terms
J: Infrared Testing (IRT) Terms
K: Holographic Testing (HT) Terms
L: Visual Testing (VT) Terms
1. Scope
1.1 This standard defines the terminology used in the standards prepared by the E07 Committee on Nondestructive Testing.
These nondestructive testing (NDT) methods include: acoustic emission, electromagnetic testing, gamma- and X-radiology, leak
testing, liquid penetrant testing, magnetic particle testing, neutron radiology and gauging, ultrasonic testing, and other technical
methods.
1.2 Committee E07 recognizes that the terms examination, testing and inspection are commonly used as synonyms in
nondestructive testing. For uniformity and consistency in E07 nondestructive testing standards, Committee E07 encourages the use
of the term examination and its derivatives when describing the application of nondestructive test methods. There are, however,
appropriate exceptions when the term test and its derivatives may be used to describe the application of a nondestructive test, such
as measurements which produce a numeric result (for example, when using the leak testing method to perform a leak test on a
component, or an ultrasonic measurement of velocity). Additionally, the term test should be used when referring to the NDT
method, that is, Radiologic Testing (RT), Ultrasonic Testing (UT), and so forth. (Example: Radiologic Testing (RT) is often used
to examine material to detect internal discontinuities.)
1.3 Section A defines terms that are common to multiple NDT methods, whereas, the subsequent sections define terms
pertaining to specific NDT methods.
1.4 As shown on the chart below, when nondestructive testing produces an indication, the indication is subject to interpretation
as false, nonrelevant or relevant. If it has been interpreted as relevant, the necessary subsequent evaluation will result in the
decision to accept or reject the material. With the exception of accept and reject, which retain the meaning found in most
dictionaries, all the words used in the chart are defined in Section A.
1
This terminology is under the jurisdiction of Committee E07 on Nondestructive Testing and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E07.92 on Editorial Review.
Current edition approved Dec. 1, 2013June 1, 2014. Published December 2013June 2014. Originally approved in 1989. Last previous edition approved in 2013 as
E1316 – 13c.E1316 – 13d. DOI: 10.1520/E1316-13D.10.1520/E1316-14.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
E1316 − 14
2
---------------------- Page: 2 ----------------------
E1316 − 14
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
NOTE 1—This standard defines the terminology used in the standards prepared by Committee E07 on Nondestructive Testing and published in the
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Volume 03.03.
3. Significance and Use
3.1 The terms found in this standard are intended to be used uniformly and consistently in all nondestructive testing standards.
The purpose of this standard is to promote a clear understanding and interpretation of the NDT standards in which they are used.
4. Terminology
Section A: Common NDT Terms
The terms defined in Section A are the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E07.92, Editorial Review.
acceptable quality level—the maximum percent defective or the maximum number of units defective per hundred units that, for
the purpose of sampling test, can be considered satisfactory as a process average.
calibration, instrument, n—the comparison of an instrument with, or the adjustment of an instrument to, a known reference(s)
often traceable to the National I
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.