ASTM D2229-02
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Adhesion Between Steel Tire Cords and Rubber
Standard Test Method for Adhesion Between Steel Tire Cords and Rubber
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the force required to pull a steel cord from a block of vulcanized rubber.
1.2 Although designed primarily for steel cord, this test method may be applied with modifications to wire used in rubber products.
1.3 This test method can also be used for evaluating rubber compound performance with respect to adhesion to steel cord.
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D 2229 – 02
Standard Test Method for
1
Adhesion Between Steel Tire Cords and Rubber
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 2229; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 3.1.2 For definitions of terms related to rubber, refer to
Terminology D 1566.
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the force
3.1.3 For definitions of trms related to textiles, refer to
required to pull a steel cord from a block of vulcanized rubber.
Terminology D 123.
1.2 Although designed primarily for steel cord, this test
method may be applied with modifications to wire used in
4. Summary of Test Method
rubber products.
4.1 The steel cords are vulcanized into a block of rubber and
1.3 This test method can also be used for evaluating rubber
the force necessary to pull the cords linearly out of the rubber
compound performance with respect to adhesion to steel cord.
is measured.
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
5. Significance and Use
standard.
5.1 This test method is considered satisfactory for the
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the
acceptance testing of commercial shipments of steel tire cord
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
because current estimates of between-laboratory precision for
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
single materials are considered acceptable and the method has
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
been used extensively in the trade for acceptance testing.
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
5.1.1 If there are differences or practical significances be-
tween reported test results for two laboratories (or more),
2. Referenced Documents
comparative tests should be performed to determine if there is
2.1 ASTM Standards:
a statistical bias between them, using competent statistical
D 76 Specification for Tensile Testing Machines for Tex-
2
assistance. As a minimum, the test samples should be used that
tiles
2 are as homogenous as possible, that are drawn from the
D 123 Terminology Relating to Textiles
2 material from which the disparate test results were obtained,
D 1566 Terminology Relating to Rubber
and that are randomly assigned in equal numbers to each
D 2904 Practice for Interlaboratory Testing of a Textile Test
2 laboratory for testing. Other materials with established test
Method that Produces Normally Distributed Data
values may be used for this purpose. The test results from the
D 6477 Terminology Relating to Tire Cord, Bead Wire,
3 two laboratories should be compared using a statistical test for
Hose Reinforcing Wire,and Fabrics
4 unpaired data, at a probability level chosen prior to the testing
E 105 Practice for Probability Sampling of Materials
series. If a bias is found, either its cause must be found and
E 122 Practice for Choice of Sample Size to Estimate a
4 corrected, or future test results must be adjusted in consider-
Measure of Quality for a Lot or Process
ation of the known bias.
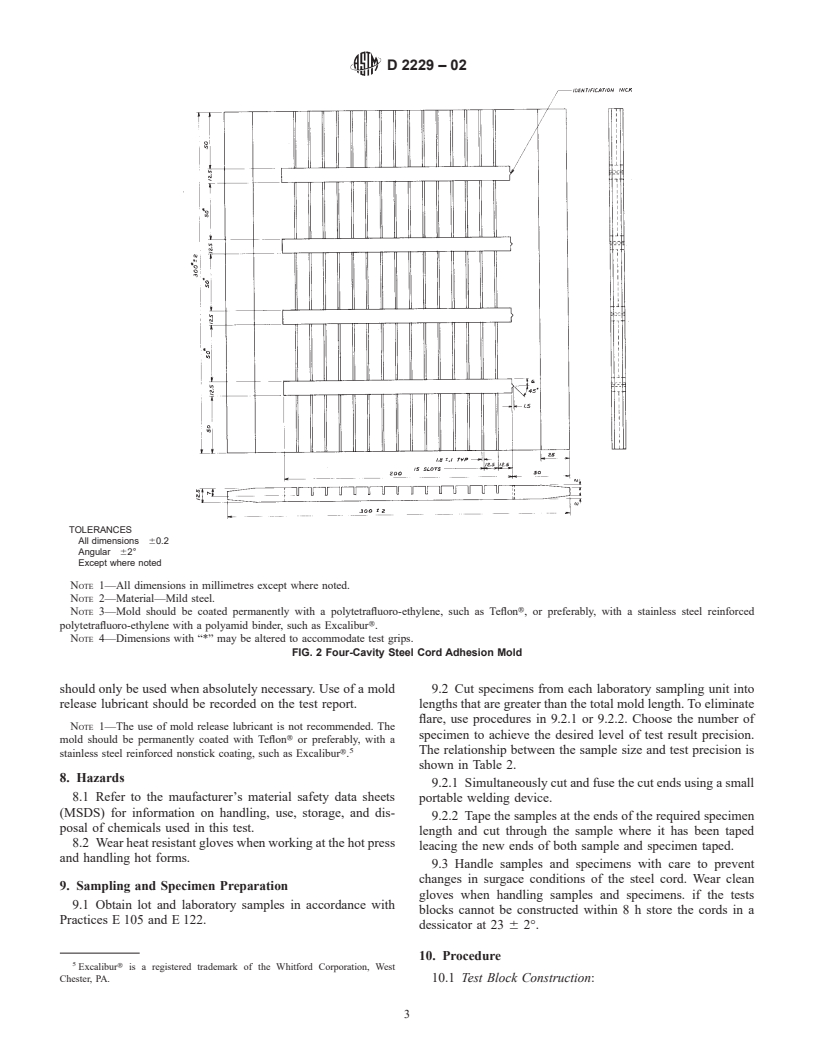
3. Terminology 5.2 The mold described in this test method is primarily
designed for quality acceptance testing for steel cord where the
3.1 Definitions
sample size for each cord is 4 or a multiple thereof, but any
3.1.1 For definitions of terms relating to tire cord, bead wire,
mold/cavity combination which will provide the required test
hose wire, and tire cord fabrics, refer to Terminology D 6477.
block dimensions (Figs. 1 and 2) is acceptable.
5.3 Appendix X1 contains suggested ranges of environmen-
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D13 on Textiles
tal conditions for aging tests.
and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D13.19 on Tire Cord and Fabrics.
5.4 The property measured by this test method indicates
Current edition approved Sept. 10, 2002. Published October 2002. Originally
whether the adhesion of the steel cord to the rubber is greater
published as D 2229 –63 T. Last previous edition D 2229 – 99.
2
than the cohesion of the rubber, that is, complete rubber
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 07.01.
3
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 07.02.
4
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 14.02.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D2229–02
FIG. 1 Definition of Test Block Dimensions
coverage of the steel cord, or less than the cohesion of the area of the mold plate. Electrical or steam heat for the top
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.