ASTM D6010-96(2006)
(Practice)Standard Practice for Closed Vessel Microwave Solvent Extraction of Organic Compounds from Solid Matrices
Standard Practice for Closed Vessel Microwave Solvent Extraction of Organic Compounds from Solid Matrices
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
Extraction of organic pollutants from wastes can provide information on the susceptibility of compounds to leeching, water quality changes, or other site conditions.
Rapid heating, in combination with temperatures in excess of the atmospheric boiling point of organic solvents, reduces sample extraction times.
Small amounts of solvents (30 mL) are used resulting in reduced sample preparation cost and time.
SCOPE
1.1 This practice describes the closed vessel microwave extraction of soils, sediments, sludges, and wastes for subsequent determination of solvent extractable semivolatile and nonvolatile organic compounds by such techniques as gas chromatography and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry.
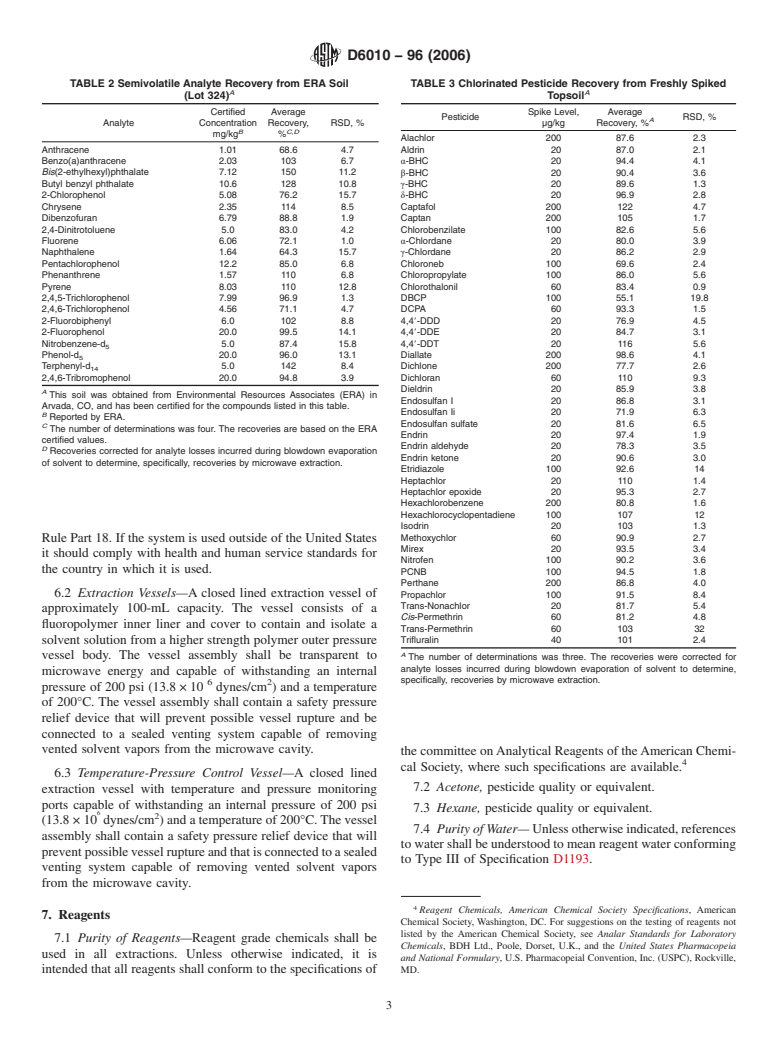
1.1.1 Compounds listed in Tables 1-5 can be extracted from the preceding materials.
1.2 This test method is applicable to samples that will pass through a 10-mesh (approximately 2-mm opening) screen.
1.3 The detection limit and linear concentration range for each compound is dependent on the gas chromatograph or gas chromatograph-mass spectrometer technique employed and may be found in the manual accompanying the instrument used.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. See Section for specific hazard statements.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D6010 − 96(Reapproved 2006)
Standard Practice for
Closed Vessel Microwave Solvent Extraction of Organic
1
Compounds from Solid Matrices
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D6010; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 2.2 Other Standards:
United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA),
1.1 This practice describes the closed vessel microwave
Test Methods for Evaluating Solid Waste Volume
extraction of soils, sediments, sludges, and wastes for subse-
3
1A:Laboratory Manual Physical/Chemical Methods
quent determination of solvent extractable semivolatile and
Title21,CodeofFederalRegulations(CFR),Part1030,and
nonvolatile organic compounds by such techniques as gas
3
Title 47, Part 18
chromatography and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry.
1.1.1 CompoundslistedinTables1–5canbeextractedfrom
3. Summary of Practice
the preceding materials.
3.1 This procedure ensures intimate contact of the sample
1.2 This test method is applicable to samples that will pass
matrix with 115°C extraction solvent.
through a 10-mesh (approximately 2-mm opening) screen.
3.2 A1 to 5-g portion of a solid sample is extracted in a
1.3 The detection limit and linear concentration range for
sealed microwave transparent extraction vessel with 30 mL of
each compound is dependent on the gas chromatograph or gas
acetone-hexane (1+1).
chromatograph-mass spectrometer technique employed and
3.3 Up to 12 samples may be extracted simultaneously.
may be found in the manual accompanying the instrument
3.4 After extraction the vessels are cooled to room
used.
temperature, opened, and the solvent and sample are separated
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
by decanting, filtration, or centrifuging.
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
3.5 This practice provides a sample suitable for analysis by
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
gas chromatography or gas chromatography-mass spectrom-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
etry.
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. See Section 8 for
specific hazard statements.
4. Significance and Use
4.1 Extraction of organic pollutants from wastes can pro-
2. Referenced Documents
vide information on the susceptibility of compounds to
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
leeching, water quality changes, or other site conditions.
D1193Specification for Reagent Water
4.2 Rapid heating, in combination with temperatures in
D3976Practice for Preparation of Sediment Samples for
excess of the atmospheric boiling point of organic solvents,
Chemical Analysis
reduces sample extraction times.
D5368TestMethodsforGravimetricDeterminationofTotal
Solvent Extractable Content (TSEC) of Solid Waste
4.3 Smallamountsofsolvents(30mL)areusedresultingin
Samples
reduced sample preparation cost and time.
5. Interferences
1
This practice is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D34 on Waste
5.1 Methodinterferencesmaybecausedbycontaminantsin
Management and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D34.01.06 on
solvents, labware, and other hardware used in sample process-
Analytical Methods.
ing that lead to discrete artifacts or elevated baselines in gas
Current edition approved Feb. 1, 2006. Published March 2006. Originally
approved in 1996. Last previous edition approved in 2001 as D6010-96(2001). chromatograms. The analyst must demonstrate, through the
DOI: 10.1520/D6010-96R06.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
3
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Available from the Superintendent of Documents, U.S. Government Printing
the ASTM website. Office, Washington, DC 20402.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D6010 − 96 (2006)
TABLE 1 Continued
analysisofreagentblanks,thatthesystemandthematerialsare
Spike Level, Average
free from interferents.
Analyte RSD, %
A
mg/kg Recovery, %
5.2 The use of high-purity solvents helps to minimize
3-Methylcholanthrene 5.0 117 8.6
interference problems.
Methyl methanesulfonate 5.0 48.5 28
2-Methylnaphthalene 5.0 104 9.3
5.3 Matrixinterferencesarecausedbycontaminantsthatare
2-Methylphenol 5.0 95.1 8.5
coextracted from the sample. The extent of matrix interfer-
4-Methylphenol 5.0 92.4 11
ences may vary considerably from sample to sample.
Naphthalene 5.0 95.0 12
1-Naphthylamine 5.0
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.