ASTM A536-84(2014)
(Specification)Standard Specification for Ductile Iron Castings
Standard Specification for Ductile Iron Castings
ABSTRACT
This specification covers ductile iron castings, also known as spheroidal or nodular iron, that is described as cast iron with the graphite substantially spheroidal in shape and essentially free of other forms of graphite. Appropriate heat treatment shall be identified according to grades, as follows: a full ferritizing anneal for 60-40-18; a quench and temper, or normalize and temper, or isothermal heat treatment for 100-70-03 and 120-90-02; and as-cast for 65-45-12 and 80-55-06. Castings shall be tested and conform to specified tensile requirements such as tensile strength, yield strength, and elongation. When indicated in the contract or purchase order, castings shall also adhere to special requirements like hardness, chemical composition, microstructure, pressure tightness, radiographic soundness, magnetic particle inspection dimensions, and surface finish.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers castings made of ductile iron, also known as spheroidal or nodular iron, that is described as cast iron with the graphite substantially spheroidal in shape and essentially free of other forms of graphite, as defined in Terminology A644.
1.2 No precise quantitative relationship can be stated between the properties of the iron in various locations of the same casting or between the properties of castings and those of a test specimen cast from the same iron (see Appendix X1).
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:A536 −84 (Reapproved 2014)
Standard Specification for
1
Ductile Iron Castings
This standard is issued under the fixed designation A536; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope 3.1.1 ASTM designation,
3.1.2 Grade of ductile iron required (see Table 1, and
1.1 This specification covers castings made of ductile iron,
Sections 4 and 9),
also known as spheroidal or nodular iron, that is described as
3.1.3 Special properties, if required (see Section 7),
castironwiththegraphitesubstantiallyspheroidalinshapeand
3.1.4 If a different number of samples are required (see
essentially free of other forms of graphite, as defined in
Section 10),
Terminology A644.
3.1.5 Certification, if required (see Section 14), and
1.2 No precise quantitative relationship can be stated be-
3.1.6 Special preparation for delivery, if required (see Sec-
tweenthepropertiesoftheironinvariouslocationsofthesame
tion 15).
castingorbetweenthepropertiesofcastingsandthoseofatest
specimen cast from the same iron (see Appendix X1).
4. Tensile Requirements
1.3 Thevaluesstatedininch-poundunitsaretoberegarded
4.1 The iron represented by the test specimens shall con-
as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
form to the requirements as to tensile properties presented in
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only
Tables 1 and 2. The irons listed in Table 1 cover those in
and are not considered standard.
general use, while those listed in Table 2 are used for special
applications (such as pipes, fittings, etc.).
2. Referenced Documents
4.2 Theyieldstrengthshallbedeterminedat0.2%offsetby
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
the offset method (see Test Methods E8). Other methods may
A370Test Methods and Definitions for Mechanical Testing
be used by mutual consent of the manufacturer and purchaser.
of Steel Products
A644Terminology Relating to Iron Castings
5. Heat Treatment
A732/A732MSpecification for Castings, Investment, Car-
5.1 The 60-40-18 grade will normally require a full ferritiz-
bon and Low Alloy Steel for General Application, and
ing anneal.The 120-90-02 and the 100-70-03 grades generally
Cobalt Alloy for High Strength at Elevated Temperatures
require a quench and temper or a normalize and temper, or an
E8Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials
isothermal heat treatment. The other two grades can be met
3
2.2 Military Standard:
either as-cast or by heat treatment. Ductile iron, which is heat
MIL-STD-129Marking for Shipment and Storage
treated by quenching to martensite and tempering, may have
substantially lower fatigue strength than as-cast material of the
3. Ordering Information
same hardness.
3.1 Ordersformaterialtothisspecificationshallincludethe
following information:
6. Test Coupons
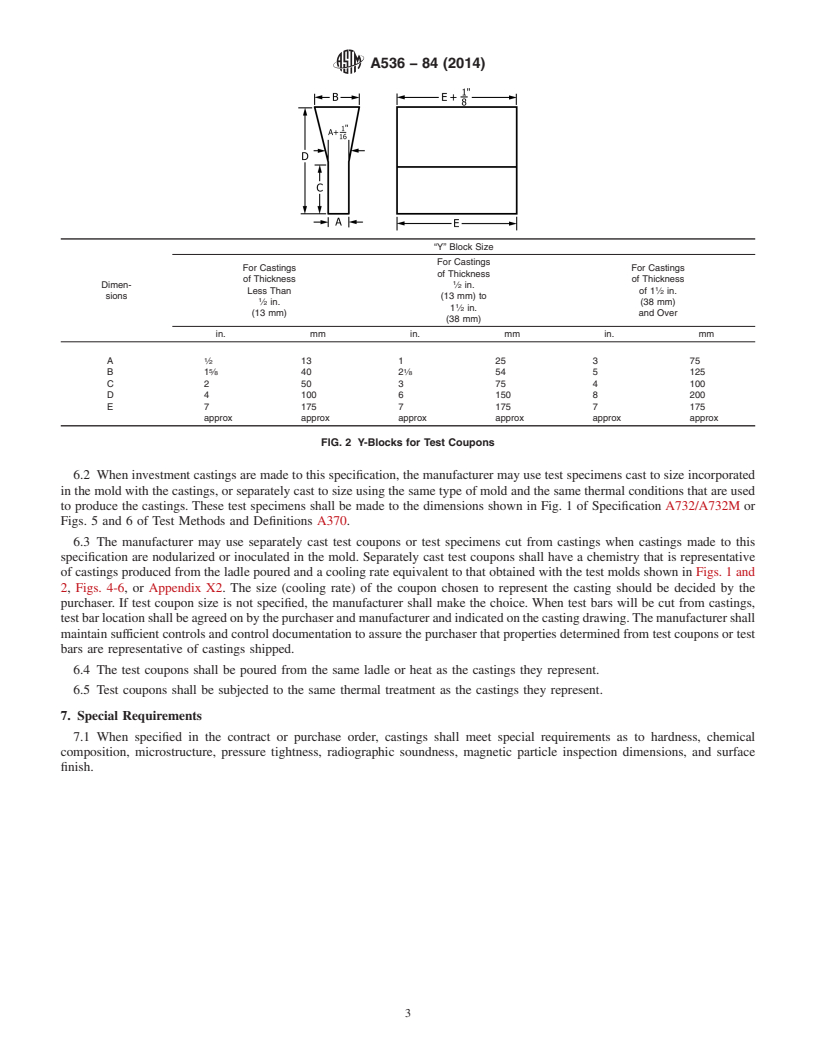
6.1 The separately cast test coupons from which the tension
test specimens are machined shall be cast to the size and shape
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of the ASTM Committee A04 on
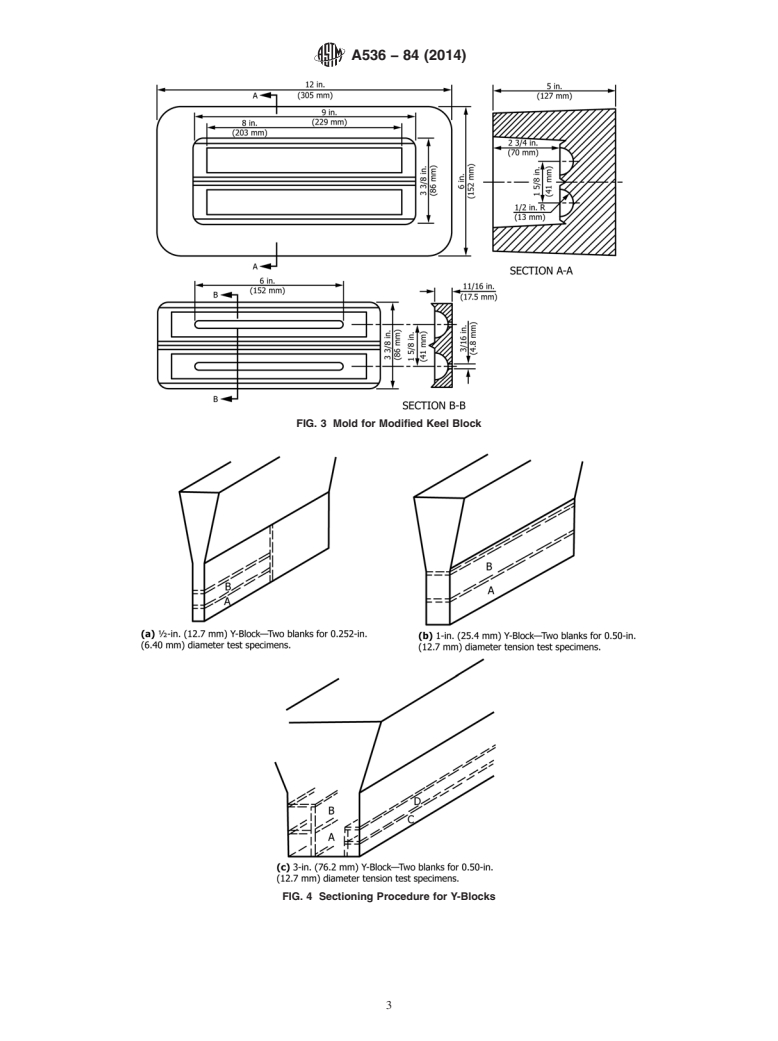
shown in Fig. 1 or Fig. 2.Amodified keel block cast from the
IronCastingsandisthedirectresponsibilityofSubcommitteeA04.02onMalleable
and Ductile Iron Castings.
mold shown in Fig. 3 may be substituted for the 1-in. Y-block
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2014. Published October 2014. Originally
or the 1-in. keel block. The test coupons shall be cast in open
approvedin1965.Lastpreviouseditionapprovedin2009asA536–84(2009).DOI:
molds made of suitable core sand having a minimum wall
10.1520/A0536-84R14.
1 1
2
thickness of 1 ⁄2 in. (38 mm) for the ⁄2-in. (12.5 mm) and 1-in.
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
(25-mm) sizes and 3 in. (75 mm) for the 3-in. size. The
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
coupons shall be left in the mold until they have cooled to a
the ASTM website.
3
blackcolor(approximately900°F(482°C)orless).Thesizeof
Available from Standardization Documents Order Desk, DODSSP, Bldg. 4,
Section D, 700 Robbins Ave., Philadelphia, PA 19111-5098 couponcasttorepresentthecastingshallbeattheoptionofthe
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
A536−84 (2014)
TABLE 1 Tensile Requirements
Grade Grade Grade Grade Grade
60-40-18 65-45-12 80-55-06 100-70-03 120-90-02
Tensile strength, min, psi 60 000 65 000 80 000 100 000 120 000
Tensil
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: A536 − 84 (Reapproved 2009) A536 − 84 (Reapproved 2014)
Standard Specification for
1
Ductile Iron Castings
This standard is issued under the fixed designation A536; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope
1.1 This specification covers castings made of ductile iron, also known as spheroidal or nodular iron, that is described as cast
iron with the graphite substantially spheroidal in shape and essentially free of other forms of graphite, as defined in Terminology
A644.
1.2 No precise quantitative relationship can be stated between the properties of the iron in various locations of the same casting
or between the properties of castings and those of a test specimen cast from the same iron (see Appendix X1).
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
A370 Test Methods and Definitions for Mechanical Testing of Steel Products
A644 Terminology Relating to Iron Castings
A732/A732M Specification for Castings, Investment, Carbon and Low Alloy Steel for General Application, and Cobalt Alloy
for High Strength at Elevated Temperatures
E8 Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials
3
2.2 Military Standard:
MIL-STD-129 Marking for Shipment and Storage
3. Ordering Information
3.1 Orders for material to this specification shall include the following information:
3.1.1 ASTM designation,
3.1.2 Grade of ductile iron required (see Table 1, and Sections 4 and 9),
3.1.3 Special properties, if required (see Section 7),
3.1.4 If a different number of samples are required (see Section 10),
3.1.5 Certification, if required (see Section 14), and
3.1.6 Special preparation for delivery, if required (see Section 15).
4. Tensile Requirements
4.1 The iron represented by the test specimens shall conform to the requirements as to tensile properties presented in Tables 1
and 2. The irons listed in Table 1 cover those in general use, while those listed in Table 2 are used for special applications (such
as pipes, fittings, etc.).
4.2 The yield strength shall be determined at 0.2 % offset by the offset method (see Test Methods E8). Other methods may be
used by mutual consent of the manufacturer and purchaser.
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of the ASTM Committee A04 on Iron Castings and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee A04.02 on Malleable and
Ductile Iron Castings.
Current edition approved May 1, 2009Oct. 1, 2014. Published August 2009October 2014. Originally approved in 1965. Last previous edition approved in 20042009 as
ε1
A536–84 (2004)(2009). . DOI: 10.1520/A0536-84R09.10.1520/A0536-84R14.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
Available from Standardization Documents Order Desk, DODSSP, Bldg. 4, Section D, 700 Robbins Ave., Philadelphia, PA 19111-5098
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
A536 − 84 (2014)
TABLE 1 Tensile Requirements
Grade Grade Grade Grade Grade
60-40-18 65-45-12 80-55-06 100-70-03 120-90-02
Tensile strength, min, psi 60 000 65 000 80 000 100 000 120 000
Tensile strength, min, MPa 414 448 552 689 827
Yield strength, min, psi 40 000 45 000 55 000 70 000 90 000
Yield strength, min, MPa 276 310 379 483 621
Elongation in 2 in. or 50 mm, min, % 18 12 6.0 3.0 2.0
TABLE 2 Tensile Requirements for Special Applications
Grade Grade Grade
60-42-10 70-50-05 80-60-03
Tensile strength, min, psi 60 000 70 000 80 000
Tensile strength, min, MPa 415 485 555
Yield strength, min, psi 42 000 50 000 60 000
Yield strength, min, MPa 290 345 415
Elongation in 2 in. or 50 mm, 10 5 3
min, %
5. Heat Treatment
5.1 The 60-40-18 grade will normally require a full ferritizing anneal. The 120-90-02 and the 100-70-03 grades generally
require a quench and temper or a normali
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.