ASTM A436-84(2020)
(Specification)Standard Specification for Austenitic Gray Iron Castings
Standard Specification for Austenitic Gray Iron Castings
ABSTRACT
This specification covers austenitic gray iron castings that are used primarily for their resistance to heat, corrosion, and wear. The types of castings covered here are: Type 1, Type 1b, Type 2, Type 2b, Type 3, Type 4, Type 5, and Type 6. The materials shall be manufactured by melting in any furnace that produces castings which includes cupolas, air furnaces, electric furnaces, crucible furnaces, and so forth. Heat and product analyses shall be performed wherein specimens shall conform to required chemical composition of carbon, silicon, manganese, nickel, copper, chromium, sulfur, and molybdenum. The materials shall undergo a nonmagnetic test which is based on the material's attraction to a small steel horseshoe-type magnet and a magnetic permeability test in the event that nonmagnetic castings are specified. Tension tests shall be performed wherein specimens shall conform to required tensile strength and Brinell hardness.
SCOPE
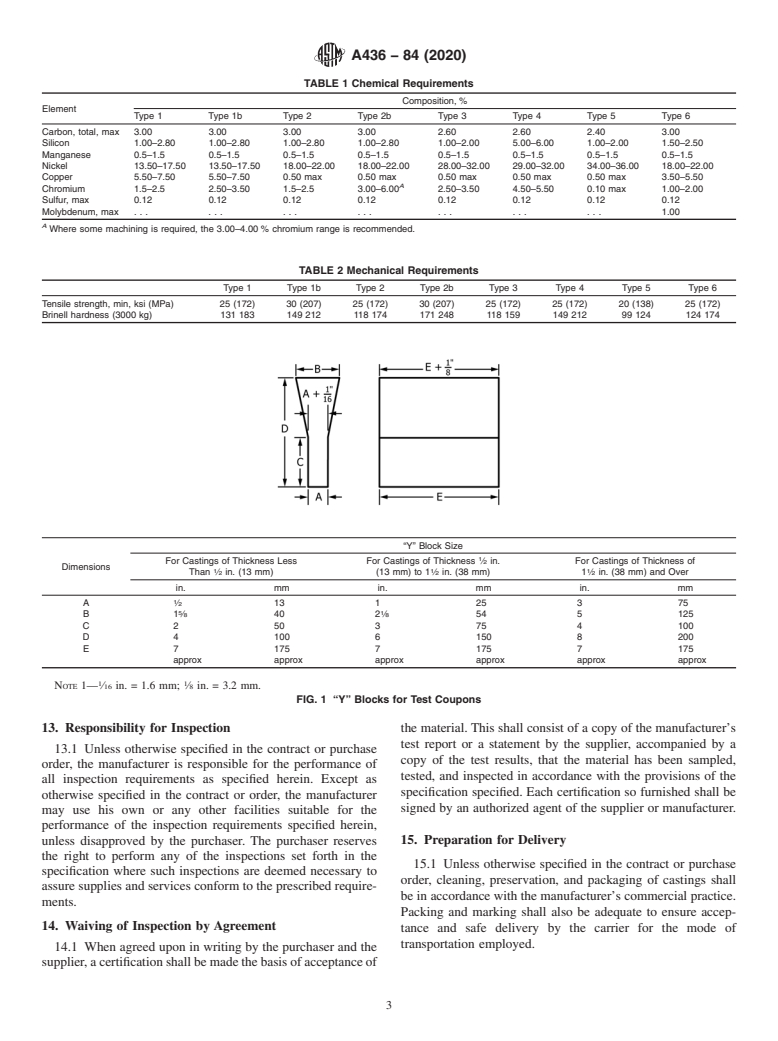
1.1 This specification covers austenitic gray iron castings that are used primarily for their resistance to heat, corrosion, and wear. Austenitic gray iron is characterized by uniformly distributed graphite flakes, some carbides, and the presence of sufficient alloy content to produce an austenitic structure.
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.3 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: A436 −84 (Reapproved 2020)
Standard Specification for
Austenitic Gray Iron Castings
This standard is issued under the fixed designation A436; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope E446 Reference Radiographs for Steel Castings Up to 2 in.
(50.8 mm) in Thickness
1.1 This specification covers austenitic gray iron castings
that are used primarily for their resistance to heat, corrosion,
3. Ordering Information
and wear. Austenitic gray iron is characterized by uniformly
3.1 Orders for material to this specification shall include the
distributed graphite flakes, some carbides, and the presence of
following information:
sufficient alloy content to produce an austenitic structure.
3.1.1 ASTM designation and date of issue,
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
3.1.2 Type of austenitic gray iron required (see 5.1),
as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
3.1.3 Heat treatment required (see 4.2 – 4.5),
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only
3.1.4 If repair of castings is permitted (see 4.6),
and are not considered standard.
3.1.5 Size and number of test bars required (see 11 through
1.3 This international standard was developed in accor- 8.4 and 12.1),
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
3.1.6 If special tests are required (see Section 7 and 9.1),
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the 3.1.7 If certification is required (see 14.1), and
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
3.1.8 If different preparation for delivery requirements is
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical needed (see 15.1).
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
4. Materials and Manufacture
2. Referenced Documents
4.1 Melting may be done in any furnace that produces
2.1 ASTM Standards: castings meeting the chemical compositions and mechanical
properties outlined in this specification. These include cupolas,
E30 Test Methods for ChemicalAnalysis of Steel, Cast Iron,
Open-Hearth Iron, and Wrought Iron (Withdrawn 1995) air furnaces, electric furnaces, crucible furnaces, and so forth.
E59 Practice for Sampling Steel and Iron for Determination
4.2 By agreement between the manufacturer and the
of Chemical Composition (Withdrawn 1996)
purchaser, the castings may be stress relieved by heating to and
E94/E94M Guide for Radiographic Examination Using In-
holding in the temperature range from 1150 to 1200 °F (620 to
dustrial Radiographic Film
650 °C) for not less than 1 nor more than 2 h/in. of thickness
E165/E165M Practice for Liquid Penetrant Testing for Gen-
in the thickest section. Heating and cooling shall be uniform
eral Industry
and shall be not more than 400 °F (222 °C)⁄h for castings less
E351 Test Methods for ChemicalAnalysis of Cast Iron—All
than 1 in. in maximum thickness, nor more than 400 °F⁄h
Types
dividedbythemaximumsectionthicknessininchesforthicker
E433 Reference Photographs for Liquid Penetrant Inspec-
castings. During the cooling cycle, castings may be cooled in
tion
still air after the temperature has dropped to 600 °F (315 °C).
4.3 If the manufacturer can demonstrate that another treat-
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee A04 on Iron
ment provides satisfactory stress relief, it may be used by
CastingsandisthedirectresponsibilityofSubcommitteeA04.01onGreyandWhite
agreement between the manufacturer and the purchaser.
Iron Castings.
Current edition approved May 1, 2020. Published May 2020. Originally
4.4 Whenever dimensional changes in high-temperature
approved in 1959. Last previous edition approved in 2015 as A436 – 84 (2015).
service are a problem, by agreement between the manufacturer
DOI: 10.1520/A0436-84R20.
and the purchaser, the castings may be stabilized by heating at
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
1600 °F (870 °C) for 1 h/in. of section, for a minimum of 1 h.
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
Otherwise, the austenite that is supersaturated with respect to
the ASTM website.
carbon may reject carbon during service and produce dimen-
The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
www.astm.org. sional changes.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
A436 − 84 (2020)
4.5 By agreement between the manufacturer and the bars shall be cast in open molds made of suitable core sand
purchaser, castings with chilled edges or excessive carbides with a minimum of 1 ⁄2 in. (38 mm) of sand on all sides and
1 1
may be annealed at 1750 to 1900 °F (955 to 1040 °C) for ⁄2 to bottomofthe ⁄2-in.(13-mm)and1-in.(25-mm)sizes,and3in.
5 h, followed by uniform cooling, preferably in still air. (76 mm) of sand for the 3-in. test bar.
4.6 Castings shall not be repaired by welding, plugging, or 8.2 By agreement between the manufacturer and the
other methods without written permission from the purchaser. purchaser,the1-in.(25-mm)keelblockshowninFig.2maybe
used. It shall be an open mold made of suitable core sand with
5. Chemical Composition
aminimumof1 ⁄2 in.(38mm)ofsandonallsidesandbottom.
5.1 Many combinations of alloys can be used to obtain an
8.3 It is recommended that test bars be poured immediately
austenitic gray iron. This specification includes only the six
after the castings and from the same ladle of metal. If castings
types defined by the chemical composition limits specified in
are to be heat treated, test bars shall be included in the same
Table 1.
furnace load.
5.2 The chemical analysis for total carbon shall be made on
8.4 By agreement between the manufacturer and the
chilled cast pencil-type specimens or from thin wafers approxi- purchaser, tension test specimens may be cut directly from
mately ⁄32 in. (0.8 mm) thick cut from test coupons. Drillings
centrifugal or other permanent mold castings. The location and
are not reliable because of the probable loss of graphite. orientation of such tension test specimens cut from castings
shall be specified as agreed upon by the manufacturer and the
5.3 Drillings taken from test coupons, broken test
purchaser.
specimens, or castings shall conform to the requirements for
chemical composition as given in Table 1. Sampling shall be
9. Workmanship, Finish, and Appearance
conducted in accordance with Practice E59 and chemical
9.1 The castings shall conform substantially to the dimen-
analysis in accordance with Test Methods E351 and Test
sions on the drawings furnished by the purchaser, or if no
Methods E30. Test Methods E30 should only be used for
drawing has been provided, to the dimensions predicated by
analyzing those elements for which specific coverage is not
the pattern supplied by the purchaser.The castings shall be free
provided for in Test Methods E351.
of injurious defects. Surfaces of the castings shall be free of
5.4 Spectrometric techniques may also be used for analysis,
burnt-on sand and shall be reasonably smooth. In other
but should a dispute arise concerning chemical composition,
respects, the castings shall conform to whatever points may be
chemical analyses determined by Test Methods E351 and Test
specifically agreed upon between the manufacturer and the
Methods E30 shall be used for referee analysis.
purchaser.
6. Mechanical Properties
10. Tension Test Specimens
6.1 Although these irons are not used primarily for their
10.1 The round tension
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.