ASTM E749-07
(Practice)Standard Practice for Acoustic Emission Monitoring During Continuous Welding
Standard Practice for Acoustic Emission Monitoring During Continuous Welding
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
Detection and location of AE sources in weldments during fabrication may provide information related to the integrity of the weld. Such information may be used to direct repair procedures on the weld or as a guide for application of other nondestructive evaluation (NDE) methods. A major attribute of applying AE for in-process monitoring of welds is the ability of the method to provide immediate real-time information on weld integrity. This feature makes the method useful to lower weld costs by repairing defects at the most convenient point in the production process. The AE activity from discontinuities in the weldment is stimulated by the thermal stresses from the welding process. The AE activity resulting from this stimulation is detected by AE sensors in the vicinity of the weldment, which convert the acoustic waves into electronic signals. The AE instrumentation processes signals and provides means for immediate display or indication of AE activity and for permanent recordings of the data.
Items to be considered in preparation and planning for monitoring should include but not be limited to the following:
4.2.1 Description of the system or object to be monitored or examined,
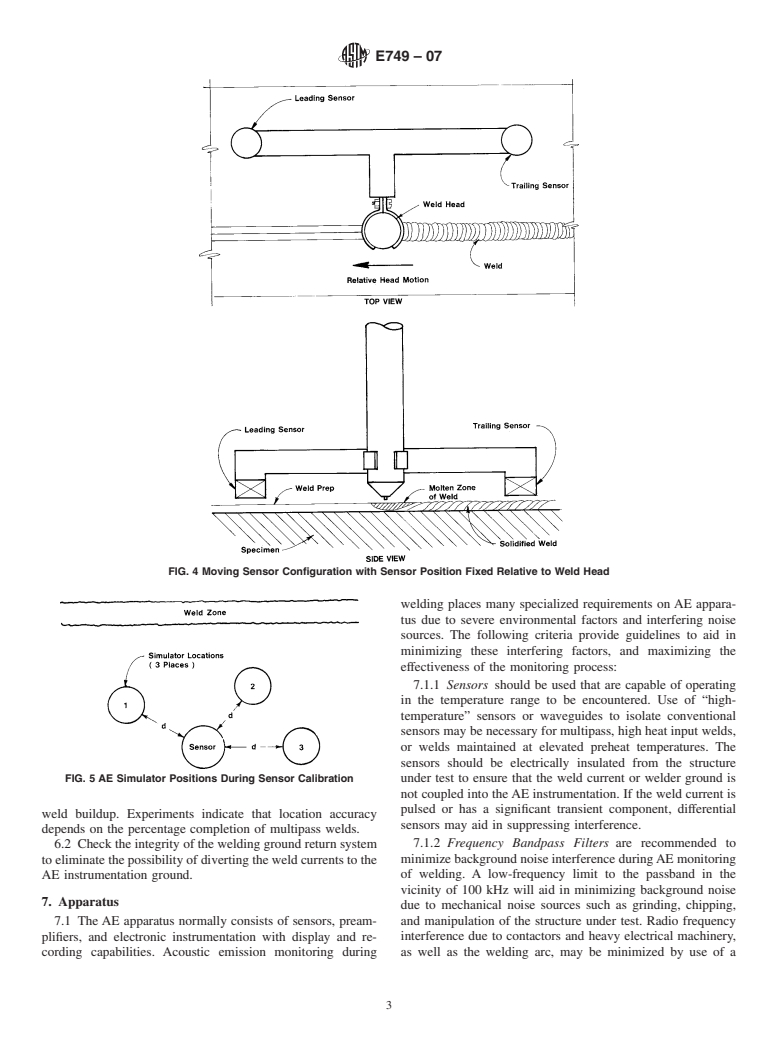
4.2.2 Extent of monitoring, that is, entire weld, cover passes only, and so forth,
4.2.3 Limitations or restrictions on the sensor mounting procedures, if applicable,
4.2.4 Performance parameters to be established and maintained during the AE system verification procedure (sensitivity, location accuracy, and so forth),
4.2.5 Maximum time interval between AE system verification checks,
4.2.6 Performance criteria for purchased equipment,
4.2.7 Requirements for permanent records of the AE response, if applicable,
4.2.8 Content and format of test report, if required, and
4.2.9 Operator qualification and certification, if required.
SCOPE
1.1 This practice provides recommended guidelines for acoustic emission (AE) monitoring of weldments during and immediately following their fabrication by continuous welding processes.
1.2 The procedure described in this practice is applicable to the detection and location of AE sources in weldments and in their heat-affected zone during fabrication, particularly in those cases where the time duration of welding is such that fusion and solidification take place while welding is still in progress.
1.3 The effectiveness of acoustic emission to detect discontinuities in the weldment and the heat-affected zone is dependent on the design of the AE system, the AE system verification procedure, the weld process, and the material type. Materials that have been monitored include low-carbon steels, low-alloy steels, stainless steels, and some aluminum alloys. The system performance must be verified for each application by demonstrating that the defects of concern can be detected with the desired reliability.
This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: E749 – 07
Standard Practice for
1
Acoustic Emission Monitoring During Continuous Welding
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E749; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
3
1. Scope 2.2 ASNT Standards:
SNT-TC-1A Recommended Practice for Nondestructive
1.1 This practice provides recommended guidelines for
Testing Personnel Qualification and Certification
acoustic emission (AE) monitoring of weldments during and
ANSI/ASNT CP-189 Standard for Qualification and Certi-
immediately following their fabrication by continuous welding
fication of Nondestructive Testing Personnel
processes.
4
2.3 AIA Standard:
1.2 The procedure described in this practice is applicable to
NAS-410 Certification and Qualification of Nondestructive
the detection and location of AE sources in weldments and in
Personnel (Quality Assurance Committee)
theirheat-affectedzoneduringfabrication,particularlyinthose
cases where the time duration of welding is such that fusion
3. Terminology
and solidification take place while welding is still in progress.
3.1 Definitions—Fordefinitionsoftermsrelatingtoacoustic
1.3 The effectiveness of acoustic emission to detect discon-
emission testing, see Section B of Terminology E1316.
tinuities in the weldment and the heat-affected zone is depen-
dentonthedesignoftheAEsystem,theAEsystemverification
4. Significance and Use
procedure, the weld process, and the material type. Materials
4.1 Detection and location of AE sources in weldments
that have been monitored include low-carbon steels, low-alloy
during fabrication may provide information related to the
steels, stainless steels, and some aluminum alloys. The system
integrity of the weld. Such information may be used to direct
performance must be verified for each application by demon-
repair procedures on the weld or as a guide for application of
strating that the defects of concern can be detected with the
other nondestructive evaluation (NDE) methods. A major
desired reliability.
attribute of applying AE for in-process monitoring of welds is
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
the ability of the method to provide immediate real-time
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
information on weld integrity. This feature makes the method
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
useful to lower weld costs by repairing defects at the most
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
convenient point in the production process. The AE activity
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
from discontinuities in the weldment is stimulated by the
2. Referenced Documents thermal stresses from the welding process. The AE activity
2 resulting from this stimulation is detected byAE sensors in the
2.1 ASTM Standards:
vicinity of the weldment, which convert the acoustic waves
E543 Specification for Agencies Performing Nondestruc-
into electronic signals. The AE instrumentation processes
tive Testing
signalsandprovidesmeansforimmediatedisplayorindication
E569 Practice for Acoustic Emission Monitoring of Struc-
of AE activity and for permanent recordings of the data.
tures During Controlled Stimulation
4.2 Items to be considered in preparation and planning for
E650 Guide for Mounting Piezoelectric Acoustic Emission
monitoring should include but not be limited to the following:
Sensors
4.2.1 Description of the system or object to be monitored or
E1316 Terminology for Nondestructive Examinations
examined,
4.2.2 Extent of monitoring, that is, entire weld, cover passes
1
This practice is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E07 on Nonde-
only, and so forth,
structive Testing and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E07.04 on
4.2.3 Limitations or restrictions on the sensor mounting
Acoustic Emission Method.
procedures, if applicable,
Current edition approved Feb. 15, 2007. Published March 2007. Originally
approved in 1980. Last previous edition approved in 2001 as E749 - 01. DOI:
10.1520/E0749-07.
2 3
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or AvailablefromAmericanSocietyforNondestructiveTesting(ASNT),P.O.Box
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM 28518, 1711 Arlingate Ln., Columbus, OH 43228-0518, http://www.asnt.org.
4
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Available fromAerospace IndustriesAssociation ofAmerica, Inc. (AIA), 1000
the ASTM website. WilsonBlvd.,Suite1700,Arlington,VA22209-3928,http://www.aia-aerospace.org.
Copyright © ASTM International,
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.