ASTM D4084-05
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Analysis of Hydrogen Sulfide in Gaseous Fuels (Lead Acetate Reaction Rate Method)
Standard Test Method for Analysis of Hydrogen Sulfide in Gaseous Fuels (Lead Acetate Reaction Rate Method)
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of hydrogen sulfide (H2S) in gaseous fuels. It is applicable to the measurement of H2S in natural gas, liquefied petroleum gas (LPG), substitute natural gas, and mixtures of fuel gases. Air does not interfere. The applicable range is 0.1 to 16 parts per million by volume (ppm/v) (approximately 0.1 to 22 mg/m3) and may be extended to 100 % H2S by manual or automatic volumetric dilution.
This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D 4084 – 05
Standard Test Method for
Analysis of Hydrogen Sulfide in Gaseous Fuels (Lead
1
Acetate Reaction Rate Method)
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 4084; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope Pure H S is used as a primary standard and mixed volumetri-
2
callywithasulfurfreecarriergasthatisofthesametypeasthe
1.1 This test method covers the determination of hydrogen
gas to be analyzed. A gaseous sample at constant flow is
sulfide (H S) in gaseous fuels. It is applicable to the measure-
2
humidified and passed over lead-acetate-impregnated paper.
ment of H S in natural gas, liquefied petroleum gas (LPG),
2
H Sreactswithleadacetatetoformabrownstainonthepaper.
2
substitute natural gas, and mixtures of fuel gases.Air does not
The rate of reaction and resulting rate of color change is
interfere. The applicable range is 0.1 to 16 parts per million by
3
proportional to the concentration of H S in the sample. An
2
volume (ppm/v) (approximately 0.1 to 22 mg/m ) and may be
optical system, photodetectors, a means to obtain the first
extended to 100 % H S by manual or automatic volumetric
2
derivativeofthephotodetectorsignal,andameanstoobtainan
dilution.
output from the differentiation process comprises the analyzer.
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the
When there is no change in the color of the tape, and no
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
resultingchangeinphotodetectoroutput, E,thefirstderivative,
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
dE/dt, is zero. This results in an analyzer that automatically
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
zeroes when there is no H S.
2
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
4. Significance and Use
2. Referenced Documents
2
4.1 This test method is useful in determining the concentra-
2.1 ASTM Standards:
tionofhydrogensulfideingaseoussamplestoverifythatlimits
D 1193 Specification for Reagent Water
setforH Sintheproductgasarecompliedwith.Theautomatic
2
D 1914 Practice for Conversion Units and Factors Relating
operation of this method allows unattended measurement of
to Sampling and Analysis of Atmospheres
H S concentration.
2
D 2420 Test Method for Hydrogen Sulfide in Liquefied
Petroleum (LP) Gases (Lead Acetate Method)
5. Apparatus
D 3609 Practice for Calibration Techniques Using Perme-
5.1 Volumetric Measuring Devices—a graduated 10-L cyl-
ation Tubes
inder (see Fig. 1) having a movable piston for volumetrically
D 5504 Test Method for Determination of Sulfur Com-
measuring test gas. Gastight syringes of 0.1- and 0.5-mL
pounds in Natural Gas and Gaseous Fuels by Gas Chro-
volume for volumetrically measuring 100 % H S. Gas tight
2
matography and Chemiluminescence
syringes of other volumes can be used. These graduated
3. Summary of Test Method devices are not needed if the permeation tube method of
dynamic mixing is used to prepare the reference sample as this
3.1 Measurement of H S is accomplished by ratiometrically
2
method may be used to generate reference mixture.
comparing a reading of an unknown sample with that of a
5.2 Sample Pump—a pump capable of providing more than
known standard sample using a colorimetric analysis method.
3
8 mL/s (approximately 1 ft /h) or less than 1 mL/s at 70 kPa
(approximately 10.15 psig). Gas-wetted parts are to be either
1
ThistestmethodisunderthejurisdictionofASTMCommitteeD03onGaseous aluminum or polytetrafluorethylene (PTFE). Stainless steel is
Fuels and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D03.05 on Determination of
less preferable but may be used for the purpose of improving
Special Constituents of Gaseous Fuels.
safety if applicable.
Current edition approved Feb. 1, 2005. Published February 2005. Originally
5.3 Colorimetric Rate of Reaction Sensor—select a device
approved in 1981. Last previous editionapproved in 1999 as D 4084 – 94 (1999).
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
of sufficient sensitivity to measure a minimum rate of change
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
of color density corresponding to 0.1-ppm H S by volume in
2
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
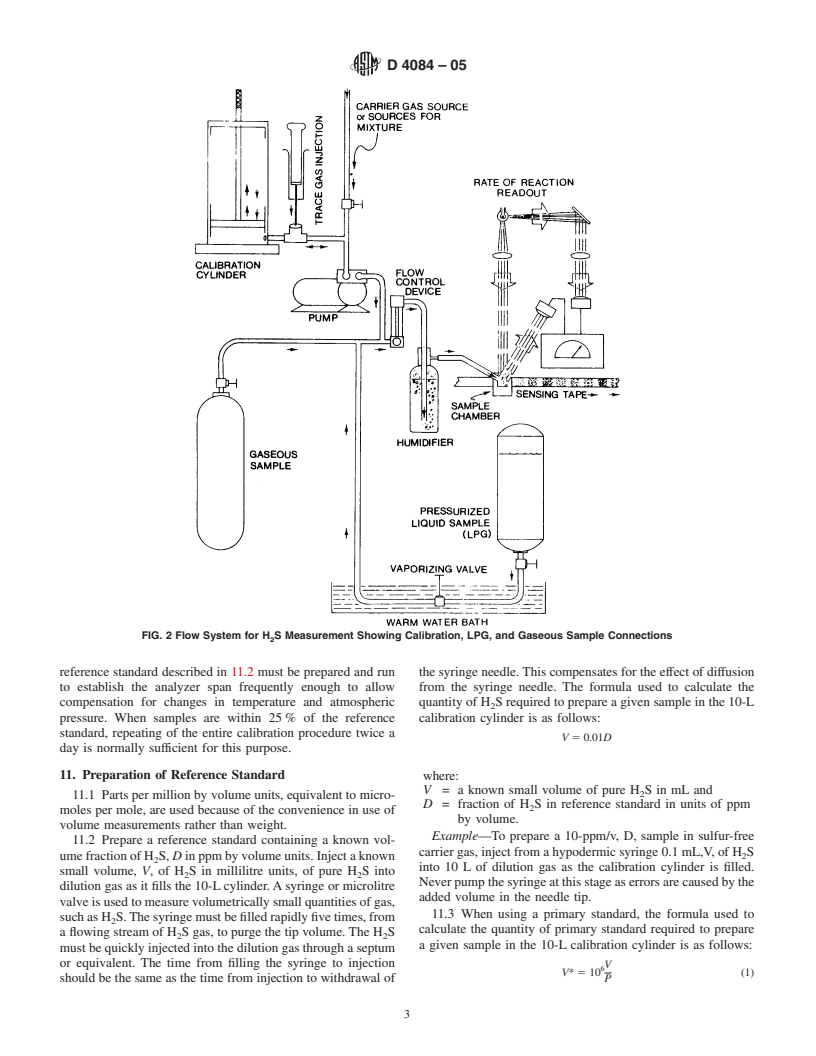
the sample gas. (See Fig. 2.)
the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D4084–05
be properly stored and used only within the stated validity
period. In the
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.