ASTM D892-02
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Foaming Characteristics of Lubricating Oils
Standard Test Method for Foaming Characteristics of Lubricating Oils
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the foaming characteristics of lubricating oils at 24°C and 93.5°C. Means of empirically rating the foaming tendency and the stability of the foam are described.
1.2 The values stated in acceptable SI units are to be regarded as the standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific hazard statements, see Sections 7, 8, and 9.1.1.
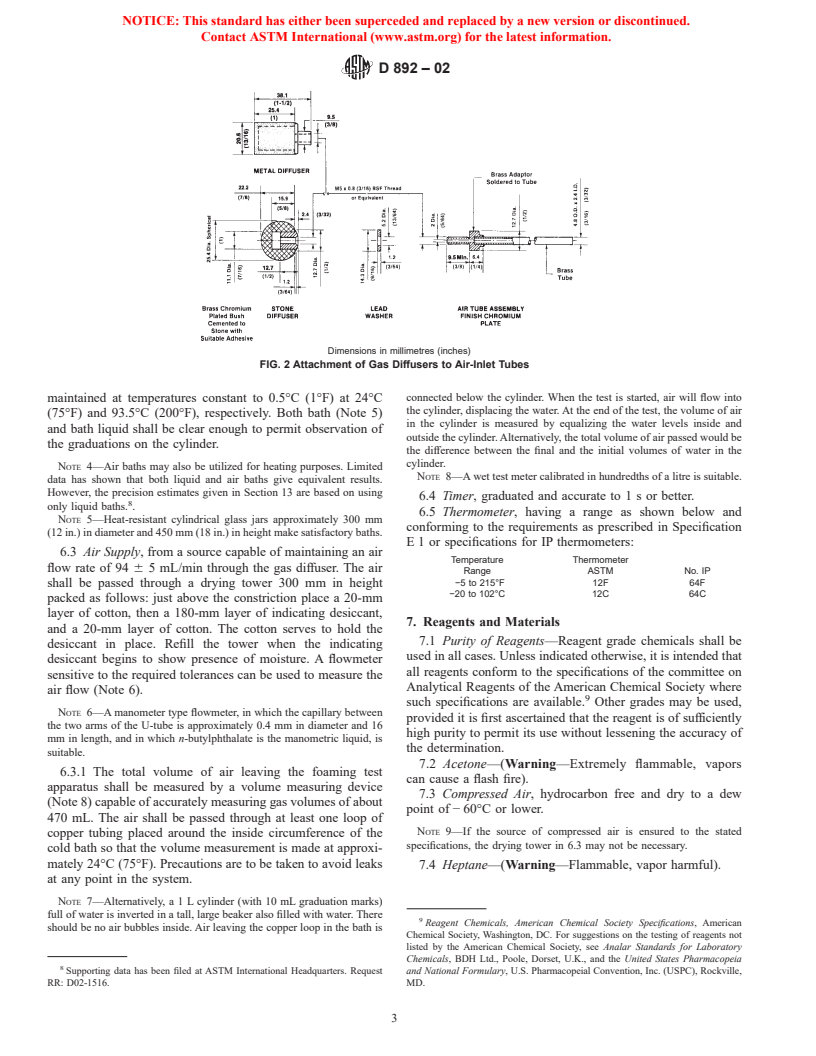
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superceded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
An American National Standard
Designation: D 892 – 02
British Standard 5092
Designation: 146/2000
Standard Test Method for
1
Foaming Characteristics of Lubricating Oils
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 892; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
This test method has been approved by the sponsoring committees and accepted by the cooperating societies in accordance with
established procedures.
1. Scope 3.1.2 foam, n—in liquids, a collection of bubbles formed in
the liquid or on (at) its surface in which the air (or gas) is the
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the foam-
major component on a volumetric basis.
ing characteristics of lubricating oils at 24°C and 93.5°C.
3.1.3 entrained air (or gas), n—in liquids, a two-phase
Means of empirically rating the foaming tendency and the
mixture of air (or gas) dispersed in a liquid in which the
stability of the foam are described.
volume of the liquid is the major component.
1.2 The values stated in acceptable SI units are to be
3.1.3.1 Discussion—The air (or gas) is in the form of
regarded as the standard.
discrete bubbles of about 10 to 1000 μm in diameter. The
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
bubbles are not uniformly dispersed. In time they tend to rise
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
to the surface to coalesce to form larger bubbles which break or
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
form foam. Subsurface coalescence can also occur, in which
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
case, the bubbles rise more rapidly.
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific hazard
3.1.4 lubricant, n—any material interposed between two
statements, see Sections 7, 8, and 9.1.1.
surfaces that reduces the friction or wear between them.
2. Referenced Documents D4175–88
3.1.4.1 Discussion—In this test method, the lubricant is an
2.1 ASTM Standards:
oil which can or can not contain additives such as foam
D 445 Test Method for Kinematic Viscosity of Transparent
2
inhibitors.
and Opaque Liquids
3.1.5 maximum pore diameter, n—in gas diffusion, the
D 4175 Terminology Relating to Petroleum, Petroleum
3
diameter a capillary of circular cross section which is equiva-
Products, and Lubricants
4
lent (with respect to surface tension effects) to the largest pore
E 1 Specification for ASTM Thermometers
of the diffuser under consideration.
E 128 Test Method for Maximum Pore Diameter and Per-
5
3.1.5.1 Discussion—The pore dimension is expressed in
meability of Rigid, Porous Filters for Laboratory Use
micrometres in this test method.
3. Terminology
3.1.6 permeability, n—in gas diffusion, the flow of gas,
through the gas diffuser.
3.1 Definitions:
3.1.7 Discussion—In this test method, the permeability is
3.1.1 diffuser, n—for gas, a device for dispersing gas into a
measured at a pressure of 2.45 kPa (250 mm of water) in
fluid.
millilitres per minute.
3.1.1.1 Discussion—In this test method the diffuser may be
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
made of either metallic or non-metallic materials.
3.2.1 dynamic bubble, n—the first bubble to pass through
and escape from the diffuser followed by a continuous succes-
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on
sion of bubbles when testing for the maximum pore diameter in
Petroleum Products and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
Annex A1.
D02.06 on Analysis of Lubricants.
Current edition approved Jan. 10, 2002. Published March 2002. Originally
3.2.1.1 Discussion—When a diffuser is immersed in a
published as D 892 – 46. Last previous edition D 892 – 01.
liquid, air can be trapped in the pores. It can escape eventually
In the IP, this method is under the jurisdiction of the Standardization Committee.
2 or as soon as a pressure is applied to the diffuser. When testing
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 05.01.
3
for maximum pore diameter (Annex A1) the escape of such
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 05.02.
4
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 14.03.
bubble shall be ignored.
5
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 14.02.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
NOTICE: This standard has either been superceded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest info
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.