ASTM E883-02
(Guide)Standard Guide for Reflected-Light Photomicrography
Standard Guide for Reflected-Light Photomicrography
SCOPE
1.1 This guide outlines various methods which may be followed in the photography of metals and materials with the reflected-light microscope. Methods are included for preparation of prints and transparencies in black-and-white and in color, using both direct rapid and wet processes.
1.2 Guidelines are suggested to yield photomicrographs of typical subjects and, to the extent possible, of atypical subjects as well. Information is included concerning techniques for the enhanced display of specific material features. Descriptive material is provided where necessary to clarify procedures. References are cited where detailed descriptions may be helpful.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory requirements prior to use. Specific precautionary statements are given in X1.7.Referenced documents2Terminology3Significance and use4Magnification5Reproduction of photomicrographs6Optical systems7Illumination sources8Illumination of specimens9Focusing10Filters for photomicrography11Illumination techniques12Instant-processing films13Photographic materials14Photographic exposure15Photographic processing16Keyword17Suggestions for visual use of metallographic microscopesX1Guide for metallographic phhotmacrographyX2Electronic photographyX3
General Information
Relations
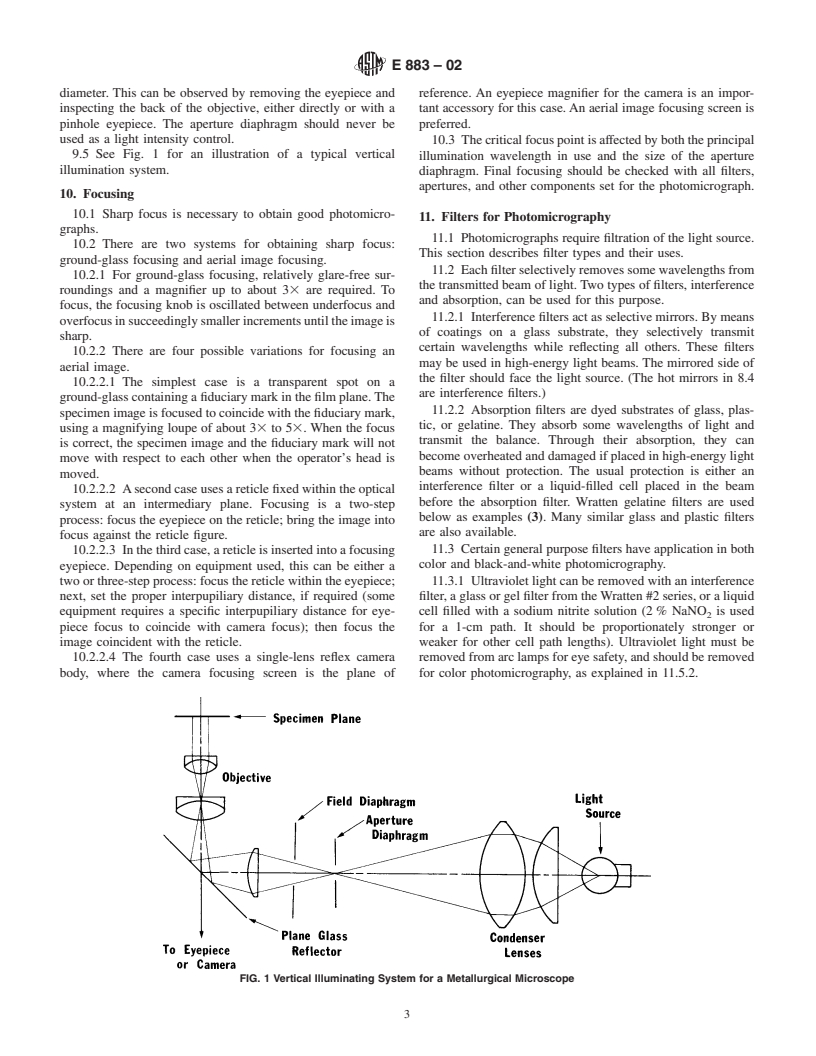
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: E 883 – 02
Standard Guide for
1
Reflected–Light Photomicrography
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E 883; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
2
1. Scope E 7 Terminology Relating to Metallography
3
E 175 Terminology of Microscopy
1.1 This guide outlines various methods which may be
E 768 Practice for Preparing and Evaluating Specimens for
followed in the photography of metals and materials with the
2
Automatic Inclusion Assessment of Steel
reflected-light microscope. Methods are included for prepara-
E 1951 Guide for Calibrating Reticles and Light Micro-
tion of prints and transparencies in black-and-white and in
2
scope Magnifications
color, using both direct rapid and wet processes.
1.2 Guidelines are suggested to yield photomicrographs of
3. Terminology
typical subjects and, to the extent possible, of atypical subjects
3.1 Definitions—For definitions of terms used in this guide,
as well. Information is included concerning techniques for the
see Terminologies E 7 and E 175.
enhanced display of specific material features. Descriptive
material is provided where necessary to clarify procedures.
4. Significance and Use
References are cited where detailed descriptions may be
4.1 This guide is useful for the photomicrography and
helpful.
photomacrography of metals and other materials.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
4.2 The subsequent processing of the photographic materi-
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
als is also treated.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
5. Magnification
bility of regulatory requirements prior to use. Specific precau-
5.1 Photomicrographs shall be made at preferred magnifi-
tionary statements are given in X1.7.
cations, except in those special cases where details of the
1.4 The sections appear in the following order:
microstructure are best revealed by unique magnifications.
Referenced documents 2
5.2 The preferred magnifications for photomicrographs, are:
Terminology 3
Significance and use 4 253,503,753, 1003, 2003, 2503, 4003, 5003, 7503,
Magnification 5
8003, and 10003.
Reproduction of photomicrographs 6
5.3 Magnifications are normally calibrated using a stage
Optical systems 7
Illumination sources 8 micrometer. Calibration procedures in Guide E 1951 should be
Illumination of specimens 9
followed.
Focusing 10
Filters for photomicrography 11
6. Reproduction of Photomicrographs
Illumination techniques 12
Instant-processing films 13
6.1 Photomicrographs should be at one of the preferred
Photographic materials 14
magnifications. A milli- or micrometre marker shall be super-
Photographic exposure 15
Photographic processing 16
imposed on the photomicrograph to indicate magnification, in
Keywords 17
a contrasting tone. The published magnification, if known,
Suggestions for visual use of metallographic microscopes X1
should be stated in the caption.
Guide for metallographic photomacrography X2
Electronic photography X3 6.2 Photomicrograph captions should include basic back-
ground information (for example, material identification,
2. Referenced Documents
etchant, mechanical or thermal treatment details) and should
2.1 ASTM Standards:
briefly describe what is illustrated so that the photomicrograph
2
E 3 Methods of Preparation of Metallographic Specimens
can stand independent of the text.
6.3 Arrows or other markings, in a contrasting tone, shall be
used to designate specific features in a photomicrograph. Any
1
This guide is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E04 on Metallogra-
marking used shall be referenced in the caption.
phyand is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E04.03 on Light Microscopy.
Current edition approved Nov 10, 2002. Published April 2003. Originally
published as E 883 – 82. Last previous edition E 883 – 99.
2 3
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 03.01. Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 14.02.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
E883–02
7. Optical Systems Tungsten-halogen lamps minimize envelope blackening, main-
taining constant brightness and color temperature for most of
7.1 Microscope objectives are available in increasing order
their life.The high brightness and 3200 K color temperature of
of correction as achromats, semiapochromats (fluorites) and
these lamps makes them especially suitable for color photomi-
apochromats (see Terminologies E 7 and E 1
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.