ASTM G195-08
(Guide)Standard Guide for Conducting Wear Tests Using a Rotary Platform, Double-Head Abraser
Standard Guide for Conducting Wear Tests Using a Rotary Platform, Double-Head Abraser
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
This test guide provides a means to quantify the abrasion resistance of material surfaces, and may be related to end-use performance, or used to comparatively rank material performance, or both. The resistance of material surfaces to abrasion, as measured on a testing machine in the laboratory, is generally only one of several factors contributing to wear performance as experienced in the actual use of the material. Other factors may need to be considered in any calculation of predicted life from specific abrasion data.
The resistance of material surfaces to abrasion may be affected by factors including test conditions; type of abradant; pressure between the specimen and abradant; mounting or tension of the specimen; and type, kind, or amount of finishing materials.
Abrasion tests utilizing the rotary platform, double head abraser may be subject to variation due to changes in the abradant during the course of specific tests. Depending on abradant type and test specimen, the abrading wheel surface may change (i.e. become clogged) due to the pick-up of finishing or other materials from test specimens. To reduce this variation, the abrading wheels should be resurfaced at regularly defined intervals. See Appendix X2.
The measurement of the relative amount of abrasion may be affected by the method of evaluation and influenced by the judgment of the operator.
SCOPE
1.1 This guide covers and is intended to assist in establishing procedures for conducting wear tests of rigid or flexible materials utilizing the rotary platform, double-head abraser (RPDH).
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.2.1 Exception—English units are used when determining coating thickness.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: G195 − 08
StandardGuide for
Conducting Wear Tests Using a Rotary Platform, Double-
Head Abraser
This standard is issued under the fixed designation G195; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope D4060 Test Method for Abrasion Resistance of Organic
Coatings by the Taber Abraser
1.1 This guide covers and is intended to assist in establish-
D4685 Test Method for Pile Fabric Abrasion
ing procedures for conducting wear tests of rigid or flexible
D4712 Guide for Testing Industrial Water-Reducible Coat-
materials utilizing the rotary platform, double-head abraser
ings
(RPDH).
D5034 TestMethodforBreakingStrengthandElongationof
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
Textile Fabrics (Grab Test)
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
D5035 Test Method for Breaking Force and Elongation of
standard.
Textile Fabrics (Strip Method)
1.2.1 Exception—English units are used when determining
D5144 Guide for Use of Protective Coating Standards in
coating thickness.
Nuclear Power Plants
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the D5146 Guide to Testing Solvent-Borne Architectural Coat-
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
ings
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro- D5324 Guide for Testing Water-Borne Architectural Coat-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
ings
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. D6037 Test Methods for Dry Abrasion Mar Resistance of
High Gloss Coatings
2. Referenced Documents
D7255 Test Method for Abrasion Resistance of Leather
(Rotary Platform, Double-Head Method)
2.1 ASTM Standards:
F362 Test Method for Determining the Erasability of Inked
C501 Test Method for Relative Resistance to Wear of
Ribbons
Unglazed Ceramic Tile by the Taber Abraser
F510 Test Method for Resistance to Abrasion of Resilient
C1353 Test Method for Abrasion Resistance of Dimension
Floor Coverings Using an Abrader with a Grit Feed
Stone Subjected to Foot Traffic Using a Rotary Platform,
Method
Double-Head Abraser
F1344 Specification for Rubber Floor Tile
D1044 Test Method for Resistance ofTransparent Plastics to
F1478 Test Method for Determination of Abrasion Resis-
Surface Abrasion
tance of Images Produced from Copiers and Printers
D3389 Test Method for Coated FabricsAbrasion Resistance
(Taber Method)
(Rotary Platform Abrader)
F1978 Test Method for Measuring Abrasion Resistance of
D3451 Guide for Testing Coating Powders and Powder
Metallic Thermal Spray Coatings by Using the Taber
Coatings
Abraser
D3730 Guide for Testing High-Performance Interior Archi-
G40 Terminology Relating to Wear and Erosion
tectural Wall Coatings
D3884 Test Method for Abrasion Resistance of Textile
3. Terminology
Fabrics (Rotary Platform, Double-Head Method)
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3.1.1 abraser—wear testing instrument to evaluate abrasion
This guide is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee G02 on Wear and
resistance, also referred to as an abrader.
Erosion and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee G02.30 on Abrasive Wear.
3.1.2 abrasion cycle—in abrasion testing, one or more
Current edition approved May 1, 2008. Published May 2008. DOI: 10.1520/
G0195-08.
movements of the abradant across a material surface, or the
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
material surface across the abradant, that permits a return to its
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
starting position. In the case of the rotary platform test method,
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. it consists of one complete rotation of the specimen.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
G195 − 08
3.1.3 resurface—procedure of cleaning and refreshing the
running surface of an abrasive wheel prior to use in testing.
3.2 For definitions of other wear terms used in this test
method, refer to Terminology G40.
4. Summary of Practice
4.1 Aspecimenisabradedusingrotaryrubbingactionunder
controlled conditions of pressure and abrasive action. The test
specimen, mounted on a turntable platform, turns on a vertical
axis, against the sliding rotation of two abrading wheels. One
abrading wheel rubs the specimen outward toward the periph-
ery and the other, inward toward the center. The resulting
abrasion marks form a pattern of crossed arcs over an area of
approximately 30 cm . Resistance to abrasion is evaluated by
various means which are described in Section 12.
FIG. 1 Rotary Platform, Double-Head (RPDH) Abraser
5. Significance and Use
6.1.2 Amotor capable of rotating the turntable platform at a
5.1 This test guide provides a means to quantify the abra-
speed of either 72 6 2 rpm or 60 6 2 rpm.
sion resistance of material surfaces, and may be related to
6.1.3 A pair of pivoted arms to which the abrasive wheels
end-use performance, or used to comparatively rank material
and accessory weights or counterweights are attached.
performance, or both. The resistance of material surfaces to
6.1.4 A vacuum suction system and vacuum pickup nozzle
abrasion, as measured on a testing machine in the laboratory, is
to remove debris and abrasive particles from the specimen
generally only one of several factors contributing to wear
surface during testing. The vacuum suction force shall be 137
performance as experienced in the actual use of the material.
millibar (55 in. of water column) or greater, as measured by a
Other factors may need to be considered in any calculation of
vacuum gage at the vacuum pick-up nozzle port. The height of
predicted life from specific abrasion data.
the vacuum pickup nozzle shall be adjustable, and the nozzle
5.2 The resistance of material surfaces to abrasion may be
will have two 8 mm openings. One opening shall be positioned
affected by factors including test conditions; type of abradant;
between the two wheels and over the wear path and the other
pressure between the specimen and abradant; mounting or
placed diametrically opposite, with the distance between the
tension of the specimen; and type, kind, or amount of finishing
axes of the two openings 76.0 6 1.0 mm.
materials.
6.1.5 A counter to record the number of abrasion cycles
(revolutions) made by the turntable platform.
5.3 Abrasion tests utilizing the rotary platform, double head
abraser may be subject to variation due to changes in the
6.2 Abrasive Wheels, which are attached to the free end of
abradant during the course of specific tests. Depending on the pivoted arms and are able to rotate freely about horizontal
abradant type and test specimen, the abrading wheel surface
spindles.
may change (i.e. become clogged) due to the pick-up of 6.2.1 The wheels shall be 12.7 6 0.3 mm thick and have an
finishing or other materials from test specimens.To reduce this
external diameter of 51.9 6 0.5 mm when new, and in no case
variation,theabradingwheelsshouldberesurfacedatregularly less than 44.4 mm. The abrasive wheels are either resilient or
defined intervals. See Appendix X2.
vitrified based, with both types of wheels consisting of hard
particles embedded in a binder material and manufactured in
5.4 The measurement of the relative amount of abrasion
different grades of abrasive quality. Other types of wheels,
may be affected by the method of evaluation and influenced by
which do not include hard particles embedded in a binder
the judgment of the operator.
material, may also be used.
6.2.2 The internal faces of the abrasive wheels shall be 52.4
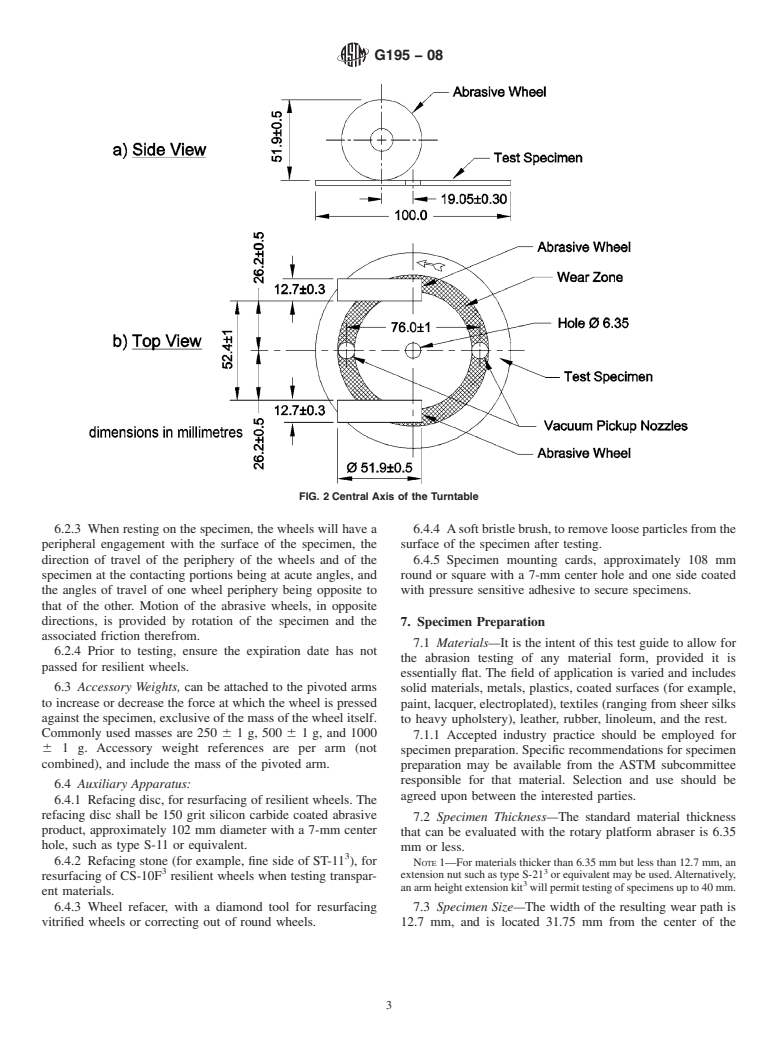
6. Apparatus
6 1.0 mm apart and the hypothetical line through the two
6.1 Rotary Platform, Double-Head (RPDH) Abraser, con-
spindles shall be 19.05 6 0.3 mm away from the central axis
sisting of the elements described in 6.1.1 to 6.1.5 (see Fig. 1).
of the turntable (see Fig. 2). The wheels should be spaced
6.1.1 A turntable specimen platform, which is removable,
equally on both sides from the wheel-mounting flange to the
that includes a rubber pad, clamp plate, centrally located
center of the specimen holder. The distance from the inside of
threaded post and nut. When testing flexible specimens, the
the wheel mounting flange to the center of the specimen holder
specimen platform will also include a clamping ring. The
shall be 38.9 6 0.5 mm.
turntable shall be motor driven, and mounted so as to produce
a circular surface travel of a flat specimen in the plane of its
The sole source of supply of the apparatus known to the committee at this time
surface. The specimen platform should rotate with no visible
is Taber Industries, 455 Bryant Street, North Tonawanda, NY 14120. If you are
wobble. This can be checked with a dial indicator at the top
aware of alternative suppliers, please provide this information to ASTM Interna-
outer edge of the platform to make sure it runs true within 0.5
tional Headquarters.Your comments will receive careful consideration at a meeting
mm. of the responsible technical committee, which you may attend.
G195 − 08
FIG. 2 Central Axis of the Turntable
6.2.3 When resting on the specimen, the wheels will have a 6.4.4 Asoft bristle brush, to remove loose particles from the
peripheral engagement with the surface of the specimen, the surface of the specimen after testing.
direction of travel of the periphery of the wheels and of the 6.4.5 Specimen mounting cards, approximately 108 mm
specimen at the contacting portions being at acute angles, and round or square with a 7-mm center hole and one side coated
the angles of travel of one wheel periphery being opposite to with pressure sensitive adhesive to secure specimens.
that of the other. Motion of the abrasive wheels, in opposite
directions, is provided by rotation of the specimen and the 7. Specimen Preparation
associated friction therefrom.
7.1 Materials—It is the intent of this test guide to allow for
6.2.4 Prior to testing, ensure the expiration date has not
the abrasion testing of any material form, provided it is
passed for resilient wheels.
essentially flat. The field of application is varied and includes
6.3 Accessory Weights, can be attached to the pivoted arms solid materials, metals, plastics, coated surfaces (for example,
to increase or decrease the force at which the wheel is pressed
paint, lacquer, electroplated), textiles (ranging from sheer silks
against the specimen, exclusive of the mass of the wheel itself.
to heavy upholstery), leather, rubber, linoleum, and the rest.
Commonly used masses are 250 61g,500 6 1 g, and 1000
7.1.1 Accepted industry practice should be employed for
6 1 g. Accessory weight references are per arm (not
specimen preparation. Specific recommendations for specimen
combined), and include the mass of the pivoted arm.
preparation may be available from the ASTM subcommittee
responsible for that material. Selection and use should be
6.4 Auxiliary Apparatus:
agreed upon between the interested parties.
6.4.1 Refacing disc, for resurfacing of resilient wheels. The
refacing disc shall be 150 grit silicon carbide coated abrasive
7.2 Specimen Thickness—The standard material thickness
product, approximately 102 mm diameter with a 7-mm center
that can be evaluated with the rotary platform abraser is 6.35
hole, such as type S-11 or equivalent.
mm or less.
6.4.2 Refacing stone (for example, fine side of ST-11 ), for NOTE 1—For materials thicker than 6.35 mm but less than 12.7 mm, an
extension nut such as type S-21 or equivalent may be used.Alternatively,
resurfacing of CS-10F resilient wheels when testing transpar-
anarmheightextensionkit willpermittestingofspecimensupto40mm.
ent materials.
6.4.3 Wheel refacer, with a diamond tool for resurfacing 7.3 Specimen Size—The width of the resulting wear path is
vitrified wheels or correcting out of round wheels. 12.7 mm, and is located 31.75 mm from the center of the
G195 − 08
specimen.Thesizeofthespecimenmayvarydependingonthe 11. Procedure
material being evaluated:
11.1 Mount the wheels on their respective flanged holders,
7.3.1 For most rigid materials, a sample approximately 100
taking care not to handle them by their abrasive surfaces. Prior
mm square is recommended with a 6.35 mm diameter center
to testing, ensure that the wheels have been resurfaced accord-
hole.
ing to Section 9 if necessary.
7.3.2 Flexible specimens are typically circular and require
11.2 Depending on the type of evaluation criteria being
the use of the clamp ring. If a mounting card is used, the
utilized (see Section 12), it may be necessary to measure and
specimen should be approximately 105 mm in diameter with a
record specific parameters of the unabraded specimen prior to
6.35 mm diameter center hole. If no mounting card is used, an
conducting the test:
approximately 135 mm specimen is required such that the
11.2.1 Mass loss method, weigh the specimen to the nearest
clamp ring will grip overlapped material.The specimen should
mg. If using a mounting card, weigh after the specimen has
include a 6.35 mm diameter hole in the center of the specimen.
been affixed to the card and conditioned in the standard testing
A sample cutter or die has been found useful for preparing
environment.
flexible specimens.
11.2.2 Wear cycles per mil or depth of wear method, use a
7.4 Mounting Card—Certain flexible specimens may
thickness gage or other appropriate device to measure the
wrinkleorshiftduringtesting.Topreventthis,amountingcard
specimenthicknessonfourpointsalongthepathtobeabraded,
with a pressure sensitive adhesive may be used. Prior to
approximately 38 mm from the center hole and 90° apart.
adhering, clean the back of the specimen with a soft bristle
Calculate the average of the readings.
brush to remove any loose debris. Position the specimen on the
11.3 Mounting of Specimen—Place the test specimen face
cardsuchthatthespecimenisfreeoffolds,creases,orwrinkles
up over the rubber mat on the turntable platform, unless
and the center holes align.
otherwise specified. If the turntable platform was previously
8. Preparation and Set-Up of Apparatus
removed,ensureitisproperlyreplacedonthemotordriveshaft
of the abraser prior to testing.
8.1 The following set-up parameters are dependent on the
11.3.1 For rigid materials, secure the clamp plate and nut in
type of material being evaluated and shall be agreed upon by
place to hold the specimen.
th
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.