ASTM E1025-18
(Practice)Standard Practice for Design, Manufacture, and Material Grouping Classification of Hole-Type Image Quality Indicators (IQI) Used for Radiography
Standard Practice for Design, Manufacture, and Material Grouping Classification of Hole-Type Image Quality Indicators (IQI) Used for Radiography
ABSTRACT
This practice covers the design, material grouping classification, and manufacture of hole-type image quality indicators (IQI) used to indicate the quality of X-ray and gamma-ray radiologic images.
SCOPE
1.1 This practice2 covers the design, material grouping classification, and manufacture of hole-type image quality indicators (IQI) used to indicate the quality of radiologic images.
1.2 This practice is applicable to X-ray and gamma-ray radiology.
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation:E1025 −18
Standard Practice for
Design, Manufacture, and Material Grouping Classification
of Hole-Type Image Quality Indicators (IQI) Used for
1
Radiography
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E1025; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* B166Specification for Nickel-Chromium-IronAlloys (UNS
2
N06600, N06601, N06603, N06690, N06693, N06025,
1.1 This practice covers the design, material grouping
N06045, and N06696), Nickel-Chromium-Cobalt-
classification, and manufacture of hole-type image quality
Molybdenum Alloy (UNS N06617), and Nickel-Iron-
indicators (IQI) used to indicate the quality of radiologic
Chromium-TungstenAlloy (UNS N06674) Rod, Bar, and
images.
Wire
1.2 This practice is applicable to X-ray and gamma-ray
E746Practice for Determining Relative Image Quality Re-
radiology.
sponse of Industrial Radiographic Imaging Systems
1.3 Thevaluesstatedininch-poundunitsaretoberegarded
E747Practice for Design, Manufacture and Material Group-
as standard.
ing Classification of Wire Image Quality Indicators (IQI)
Used for Radiology
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
E1735Test Method for Determining Relative Image Quality
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
of Industrial Radiographic Film Exposed to X-Radiation
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
from4to25MeV
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
E1316Terminology for Nondestructive Examinations
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
E2662Practice for Radiographic Examination of Flat Panel
1.5 This international standard was developed in accor-
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard- Composites and Sandwich Core Materials Used in Aero-
space Applications
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
2.2 Department of Defense (DoD) Documents:
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
MIL-I-24768Insulation, Plastics, Laminated, Thermoset-
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee. 4
ting; General Specification for
5
2. Referenced Documents 2.3 ISO Documents
3
ISO 17636-1Non-Destructive Testing of Welds – Radio-
2.1 ASTM Standards:
graphic testing – Part 1: X- and Gamma-Ray Techniques
B139/B139MSpecification for Phosphor Bronze Rod, Bar,
with Film
and Shapes
ISO 17636-2Non-Destructive Testing of Welds – Radio-
B150/B150MSpecification forAluminum Bronze Rod, Bar,
graphic testing – Part 2: X- and Gamma-Ray Techniques
and Shapes
with Digital Detectors
B164Specification for Nickel-Copper Alloy Rod, Bar, and
ISO 19232-2Non-Destructive Testing – Image Quality of
Wire
Radiographs–Part2:DeterminationoftheImageQuality
Value Using Step/Hole-Type Image Quality Indicators
1
This practice is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E07 on Nonde-
ISO 19232-3Non-Destructive Testing – Image Quality of
structive Testing and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E07.01 on
Radiographs – Part 3: Image Quality Classes
Radiology (X and Gamma) Method.
Current edition approved Feb. 1, 2018. Published February 2018. Originally
approved in 1984. Last previous edition approved in 2011 as E1025-11. DOI:
10.1520/E1025-18.
2 4
For ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code applications see related Practice Available from Standardization Documents Order Desk, DODSSP, Bldg. 4,
SE-1025 in Section II of that Code. Section D, 700 Robbins Ave., Philadelphia, PA 19111-5098, http://
3
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or dodssp.daps.dla.mil.
5
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Available from International Organization for Standardization (ISO), ISO
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Central Secretariat, BIBC II, Chemin de Blandonnet 8, CP 401, 1214 Vernier,
the ASTM website. Geneva, Switzerland, http://www.iso.org.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
E1025−18
6
2.4 ASME Documents: 4.1.5.1 Alternative Identification Method—It may be desir-
BPVC (Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code) Section V Non- able for non-film applications to eliminate the lead number
destructive Exam
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: E1025 − 11 E1025 − 18
Standard Practice for
Design, Manufacture, and Material Grouping Classification
of Hole-Type Image Quality Indicators (IQI) Used for
1
RadiologyRadiography
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E1025; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope*
2
1.1 This practice covers the design, material grouping classification, and manufacture of hole-type image quality indicators
(IQI) used to indicate the quality of radiologic images.
1.2 This practice is applicable to X-ray and gamma-ray radiology.
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety safety, health, and healthenvironmental practices and determine the
applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
3
2.1 ASTM Standards:
B139/B139M Specification for Phosphor Bronze Rod, Bar, and Shapes
B150/B150M Specification for Aluminum Bronze Rod, Bar, and Shapes
B164 Specification for Nickel-Copper Alloy Rod, Bar, and Wire
B166 Specification for Nickel-Chromium-Iron Alloys (UNS N06600, N06601, N06603, N06690, N06693, N06025, N06045,
and N06696), Nickel-Chromium-Cobalt-Molybdenum Alloy (UNS N06617), and Nickel-Iron-Chromium-Tungsten Alloy
(UNS N06674) Rod, Bar, and Wire
E746 Practice for Determining Relative Image Quality Response of Industrial Radiographic Imaging Systems
E747 Practice for Design, Manufacture and Material Grouping Classification of Wire Image Quality Indicators (IQI) Used for
Radiology
E1735 Test Method for Determining Relative Image Quality of Industrial Radiographic Film Exposed to X-Radiation from 4 to
25 MeV
E1316 Terminology for Nondestructive Examinations
E2662 Practice for Radiographic Examination of Flat Panel Composites and Sandwich Core Materials Used in Aerospace
Applications
2.2 Department of Defense (DoD) Documents:
4
MIL-I-24768 Insulation, Plastics, Laminated, Thermosetting; General Specification for
1
This practice is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E07 on Nondestructive Testing and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E07.01 on Radiology (X and
Gamma) Method.
Current edition approved Dec. 15, 2011Feb. 1, 2018. Published January 2012February 2018. Originally approved in 1984. Last previous edition approved in 20052011
as E1025 - 05.E1025 -11. DOI: 10.1520/E1025-11.10.1520/E1025-18.
2
For ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code applications see related Practice SE-1025 in Section II of that Code.
3
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
4
Available from Standardization Documents Order Desk, DODSSP, Bldg. 4, Section D, 700 Robbins Ave., Philadelphia, PA 19111-5098, http://dodssp.daps.dla.mil.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
E1025 − 18
5
2.3 ISO Documents
ISO 17636-1 Non-Destructive Testing of Welds – Radiographic testing – Part 1: X- and Gamma-Ray Techniques with Film
ISO 17636-2 Non-Destructive Testing of Welds – Radiographic testing – Part 2: X- and Gamma-Ray Techniques with Digital
Detectors
ISO 19232-2 Non-Destructive Testing – Image Quality of Radiographs – Part 2: Determination of the Image Quality Value
Using Step/Hole-Type Image Quality Indicators
ISO 19232-3 Non-Destructive Testing – Image Quality of Radiographs – Part 3: Image Quality Classes
6
2.4 ASME Documents:
BPVC (Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code) Section V Nondestructive Examination, Article 2 Radiographic Examination
3. Terminology
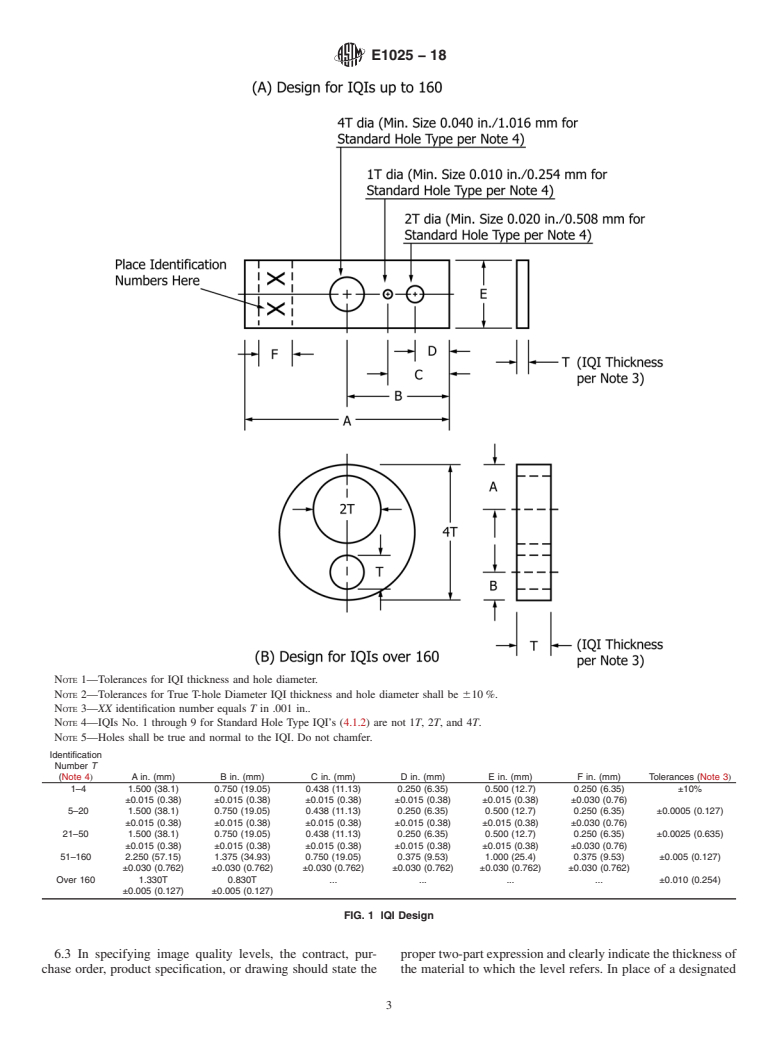
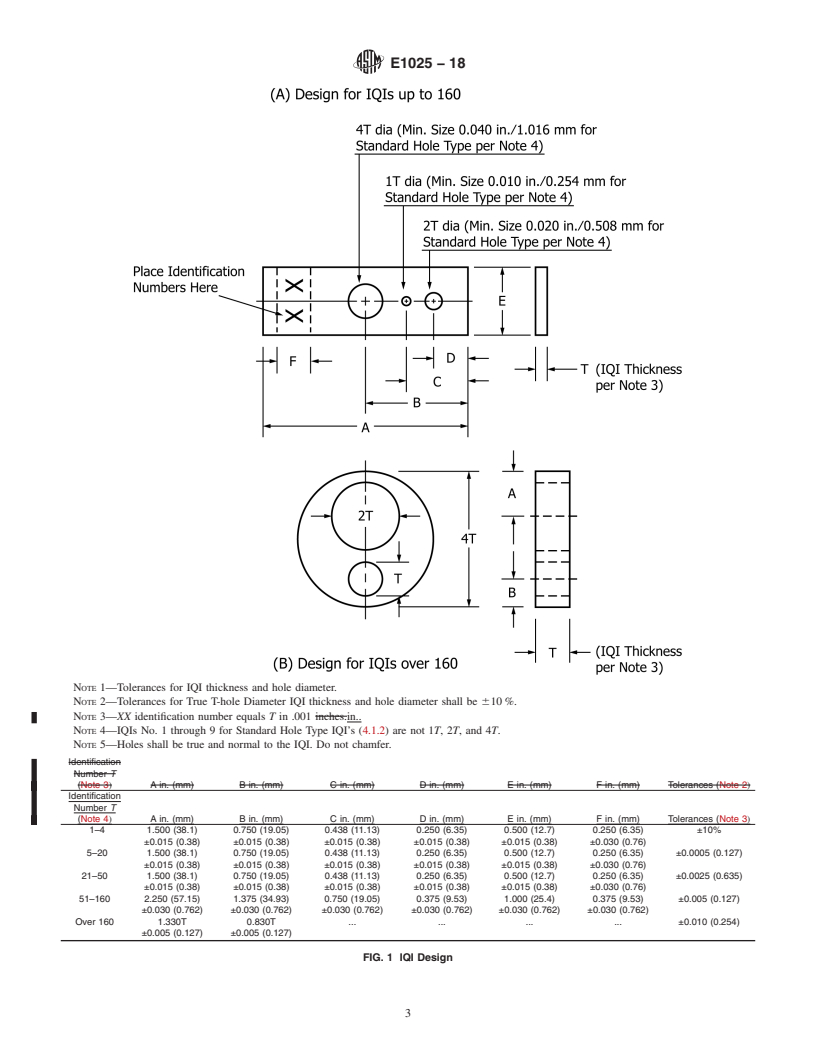
3.1 Definitions—The de
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.